WWIIEnd09
... Nazis are put on trial for the new crime of “Crimes against Humanity” All but one Nazi leader swear they were in the right until the bitter end. ...
... Nazis are put on trial for the new crime of “Crimes against Humanity” All but one Nazi leader swear they were in the right until the bitter end. ...
I: THE RISE OF FASCISM—GERMANY,ITALY, AND JAPAN
... Hitler’s secret police. Most people were proud to be Germans and proud to be Nazis. In 1936, Hitler sent troops to the Rhineland, an old section of Germany along the Rhine River, where they were not allowed according to the Treaty of Versailles. This act, another violation of the Treaty, was a clear ...
... Hitler’s secret police. Most people were proud to be Germans and proud to be Nazis. In 1936, Hitler sent troops to the Rhineland, an old section of Germany along the Rhine River, where they were not allowed according to the Treaty of Versailles. This act, another violation of the Treaty, was a clear ...
Unit 12 – WWII: Study Guide
... General Tojo ordered a surprise attack on the American naval fleet at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. Dec. 7, 1941 Japanese planes destroy or damage 19 ships, many planes, and kill over 2400 people. It was “a day that will live in infamy.” Dec. 8, 1941, President Roosevelt asks for declaration of war. ...
... General Tojo ordered a surprise attack on the American naval fleet at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. Dec. 7, 1941 Japanese planes destroy or damage 19 ships, many planes, and kill over 2400 people. It was “a day that will live in infamy.” Dec. 8, 1941, President Roosevelt asks for declaration of war. ...
WORLD WAR II TIMELINE 1931 September 18: Japan begin
... January: For the first time in his annual address to Congress, FDR proposes no domestic reforms but instead stresses the danger posed to democracy and international peace by the forces of aggression. Later in the month, the United States budget shows increased spending on national defense. March: Ge ...
... January: For the first time in his annual address to Congress, FDR proposes no domestic reforms but instead stresses the danger posed to democracy and international peace by the forces of aggression. Later in the month, the United States budget shows increased spending on national defense. March: Ge ...
The Battle for France and Great Britain
... Germany’s Jews became a problem. Hitler found that he could not get rid of Jews through emigration. So he put another part of his plan into effect. Hitler ordered Jews in all countries under his control to be moved into certain cities in Poland. In those cities, they were herded into dismal, overcro ...
... Germany’s Jews became a problem. Hitler found that he could not get rid of Jews through emigration. So he put another part of his plan into effect. Hitler ordered Jews in all countries under his control to be moved into certain cities in Poland. In those cities, they were herded into dismal, overcro ...
Paths to War
... representatives to address Hitler’s demands on Czechoslovakia. Although allied with Czechoslovakia, the British and French agreed to virtually all of Hitler’s demands. The Czechs were abandoned by their allies and forced to helplessly watch German troops occupy the Sudetenland. Hitler promised that ...
... representatives to address Hitler’s demands on Czechoslovakia. Although allied with Czechoslovakia, the British and French agreed to virtually all of Hitler’s demands. The Czechs were abandoned by their allies and forced to helplessly watch German troops occupy the Sudetenland. Hitler promised that ...
WWII Guided Reading_world and Georgia-1y9q53p
... 6. What did Britain and France do to appease Hitler? Why? ...
... 6. What did Britain and France do to appease Hitler? Why? ...
Origins of World War 1
... Effects on Americans Racial Tensions of World War II Effects on Americans Rationing - a system for limiting the distribution of food, gasoline, and other goods—so the military could have the weapons, equipment, and supplies it needed. As a result, life in the United States would change dramatical ...
... Effects on Americans Racial Tensions of World War II Effects on Americans Rationing - a system for limiting the distribution of food, gasoline, and other goods—so the military could have the weapons, equipment, and supplies it needed. As a result, life in the United States would change dramatical ...
Guided Notes: The Great Depression and WWII
... with Germany, and Germans purposely bombed several civilian targets around London. The Battle of Britain lasted nearly three months. Despite being bombed constantly, the British people did not surrender. Even though Hitler made a previous agreement with Stalin, he feared Stalin’s intentions for terr ...
... with Germany, and Germans purposely bombed several civilian targets around London. The Battle of Britain lasted nearly three months. Despite being bombed constantly, the British people did not surrender. Even though Hitler made a previous agreement with Stalin, he feared Stalin’s intentions for terr ...
WW2--Fascist Aggression
... On April 28, 1939, Hitler announced his plans to take back the Polish corridor On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland, sending in divebombers, tanks, and troops Blitzkrieg: “lightning war,” or sudden, massive attack On September 3rd, Britain and France declared war on Germany and began mobiliz ...
... On April 28, 1939, Hitler announced his plans to take back the Polish corridor On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland, sending in divebombers, tanks, and troops Blitzkrieg: “lightning war,” or sudden, massive attack On September 3rd, Britain and France declared war on Germany and began mobiliz ...
Section One: Multiple Choice. Select the BEST answer
... c) Occupation of Czechoslovakia d) Takeover of Austria by the Nazis 18. Canada joined WWII as: a) an independent nation b) a colony of Britain c) a result of the bullying from Britain and France d) an ally of the US 19. In 1939 why did Canada declare war on Germany one week after Great Britain? a) C ...
... c) Occupation of Czechoslovakia d) Takeover of Austria by the Nazis 18. Canada joined WWII as: a) an independent nation b) a colony of Britain c) a result of the bullying from Britain and France d) an ally of the US 19. In 1939 why did Canada declare war on Germany one week after Great Britain? a) C ...
World History Notes
... watching other countries fall, the Nazis came through the Northern woods of France. They circled around to trap the Allied troops ...
... watching other countries fall, the Nazis came through the Northern woods of France. They circled around to trap the Allied troops ...
Unit Outline - World War II
... Rights of Japanese Americans Integration of African Americans US reactions to the Nazi Holocaust Morality of nuclear warfare (Should the US have dropped the atomic bomb?) Treatment of war criminals What role did the US play in securing the peace after WWII? The Nazi Holocaust was an example of genoc ...
... Rights of Japanese Americans Integration of African Americans US reactions to the Nazi Holocaust Morality of nuclear warfare (Should the US have dropped the atomic bomb?) Treatment of war criminals What role did the US play in securing the peace after WWII? The Nazi Holocaust was an example of genoc ...
textbook 569-577 - San Leandro Unified School District
... THE BATTLE OF THE ATLANTIC After the attack on Pearl Harbor, Hitler ordered submarine raids against ships along America’s east coast. The German aim in the Battle of the Atlantic was to prevent food and war materials from reaching Great Britain and the Soviet Union. Britain depended on supplies from ...
... THE BATTLE OF THE ATLANTIC After the attack on Pearl Harbor, Hitler ordered submarine raids against ships along America’s east coast. The German aim in the Battle of the Atlantic was to prevent food and war materials from reaching Great Britain and the Soviet Union. Britain depended on supplies from ...
Chapter 25: World War II
... Surrender terms of Germany: Germany and its capital occupied by armies from France, Great Britain, the Soviet Union, and the United States. ...
... Surrender terms of Germany: Germany and its capital occupied by armies from France, Great Britain, the Soviet Union, and the United States. ...
Chapter 29: World War II 1933-1945
... Allied forces crushed Hitler’s armies from the west as Soviet forces pushed from the east April 1945: Hitler committed suicide May 7, 1945: German leaders agreed to an official surrender President Roosevelt died before he could see Germany surrender IV. Crimes Against Humanity When Allied ...
... Allied forces crushed Hitler’s armies from the west as Soviet forces pushed from the east April 1945: Hitler committed suicide May 7, 1945: German leaders agreed to an official surrender President Roosevelt died before he could see Germany surrender IV. Crimes Against Humanity When Allied ...
WORLD WAR II
... “puppet” government—Vichy Government. France had to sign an armistice in the same boxcar that Germany signed the WW1 armistice. Free French leader Charles De Gaulle fled to England. THE BATTLE OF BRITAIN Hitler did not want war with Britain. The countries he invaded were the ones needed to fulfill l ...
... “puppet” government—Vichy Government. France had to sign an armistice in the same boxcar that Germany signed the WW1 armistice. Free French leader Charles De Gaulle fled to England. THE BATTLE OF BRITAIN Hitler did not want war with Britain. The countries he invaded were the ones needed to fulfill l ...
The Great Depression and World War II
... Poland if Germany attacked. On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded an unsuspecting and unprepared Poland. Hitler moved his forces quickly, using a technique called blitzkrieg which means “lightning war.” Joint forces of armored tanks and bombers raced through the countryside of Poland. On September 3 ...
... Poland if Germany attacked. On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded an unsuspecting and unprepared Poland. Hitler moved his forces quickly, using a technique called blitzkrieg which means “lightning war.” Joint forces of armored tanks and bombers raced through the countryside of Poland. On September 3 ...
World War II Study Guide Vocabulary: 9. Goals of World War II Goals
... Hitler was unhappy that the Treaty of Versailles made them pay back quite a bit of money while they also lost some of their land. He wanted to take back that land and show that Germany can be powerful. 12. Why was the Battle of Britain a key victory for the Allied Powers? The Allied Powers first vic ...
... Hitler was unhappy that the Treaty of Versailles made them pay back quite a bit of money while they also lost some of their land. He wanted to take back that land and show that Germany can be powerful. 12. Why was the Battle of Britain a key victory for the Allied Powers? The Allied Powers first vic ...
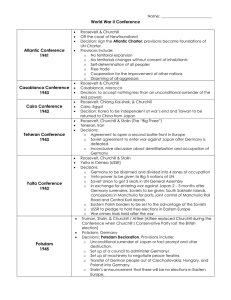
World War II Conferences
... o Germany to be disarmed and divided into 4 zones of occupation o Veto power to be given to Big 5 nations at UN o Soviet Union to get 3 seats in UN General Assembly o In exchange for entering war against Japan 2 – 3 months after Germany surrenders, Soviets to be given: South Sakhalin Islands, conces ...
... o Germany to be disarmed and divided into 4 zones of occupation o Veto power to be given to Big 5 nations at UN o Soviet Union to get 3 seats in UN General Assembly o In exchange for entering war against Japan 2 – 3 months after Germany surrenders, Soviets to be given: South Sakhalin Islands, conces ...
WWII ppt
... • In both Britain and France, many saw Hitler and fascism as a defense against a worse evil – the spread of Soviet communism. • Additionally, the Great Depression sapped the energies of the western democracies. • Finally, widespread pacifism, or opposition to all war, and disgust with the destructi ...
... • In both Britain and France, many saw Hitler and fascism as a defense against a worse evil – the spread of Soviet communism. • Additionally, the Great Depression sapped the energies of the western democracies. • Finally, widespread pacifism, or opposition to all war, and disgust with the destructi ...
The Countries Involved in WWII 1939 - 1945
... countries were successful in maintaining their neutrality, such as Ireland (Northern Ireland fought alongside Great Britain, while the independent south, Eire, remained neutral, although some citizens volunteered to fight alongside British forces during the war.) Portugal’s fascist dictator sympathi ...
... countries were successful in maintaining their neutrality, such as Ireland (Northern Ireland fought alongside Great Britain, while the independent south, Eire, remained neutral, although some citizens volunteered to fight alongside British forces during the war.) Portugal’s fascist dictator sympathi ...
Chapter 11 Test
... The act of assembling and preparing for war. _____ 1.5 million people died when this city was under siege for 900 days. ____ The man who became president of the U.S. after Roosevelt’s death. _____ Where 110 thousand Japanese-Americans were resettled and held captive. ____ Men who flew suicide missio ...
... The act of assembling and preparing for war. _____ 1.5 million people died when this city was under siege for 900 days. ____ The man who became president of the U.S. after Roosevelt’s death. _____ Where 110 thousand Japanese-Americans were resettled and held captive. ____ Men who flew suicide missio ...
U.S. History Notes Chapter 35: “America in World War II”
... front against Hitler, since Soviet forces were dying by the millions (20 million by war’s end), and the Americans were eager to comply, but the British, remembering WWI, were reluctant. i. Instead of a frontal European assault, the British devised an invasion through North Africa, so that the Allies ...
... front against Hitler, since Soviet forces were dying by the millions (20 million by war’s end), and the Americans were eager to comply, but the British, remembering WWI, were reluctant. i. Instead of a frontal European assault, the British devised an invasion through North Africa, so that the Allies ...
British propaganda during World War II

Britain re-created the World War I Ministry of Information for the duration of World War II to generate propaganda to influence the population towards support for the war effort. A wide range of media was employed aimed at local and overseas audiences. Traditional forms such as newspapers and posters were joined by new media including cinema (film), newsreels and radio. A wide range of themes were addressed, fostering hostility to the enemy, support for allies, and specific pro war projects such as conserving metal and growing vegetables.