Chapter 24 The United States in World War II
... Allied leaders Roosevelt, Winston Churchill, and Joseph Stalin— the so-called Big Three—met in the resort town of Yalta in the Soviet Union to discuss the end of the war and the peace that was to follow. A key goal was to determine what to do with Germany. The leaders agreed to divide the country in ...
... Allied leaders Roosevelt, Winston Churchill, and Joseph Stalin— the so-called Big Three—met in the resort town of Yalta in the Soviet Union to discuss the end of the war and the peace that was to follow. A key goal was to determine what to do with Germany. The leaders agreed to divide the country in ...
Race and ethnicity in wartime America
... 1) Adoption of United Nations Charter at San Francisco 2) Endorsement of United Nations Charter by U.S. Senate 2. Structure and mission: outlawed force or threat of as means of settling international disputes G. Death Toll 1. 50 million deaths a. 400,000 American combat deaths b. 20 million civilian ...
... 1) Adoption of United Nations Charter at San Francisco 2) Endorsement of United Nations Charter by U.S. Senate 2. Structure and mission: outlawed force or threat of as means of settling international disputes G. Death Toll 1. 50 million deaths a. 400,000 American combat deaths b. 20 million civilian ...
Treaty of Versallies – end of WWI
... Road to World War II Online Game for class to play on Smartboard. ...
... Road to World War II Online Game for class to play on Smartboard. ...
PART II: Checking Your Progress
... 10. Isolationists and hostile critics in 1940–1941, and even after World War II, charged Franklin Roosevelt with deliberately and sometimes deceitfully manipulating events and public opinion so as to lead the United States into war. What factual basis, if any, is there for such a charge? Which of Ro ...
... 10. Isolationists and hostile critics in 1940–1941, and even after World War II, charged Franklin Roosevelt with deliberately and sometimes deceitfully manipulating events and public opinion so as to lead the United States into war. What factual basis, if any, is there for such a charge? Which of Ro ...
ppt
... Army officers and officials who agreed with them Young people: the Swing Youth; the Edelweiss Pirates and Navajos; the White Rose group • Adds up to a tiny minority of the German people ...
... Army officers and officials who agreed with them Young people: the Swing Youth; the Edelweiss Pirates and Navajos; the White Rose group • Adds up to a tiny minority of the German people ...
World War II..Ch.32
... These laws made it legal to sell arms or lend money to nations at war. Although the United States had not yet entered the war, Roosevelt and Churchill met secretly and issued a joint declaration called the Atlantic Charter. It upheld free trade among nations and the right of people to choose their o ...
... These laws made it legal to sell arms or lend money to nations at war. Although the United States had not yet entered the war, Roosevelt and Churchill met secretly and issued a joint declaration called the Atlantic Charter. It upheld free trade among nations and the right of people to choose their o ...
World War II - California State University, Los Angeles
... ii. Germany avoided it by invading Belgium first iii. Maginot line was useless, cannons faced wrong way d. Germans advance to a few miles from Paris e. a few weeks later France surrendered 4. Roosevelt expands help to Britain a. Traded 50 destroyers for navel & air bases b. Congress gave $4 billion ...
... ii. Germany avoided it by invading Belgium first iii. Maginot line was useless, cannons faced wrong way d. Germans advance to a few miles from Paris e. a few weeks later France surrendered 4. Roosevelt expands help to Britain a. Traded 50 destroyers for navel & air bases b. Congress gave $4 billion ...
Heisenberg, Bohr, and the Bomb
... explaining why light could be seen as both a particle and a wave, though never both at the same time. Bohr would come to apply this idea philosophically as well, with the belief that evolving concepts of physics deeply affected human perspectives. With Adolf Hitler's rise in power, Bohr was able to ...
... explaining why light could be seen as both a particle and a wave, though never both at the same time. Bohr would come to apply this idea philosophically as well, with the belief that evolving concepts of physics deeply affected human perspectives. With Adolf Hitler's rise in power, Bohr was able to ...
Hitler`s war machine - MissDWorldofSocialStudies
... 4. Switzerland; Sweden was neutral, while Norway was under German rule 5. Critical Thinking: Human Systems Answers will vary, but students should note that Hitler had imposed his rule over most of Europe by 1942. Some students may argue that this shows the goal is feasible. Others may feel that Hitl ...
... 4. Switzerland; Sweden was neutral, while Norway was under German rule 5. Critical Thinking: Human Systems Answers will vary, but students should note that Hitler had imposed his rule over most of Europe by 1942. Some students may argue that this shows the goal is feasible. Others may feel that Hitl ...
Krista Henson September 3, 2008 2 nd Block History
... A bond is a special type of security. Bonds are issued by an agency which wants to generate capital, and the people who purchase them are essentially loaning money to the issuing agency. In return for the loan, the bond earns a set interest rate, and the purchaser can redeem the bond for its face va ...
... A bond is a special type of security. Bonds are issued by an agency which wants to generate capital, and the people who purchase them are essentially loaning money to the issuing agency. In return for the loan, the bond earns a set interest rate, and the purchaser can redeem the bond for its face va ...
WWII time line
... Neutrality Act of 1937 • US citizens can no longer travel aboard foreign ships ...
... Neutrality Act of 1937 • US citizens can no longer travel aboard foreign ships ...
Hitler`s Lightning War Close Read
... – WHST 4 - Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. – WHST 9 - Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. ...
... – WHST 4 - Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. – WHST 9 - Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. ...
WWII Europe and U.S. homefront outline
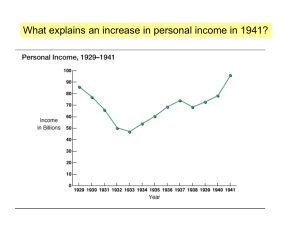
... What explains the graphic from 1929 to 1933? What explains the graphic from 1933 to 1937? Why is the year 2000 included? ...
... What explains the graphic from 1929 to 1933? What explains the graphic from 1933 to 1937? Why is the year 2000 included? ...
Standard 19-World War II Notes
... B. ways the country celebrated V-E Day C. steps taken by Germany to try to avoid losing the war D. failed domestic policies that had been intended to provide extra money for the war effort "We had to be careful not to use things up too quick. You couldn’t get more without enough points; and once you ...
... B. ways the country celebrated V-E Day C. steps taken by Germany to try to avoid losing the war D. failed domestic policies that had been intended to provide extra money for the war effort "We had to be careful not to use things up too quick. You couldn’t get more without enough points; and once you ...
WWII Review
... 48. What two Japanese cities were Atomic Bombs used on? 49. About how many people died worldwide as a result of World War II? 50. What does Genocide mean? 51. What was the Holocaust? 52. How many Jews died during the Holocaust? 53. What other groups of people were singled out by the Nazis for perse ...
... 48. What two Japanese cities were Atomic Bombs used on? 49. About how many people died worldwide as a result of World War II? 50. What does Genocide mean? 51. What was the Holocaust? 52. How many Jews died during the Holocaust? 53. What other groups of people were singled out by the Nazis for perse ...
Corporate Creativity
... Twenty percent of the Polish people died in forced labor, of hunger, or from fighting. Resistance was impossible. Even the feeblest opposition brought devastating, over-whelming reprisals. Drs. Lazowski and Matulewicz decided to resist anyway, and their solution was brilliant. They knew that the Ger ...
... Twenty percent of the Polish people died in forced labor, of hunger, or from fighting. Resistance was impossible. Even the feeblest opposition brought devastating, over-whelming reprisals. Drs. Lazowski and Matulewicz decided to resist anyway, and their solution was brilliant. They knew that the Ger ...
America in World War II
... Failure of the League of Nations • The League of Nations, created at the end of World War I and the Treaty of Versailles was supposed to provide world peace as all nations banded together to stop any aggressor nations. • The League of Nations had failed when nations like the United States and the S ...
... Failure of the League of Nations • The League of Nations, created at the end of World War I and the Treaty of Versailles was supposed to provide world peace as all nations banded together to stop any aggressor nations. • The League of Nations had failed when nations like the United States and the S ...
World_War_II_1942_1945 (1)
... The Soviet victory at Stalingrad was a turning point in World War II because the Russians began pushing towards Germany from the East by 1943 ...
... The Soviet victory at Stalingrad was a turning point in World War II because the Russians began pushing towards Germany from the East by 1943 ...
WWII Review What three countries wanted to fix their countries
... a. Pearl Harbor, Atomic Bomb, German attack Poland, Defeat of France b. Defeat of France, Pearl Harbor, German Attack Poland, Atomic Bomb c. Atomic Bomb, Pearl Harbor, German Attack Poland, Defeat of France d. German Attack Poland, Defeat France, Pearl Harbor, Atomic Bomb ...
... a. Pearl Harbor, Atomic Bomb, German attack Poland, Defeat of France b. Defeat of France, Pearl Harbor, German Attack Poland, Atomic Bomb c. Atomic Bomb, Pearl Harbor, German Attack Poland, Defeat of France d. German Attack Poland, Defeat France, Pearl Harbor, Atomic Bomb ...
The Coming of World War II. 1937-1939
... conflicting attitudes because the invasion would help the Russians crush the Germans. Fearful of their Russian allies, it was necessary to rush Allied troops to western Germany to keep the Russians from overrunning the entire continent to the North Sea. (20) In February 1945, Roosevelt and Winston C ...
... conflicting attitudes because the invasion would help the Russians crush the Germans. Fearful of their Russian allies, it was necessary to rush Allied troops to western Germany to keep the Russians from overrunning the entire continent to the North Sea. (20) In February 1945, Roosevelt and Winston C ...
11SS Slides Ch. 5 WW 2(UPDATED)
... European war. Dr. Suess was very adamant that the United States needed to get involved because he felt that it was only a matter of time before Hitler turned his attention to the United States. So, how does Dr. Suess get his message across to his viewing public? First, he uses symbols. The trees tha ...
... European war. Dr. Suess was very adamant that the United States needed to get involved because he felt that it was only a matter of time before Hitler turned his attention to the United States. So, how does Dr. Suess get his message across to his viewing public? First, he uses symbols. The trees tha ...
Graduation Exam Preparation Setup—The exam material is divided
... Great Awakening (1730s to 1740s)—religious revival in the 13 colonies, creates new denominations, creates feelings of independence and self reliance; more democratic feeling. First continental Congress (1774)—colonial representatives meet in reaction to the situation in Massachusetts. a. Series of r ...
... Great Awakening (1730s to 1740s)—religious revival in the 13 colonies, creates new denominations, creates feelings of independence and self reliance; more democratic feeling. First continental Congress (1774)—colonial representatives meet in reaction to the situation in Massachusetts. a. Series of r ...
Holocaust Webquest KEY
... of the Jewish population would be dead in these occupied countries by the end of the war? o 9 million Jews, 66% would be dead 17. How were the Jews of Eastern and Western Europe different? What two European countries had the largest Jewish population just before World War II? o Jews in Eastern Europ ...
... of the Jewish population would be dead in these occupied countries by the end of the war? o 9 million Jews, 66% would be dead 17. How were the Jews of Eastern and Western Europe different? What two European countries had the largest Jewish population just before World War II? o Jews in Eastern Europ ...
name: david longenbach
... F. 1935 - Nuremburg Laws - Sept. 15 G. 1936 - Schact eliminated unemployment ...
... F. 1935 - Nuremburg Laws - Sept. 15 G. 1936 - Schact eliminated unemployment ...
Economy of Nazi Germany

World War I caused economic and manpower losses on Germany led to a decade of economic woes, including hyperinflation in the mid-1920s. Following the Wall Street Crash of 1929, the German economy, like those of many other western nations, suffered the effects of the Great Depression, with unemployment soaring. When Hitler became Chancellor in 1933, he introduced new efforts to improve Germany's economy, including autarky and the development of the German agricultural economy by placing tariffs on agricultural imports.However, these changes—including autarky and nationalization of key industries—had a mixed record. By 1938, unemployment was practically extinct. Wages increased by 10.9% in real terms during this period. However, nationalization and a cutting off of trade meant rationing in key resources like poultry, fruit, and clothing for many Germans.In 1934 Hjalmar Schacht, the Reich Minister of Economics, introduced the Mefo bills, allowing Germany to rearm without spending Reichmarks but instead pay industry with Reichmarks and Mefo bills (Government IOU's) which they could trade with each other. Between 1933 and 1939, the total revenue was 62 billion marks, whereas expenditure (at times made up to 60% by rearmament costs) exceeded 101 billion, thus creating a huge deficit and national debt (reaching 38 billion marks in 1939) coinciding with the Kristallnacht and intensified persecutions of Jews and the outbreak of the war.