Midterm #1 - Points
... to gain a colony and to demonstrate their power over weaker countries, A) Ethiopia, B) the Soviet Union, C) Poland, D) Norway 21. The Atlantic Charter consisted of the nations of, A) Great Britain and the United States, B) Canada and the United States, C) Germany and Japan, D) the Soviet Union and J ...
... to gain a colony and to demonstrate their power over weaker countries, A) Ethiopia, B) the Soviet Union, C) Poland, D) Norway 21. The Atlantic Charter consisted of the nations of, A) Great Britain and the United States, B) Canada and the United States, C) Germany and Japan, D) the Soviet Union and J ...
World War II
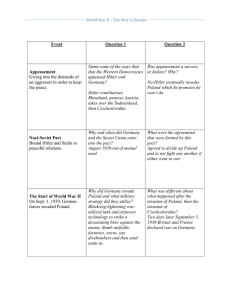
... into the Rhineland French did not want war British urged appeasement – giving in to the aggressor to keep peace France and Britain looked weak in Hitler’s eyes which served to encourage further aggression! ...
... into the Rhineland French did not want war British urged appeasement – giving in to the aggressor to keep peace France and Britain looked weak in Hitler’s eyes which served to encourage further aggression! ...
Fascism Reading
... control of private enterprise, repression of opposition and extreme nationalism. Mussolini knew how to appeal to Italy’s wounded national pride, and played on their fears of economic collapse and communism. Mussolini promised order and stability and was not content to merely rule the nation, but wit ...
... control of private enterprise, repression of opposition and extreme nationalism. Mussolini knew how to appeal to Italy’s wounded national pride, and played on their fears of economic collapse and communism. Mussolini promised order and stability and was not content to merely rule the nation, but wit ...
Dictatorships and the Second World War
... This bitterly critical cartoon by British cartoonist David Lowe (1891-1963) appeared in the London Evening News shortly after Hitler remilitarized the Rhineland. Appeasement also appealed to millions of ordinary citizens in Britain and France, who wanted to avoid another war at any cost. Originally ...
... This bitterly critical cartoon by British cartoonist David Lowe (1891-1963) appeared in the London Evening News shortly after Hitler remilitarized the Rhineland. Appeasement also appealed to millions of ordinary citizens in Britain and France, who wanted to avoid another war at any cost. Originally ...
Standard 5-4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of
... States, Great Britain, and the Soviet Union became known as the Allied Powers or the Allies. The goal of the Allies was to stop the Axis Powers and defeat them unconditionally so that they could not invade other countries again. Students should be able to explain the strategies used by the Allied Po ...
... States, Great Britain, and the Soviet Union became known as the Allied Powers or the Allies. The goal of the Allies was to stop the Axis Powers and defeat them unconditionally so that they could not invade other countries again. Students should be able to explain the strategies used by the Allied Po ...
HIST2134 The Third Reich through Documents, 1933-1945
... (esp. Ukrainians) • Inhuman SS occupation policies → general shift in mood ...
... (esp. Ukrainians) • Inhuman SS occupation policies → general shift in mood ...
WWII WIKI 3 - CoachJohnson1
... • It was then that Hitler made his pivotal mistake. He invaded the Soviet Union. – The obliteration of Bolshevism was a key element of Hitler’s ideology; however, it was a gigantic military mistake. • On June 22, 1941, Hitler launched Operation Barbarossa, consisting of an attack army of 4 million m ...
... • It was then that Hitler made his pivotal mistake. He invaded the Soviet Union. – The obliteration of Bolshevism was a key element of Hitler’s ideology; however, it was a gigantic military mistake. • On June 22, 1941, Hitler launched Operation Barbarossa, consisting of an attack army of 4 million m ...
WORLD WAR II IN SUMMARY ( 1939 - 1945 ) - SHS-AP-World
... XV) INVASION AND SURRENDER OF GERMANY A. Massive German counterattack: Battle of the Bulge 1. Unexpected by Allies that Hitler would throw full force into offensive move instead of saving troops for final defense of Germany itself a) Pushed Allies back 40-50 miles, but only really delayed the Allied ...
... XV) INVASION AND SURRENDER OF GERMANY A. Massive German counterattack: Battle of the Bulge 1. Unexpected by Allies that Hitler would throw full force into offensive move instead of saving troops for final defense of Germany itself a) Pushed Allies back 40-50 miles, but only really delayed the Allied ...
Chapter 11 Test
... A. Nazi-Soviet nonaggression pact B. anti-comintern Pact C. Rome-Berlin Axis Pact D. Co-Prosperity Pact 13. Which one of the following was invaded by Japan in 1931? A. Philippines B. Manchuria C. The Soviet Union D. Germany 14. In 1937 the Japanese begin a full-out war against: A. Russia B. India C. ...
... A. Nazi-Soviet nonaggression pact B. anti-comintern Pact C. Rome-Berlin Axis Pact D. Co-Prosperity Pact 13. Which one of the following was invaded by Japan in 1931? A. Philippines B. Manchuria C. The Soviet Union D. Germany 14. In 1937 the Japanese begin a full-out war against: A. Russia B. India C. ...
Barrington 220
... or wounded. The Allies also captured 200,000 prisoners of war (not included in the 425,000 total, above). During the fighting around the Falaise Pocket (August 1944) alone, the Germans suffered losses of around 90,000, including prisoners. ...
... or wounded. The Allies also captured 200,000 prisoners of war (not included in the 425,000 total, above). During the fighting around the Falaise Pocket (August 1944) alone, the Germans suffered losses of around 90,000, including prisoners. ...
WWII European Theater Lecture
... Was the last major offensive by the German Army. The battle got its name because the German counter achieved only a bulge in the Allied lines before being repulsed. ...
... Was the last major offensive by the German Army. The battle got its name because the German counter achieved only a bulge in the Allied lines before being repulsed. ...
World War 2 - HCC Learning Web
... The German-Italian "Axis" is formed. 1938 - Hitler annexes Austria and western Czechoslovakia. Mar 1939 - Czechoslovakia surrenders to imminent German invasion Aug 1939 - Germany and Russia sign non-aggression pact, secretly agreeing to invade Poland and share it. Germany Expansionism— Rhineland (19 ...
... The German-Italian "Axis" is formed. 1938 - Hitler annexes Austria and western Czechoslovakia. Mar 1939 - Czechoslovakia surrenders to imminent German invasion Aug 1939 - Germany and Russia sign non-aggression pact, secretly agreeing to invade Poland and share it. Germany Expansionism— Rhineland (19 ...
World War II
... regime that exalts nation and often race above the individual and that stands for a centralized autocratic government headed by a dictatorial leader, severe economic and social regimentation, and forcible suppression of opposition ...
... regime that exalts nation and often race above the individual and that stands for a centralized autocratic government headed by a dictatorial leader, severe economic and social regimentation, and forcible suppression of opposition ...
World War I to Cold War
... Black Shirts were the Italian fascists Mussolini was a virtual dictator but still technically subordinate to the King ...
... Black Shirts were the Italian fascists Mussolini was a virtual dictator but still technically subordinate to the King ...
World War II Notes
... other countries. They included Germany, Italy, and Japan. The Soviet Union had a treaty (agreement) with Germany, but did not officially join the war. ...
... other countries. They included Germany, Italy, and Japan. The Soviet Union had a treaty (agreement) with Germany, but did not officially join the war. ...
Chapter 15 Section 1 THE ROAD TO WAR - Mrs. Balk
... one of the Allies during WWI (won the war), their economy was destroyed. ...
... one of the Allies during WWI (won the war), their economy was destroyed. ...
Power Notes: World War II LEARNING OBJECTIVE: Understand
... 3) In July, 1932 the Nazis became the strongest party in the Reichstag (the German parliament), and on January 30, 1933 Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany. 4) Using arson of the Reichstag building as an excuse, Hitler abolished civil rights. The Ordinance for the Protection of the People and ...
... 3) In July, 1932 the Nazis became the strongest party in the Reichstag (the German parliament), and on January 30, 1933 Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany. 4) Using arson of the Reichstag building as an excuse, Hitler abolished civil rights. The Ordinance for the Protection of the People and ...
World War II
... Austria Hitler wanted more living space for Germans, and the “Aryan race” had the right to conquer the inferior races 1938- bullied Austrian chancellor to appoint Nazis to key government posts 3/1938- sent troops and proclaimed it part of Germany…Anschluss was created Western Democracies- no action ...
... Austria Hitler wanted more living space for Germans, and the “Aryan race” had the right to conquer the inferior races 1938- bullied Austrian chancellor to appoint Nazis to key government posts 3/1938- sent troops and proclaimed it part of Germany…Anschluss was created Western Democracies- no action ...
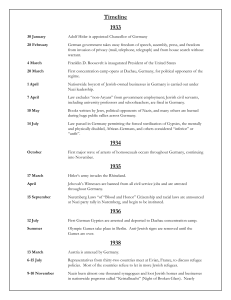
Timeline of the Holocaust
... Books written by Jews, political opponents of Nazis, and many others are burned during huge public rallies across Germany. ...
... Books written by Jews, political opponents of Nazis, and many others are burned during huge public rallies across Germany. ...
1 Social Science World War II I. THE ROOTS AND CAUSES OF
... b. The Great Depression and National Socialism in Germany c. Key characteristics of National Socialism d. Key events prior to 1938–39 4. Militarism in Japan a. Key events prior to 1937 C. Crises of 1938–39 1. Anschluss with Austria 2. Munich crisis 3. Hitler and Poland ...
... b. The Great Depression and National Socialism in Germany c. Key characteristics of National Socialism d. Key events prior to 1938–39 4. Militarism in Japan a. Key events prior to 1937 C. Crises of 1938–39 1. Anschluss with Austria 2. Munich crisis 3. Hitler and Poland ...
World War Two: Practices & Effects
... that we will escape…that this western hemisphere will not be attacked”—outraged many isolationists ...
... that we will escape…that this western hemisphere will not be attacked”—outraged many isolationists ...
New Order (Nazism)
The New Order (German: Neuordnung) or the New Order of Europe (German: Neuordnung Europas) was the political order which Nazi Germany wanted to impose on the conquered areas under its dominion. The establishment of the New Order had already begun long before the start of World War II, but was publicly proclaimed by Adolf Hitler in 1941:The year 1941 will be, I am convinced, the historical year of a great European New Order.Among other things, it entailed the creation of a pan-German racial state structured according to Nazi ideology to ensure the supremacy of an Aryan-Nordic master race, massive territorial expansion into Eastern Europe through its colonization with German settlers, the physical annihilation of the Jews and others considered to be ""unworthy of life"", and the extermination, expulsion, or enslavement of most of the Slavic peoples and others regarded as ""racially inferior"". Nazi Germany’s desire for aggressive territorial expansionism was one of the most important causes of World War II.Historians are still divided as to its ultimate goals, some believing that it was to be limited to Nazi German domination of Europe, while others maintain that it was a springboard for eventual world conquest and the establishment of a world government under German control.The Führer gave expression to his unshakable conviction that the Reich will be the master of all Europe. We shall yet have to engage in many fights, but these will undoubtedly lead to most wonderful victories. From there on the way to world domination is practically certain. Whoever dominates Europe will thereby assume the leadership of the world.