World War II and the Post
... A former German soldier named Adolf Hitler promised to make Germany a strong nation again. He declared that there would be jobs and food for everyone. He told the people that they were superior to other Europeans, and that other countries shouldn’t tell them what to do. Many Germans liked what he ha ...
... A former German soldier named Adolf Hitler promised to make Germany a strong nation again. He declared that there would be jobs and food for everyone. He told the people that they were superior to other Europeans, and that other countries shouldn’t tell them what to do. Many Germans liked what he ha ...
AMERICA AND WORLD WAR II
... Allied troops arrived in Paris in August, 1944 One occupied country after another fell Battle of the Bulge- Allies were taken by surprise driving them back 50 miles before they were stopped This last effort exhausted the German capacity for counterattack It was the bloodiest American battle since Ge ...
... Allied troops arrived in Paris in August, 1944 One occupied country after another fell Battle of the Bulge- Allies were taken by surprise driving them back 50 miles before they were stopped This last effort exhausted the German capacity for counterattack It was the bloodiest American battle since Ge ...
World War II
... ◦ Italy invaded Ethiopia and took control in 1935 ◦ Spain’s Civil War was won by the fascists in 1936 ◦ Germany 1936: Hitler had rearmed and sent troops to the Rhineland 1938: Hitler annexed Austria & demanded the Sudetenland 1938: Munich Conference (Germany, Italy, Britain, & France) Goal: To stop ...
... ◦ Italy invaded Ethiopia and took control in 1935 ◦ Spain’s Civil War was won by the fascists in 1936 ◦ Germany 1936: Hitler had rearmed and sent troops to the Rhineland 1938: Hitler annexed Austria & demanded the Sudetenland 1938: Munich Conference (Germany, Italy, Britain, & France) Goal: To stop ...
An Age of Anxiety/Nationalism/World War II
... • Anti-Semitism became the hallmark of Nazi rule • Based on nineteenth-century biological race theories, the Nazis skillfully built on deeper underlying religious hatreds to identify who was a Jew • The 1935 Nuremberg Laws deprived Germans of Jewish ancestry of their civil and citizenship rights, wh ...
... • Anti-Semitism became the hallmark of Nazi rule • Based on nineteenth-century biological race theories, the Nazis skillfully built on deeper underlying religious hatreds to identify who was a Jew • The 1935 Nuremberg Laws deprived Germans of Jewish ancestry of their civil and citizenship rights, wh ...
World War II
... 5. Why do you think the Japanese changed their approach from trying to win the support of the colonized peoples to acting as conquerors? 6. What problems did Japan face in building an empire in the ...
... 5. Why do you think the Japanese changed their approach from trying to win the support of the colonized peoples to acting as conquerors? 6. What problems did Japan face in building an empire in the ...
document
... On June 10, Mussolini declares war on France fearing that Hitler would take the entire nation for himself. June 14, Paris is captured by Germany On June 22, France surrenders – Germany takes direct control of the northern two-thirds of France ...
... On June 10, Mussolini declares war on France fearing that Hitler would take the entire nation for himself. June 14, Paris is captured by Germany On June 22, France surrenders – Germany takes direct control of the northern two-thirds of France ...
1 - My CCSD
... 3. How did fascism differ from communism? 4. Why did the Japanese invade Manchuria in 1931? 5. Why were Americans supporting a neutral position in the 1930s regarding the growing political and military tensions in Europe? 6. What was lebensraum? What moves did Hitler make to support this Germany pol ...
... 3. How did fascism differ from communism? 4. Why did the Japanese invade Manchuria in 1931? 5. Why were Americans supporting a neutral position in the 1930s regarding the growing political and military tensions in Europe? 6. What was lebensraum? What moves did Hitler make to support this Germany pol ...
The war progresses
... Allies fought valiantly but in vain - the German war machine advanced unperturbed. In England, the invasion forced Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain to resign, to be replaced by Winston Churchill. ...
... Allies fought valiantly but in vain - the German war machine advanced unperturbed. In England, the invasion forced Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain to resign, to be replaced by Winston Churchill. ...
ppt
... • Jew, anti-Nazi, pro-West • Sept. 1934: USSR joined League of Nations • May 1935: France and USSR sign pact • USSR pledged to help Czechoslovakia, if France first. ...
... • Jew, anti-Nazi, pro-West • Sept. 1934: USSR joined League of Nations • May 1935: France and USSR sign pact • USSR pledged to help Czechoslovakia, if France first. ...
Treaty of Versallies – end of WWI
... WWI killed a lot of workers and customers After years of humiliation and starvation, Germans looked for a strong leader. ...
... WWI killed a lot of workers and customers After years of humiliation and starvation, Germans looked for a strong leader. ...
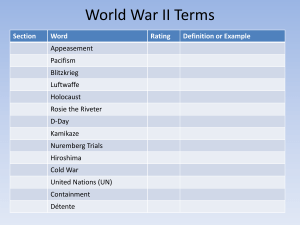
World War II Study Guide Axis Powers in WWII Germany led by Hitler
... World War II began September 1, 1939 when Hitler invaded Poland. This event marks the beginning of World War II!! ...
... World War II began September 1, 1939 when Hitler invaded Poland. This event marks the beginning of World War II!! ...
Jew from Germany
... Luxembourg, and the Netherlands (side tracks France) • Germans made it through fortifications and into France, eventually took over Paris. • France surrendered June 22, 1940. • French resistance to German occupation set up a government in London to try to recapture France. ...
... Luxembourg, and the Netherlands (side tracks France) • Germans made it through fortifications and into France, eventually took over Paris. • France surrendered June 22, 1940. • French resistance to German occupation set up a government in London to try to recapture France. ...
Chapter 16
... • Following Hitler’s invasion of the Sudetenland, four world leaders met to discuss German aggression • Neville Chamberlain (Great Britain) • Edward Daladier (France) • Benito Mussolini (Italy) • Adolf Hitler (Germany) ...
... • Following Hitler’s invasion of the Sudetenland, four world leaders met to discuss German aggression • Neville Chamberlain (Great Britain) • Edward Daladier (France) • Benito Mussolini (Italy) • Adolf Hitler (Germany) ...
World War II
... III. Hitler Marches in Europe B. Reactions Appeasement-France and Britain had adopted the policy of giving in to Hitler's demands to avoid war. Hitler broke his promise and took over all of Czechoslovakia. ...
... III. Hitler Marches in Europe B. Reactions Appeasement-France and Britain had adopted the policy of giving in to Hitler's demands to avoid war. Hitler broke his promise and took over all of Czechoslovakia. ...
Chapter 12 Notes America and World War II Section 1: The Road to
... Hitler ended democracy and established a totalitarian state. ...
... Hitler ended democracy and established a totalitarian state. ...
World War II
... •Locate and Number the countries that were ruled by totalitarian dictators at the start of World War II. •Create a key for & label the regions that Hitler annexed or rearmed in defiance of Versailles: Memel, Sudetenland (western Czechoslovakia), Austria, and the Rhineland. ...
... •Locate and Number the countries that were ruled by totalitarian dictators at the start of World War II. •Create a key for & label the regions that Hitler annexed or rearmed in defiance of Versailles: Memel, Sudetenland (western Czechoslovakia), Austria, and the Rhineland. ...
WWII
... France was not desirable – Nazi government brought Germany to ruins – Mussolini had led Italy to defeat – Vichy government in France collaborated with the ...
... France was not desirable – Nazi government brought Germany to ruins – Mussolini had led Italy to defeat – Vichy government in France collaborated with the ...
File - Miss O`Connor`s Class
... • Hitler demanded the Sudetenland – a German speaking area – from Czechoslovakia. They refused but were forced to hand it over following the Munich Conference in order to prevent war. • Hitler signed the Nazi-Soviet Pact with Stalin, which included a 10 year non-aggression pact and an agreement to d ...
... • Hitler demanded the Sudetenland – a German speaking area – from Czechoslovakia. They refused but were forced to hand it over following the Munich Conference in order to prevent war. • Hitler signed the Nazi-Soviet Pact with Stalin, which included a 10 year non-aggression pact and an agreement to d ...
History Revision 3
... • Germans under Czech and Polish rule (so he took over the Sudetenland in Sept 1938, and attacked Poland in Sept 1939). After Munich, Hitler began to pursue his other gaols of Lebensraum, Aryan supremacy and the destruction of Communist Russia: 1. Hitler said that the German population was growing a ...
... • Germans under Czech and Polish rule (so he took over the Sudetenland in Sept 1938, and attacked Poland in Sept 1939). After Munich, Hitler began to pursue his other gaols of Lebensraum, Aryan supremacy and the destruction of Communist Russia: 1. Hitler said that the German population was growing a ...
Chap 29-30 Dictators Threaten World Peace
... • Hitler believed that for Germany to thrive it needed more land at the expense of her neighbors ...
... • Hitler believed that for Germany to thrive it needed more land at the expense of her neighbors ...
World War II - Mrs. Curtis`s Social Studies Classroom
... The Battle of Britain comprised four phases: 1. Hitler bombers attack British ports. 2. Hitler attacks British ships. 3. The Blitz – Beginning September 7, 1940 the city of London was heavily bombed. Hitler hoped to destroy the morale of the British people. 4. Night Bombing - With the failure of da ...
... The Battle of Britain comprised four phases: 1. Hitler bombers attack British ports. 2. Hitler attacks British ships. 3. The Blitz – Beginning September 7, 1940 the city of London was heavily bombed. Hitler hoped to destroy the morale of the British people. 4. Night Bombing - With the failure of da ...
Appeasement

Appeasement in a political context is a diplomatic policy of making political or material concessions to an enemy power in order to avoid conflict.The term is most often applied to the foreign policy of the British Prime Ministers Ramsay Macdonald, Stanley Baldwin and Neville Chamberlain towards Nazi Germany between 1933 and 1939. Their policies of avoiding war with Germany have been the subject of intense debate for more than seventy years among academics, politicians and diplomats. The historians' assessments have ranged from condemnation for allowing Adolf Hitler's Germany to grow too strong, to the judgment that they had no alternative and acted in Britain's best interests. At the time, these concessions were widely seen as positive, and the Munich Pact concluded on 30 September 1938 among Germany, Britain, France, and Italy prompted Chamberlain to announce that he had secured ""peace for our time.""