File
... The Battle of the Bulge which lasted from December 16, 1944 to January 28, 1945 was the largest __________ battle of World War II in which the United States participated. More than a million men fought in this battle including some 600,000 Germans, 500,000 Americans, and 55,000 British. At the concl ...
... The Battle of the Bulge which lasted from December 16, 1944 to January 28, 1945 was the largest __________ battle of World War II in which the United States participated. More than a million men fought in this battle including some 600,000 Germans, 500,000 Americans, and 55,000 British. At the concl ...
AMERICA IN THE MODERN AGE - MissDWorldofSocialStudies
... with words, threats, espionage but not weapons of mass destruction ...
... with words, threats, espionage but not weapons of mass destruction ...
US Involvement in World War 2
... of nationsEurope in Eastern Europe the eminent defeat of Germany: –Stalin refused to give up Eastern Europe but he did agree to “self-determination” –Stalin agreed to send Soviet troops to the Pacific after the German surrender if the USSR ...
... of nationsEurope in Eastern Europe the eminent defeat of Germany: –Stalin refused to give up Eastern Europe but he did agree to “self-determination” –Stalin agreed to send Soviet troops to the Pacific after the German surrender if the USSR ...
Fighting World War II
... advance into the Soviet Union – “Scorched earth” policy – Stalin begs for support ...
... advance into the Soviet Union – “Scorched earth” policy – Stalin begs for support ...
World War II p. 430
... • first naval battle fought without the opposing ships making contact, 6. Battle of Midway - June 4-7, 1942, effectively destroyed Japan’s naval strength when the US destroyed four of its aircraft carriers. Japan’s navy never recovered and it was on the defensive after this battle. US on offense. ...
... • first naval battle fought without the opposing ships making contact, 6. Battle of Midway - June 4-7, 1942, effectively destroyed Japan’s naval strength when the US destroyed four of its aircraft carriers. Japan’s navy never recovered and it was on the defensive after this battle. US on offense. ...
- Sweet Home Central School District
... problems following WWI, which added to the growing tensions and hostility. The League of Nations, once proposed by Woodrow Wilson and created between European nations, had also been ineffective. As Germany began to rearm its military and move into other territories (clearly violating the Treaty of V ...
... problems following WWI, which added to the growing tensions and hostility. The League of Nations, once proposed by Woodrow Wilson and created between European nations, had also been ineffective. As Germany began to rearm its military and move into other territories (clearly violating the Treaty of V ...
PowerPoint Presentation - The Grey Zone by Tim Blake Nelson
... Immediate causes: Japan invades China, 1937, Germany invades Poland, 1939. Underlying causes: pressures from Treaty of Versailles and worldwide depression. US entered war following attack on Pearl Harbor then Philippines, Dec 7-8, 1941. Imperialism and nationalism; Japan sought more land and natural ...
... Immediate causes: Japan invades China, 1937, Germany invades Poland, 1939. Underlying causes: pressures from Treaty of Versailles and worldwide depression. US entered war following attack on Pearl Harbor then Philippines, Dec 7-8, 1941. Imperialism and nationalism; Japan sought more land and natural ...
Europe in Flames
... • 1939- Germany breaks Munich agreement and invades Poland. • 1940- Hitler’s army invades France. Paris falls in 10 days. • 1941- Germany invades the Soviet Union, breaking the NaziSoviet Nonaggression Pact. Poland was to have been divided. Lesson: Don’t make deals with Germany. • 1941- Japan attack ...
... • 1939- Germany breaks Munich agreement and invades Poland. • 1940- Hitler’s army invades France. Paris falls in 10 days. • 1941- Germany invades the Soviet Union, breaking the NaziSoviet Nonaggression Pact. Poland was to have been divided. Lesson: Don’t make deals with Germany. • 1941- Japan attack ...
Overview: The War in Europe In 1918, the Central Powers and Allies
... final push into Germany itself began. It was during this period that Italy surrendered to the Allies and Mussolini was executed by a mob of Italian partisans. Slowed only by the Germans’ final counterattack in the “bulge” of the advancing Allied lines, the Allies pushed further and further eastward. ...
... final push into Germany itself began. It was during this period that Italy surrendered to the Allies and Mussolini was executed by a mob of Italian partisans. Slowed only by the Germans’ final counterattack in the “bulge” of the advancing Allied lines, the Allies pushed further and further eastward. ...
Chapter 17 Lesson 5 Day 2
... Soviet Union, the United States, and Great Britain—met in Tehran, the capital of Iran, to discuss war strategy. Their plan for defeating Germany would have important consequences after the war. Soviet forces would meet up with U.S.-British forces along a north-south dividing line, with the Soviets l ...
... Soviet Union, the United States, and Great Britain—met in Tehran, the capital of Iran, to discuss war strategy. Their plan for defeating Germany would have important consequences after the war. Soviet forces would meet up with U.S.-British forces along a north-south dividing line, with the Soviets l ...
Slide 1
... 5) The war resumed in April of 1940 when the Nazi warmachine crashed into Denmark, Norway, the Netherlands, and Belgium. The fall of Belgium enabled German forces to invade northern France and flank past the Maginot Line. With the bulk of French forces stationed along the German border, Hitler’s for ...
... 5) The war resumed in April of 1940 when the Nazi warmachine crashed into Denmark, Norway, the Netherlands, and Belgium. The fall of Belgium enabled German forces to invade northern France and flank past the Maginot Line. With the bulk of French forces stationed along the German border, Hitler’s for ...
DAV Meets the Needs of World War II
... The war initially focused on the Pacific as a strategy against Germany and Italy was discussed between the United States and Great Britain. Faced with the losses of the Philippines, Wake Island and other strategic bases in the South Pacific, it was the successes of the Doolittle Raid, the battles of ...
... The war initially focused on the Pacific as a strategy against Germany and Italy was discussed between the United States and Great Britain. Faced with the losses of the Philippines, Wake Island and other strategic bases in the South Pacific, it was the successes of the Doolittle Raid, the battles of ...
File
... “Hitler knows that he will have to break us in this island or lose the war. If we can stand up to him, all Europe may be freed and the life of the world may ...
... “Hitler knows that he will have to break us in this island or lose the war. If we can stand up to him, all Europe may be freed and the life of the world may ...
World War to Cold War
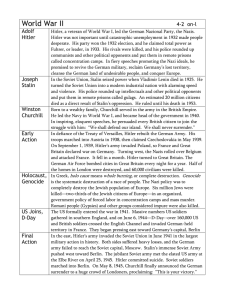
... and violence. His police rounded up intellectuals and other political opponents and put them in remote prisons called gulags. An estimated 20 million citizens died as a direct result of Stalin’s oppression. He ruled until his death in 1953. Born to a wealthy family, Churchill served in the army in t ...
... and violence. His police rounded up intellectuals and other political opponents and put them in remote prisons called gulags. An estimated 20 million citizens died as a direct result of Stalin’s oppression. He ruled until his death in 1953. Born to a wealthy family, Churchill served in the army in t ...
Chapter 10 - Cloudfront.net
... • Analyze the responses of Britain, France, and the United States to the aggressive regimes. ...
... • Analyze the responses of Britain, France, and the United States to the aggressive regimes. ...
European History Lecture 11
... It was the first time in history that a German field marshal had been captured in Battle. During the same weeks, at the northern end of the eastern front, on the Baltic sea, Soviet troops managed to open a precarious supply rout into Leningrad, which had been tightly ringed by German forces for 506 ...
... It was the first time in history that a German field marshal had been captured in Battle. During the same weeks, at the northern end of the eastern front, on the Baltic sea, Soviet troops managed to open a precarious supply rout into Leningrad, which had been tightly ringed by German forces for 506 ...
World War II Exam—Regular
... 11. ___ Two causes of the rise of dictatorships after World War I were: a) the peace treaty that ended World War I and economic depression b) new political ideas and economic depression c) the peace treaty that ended World War I and a lack of strong leadership after the war 12. ___ Which of the foll ...
... 11. ___ Two causes of the rise of dictatorships after World War I were: a) the peace treaty that ended World War I and economic depression b) new political ideas and economic depression c) the peace treaty that ended World War I and a lack of strong leadership after the war 12. ___ Which of the foll ...
Chapter Test
... 39: France and Britain wanted to avoid war with Germany because a. their military was not as strong as Germany’s b. they didn’t want to lose another generation of young men c. they agreed with Hitler’s views on the Jews d. they was yella’ 40: One way the United States helped the Allies before the co ...
... 39: France and Britain wanted to avoid war with Germany because a. their military was not as strong as Germany’s b. they didn’t want to lose another generation of young men c. they agreed with Hitler’s views on the Jews d. they was yella’ 40: One way the United States helped the Allies before the co ...
Honors United States History 2 Final Examination Review Sheet
... What historical event led to the rise of fascism in Italy and German, and totalitarianism in the Soviet Union? Chapter 24 Section 2 After Hitler invaded Czechoslovakia, where was his next target? Where did the British hold out from the German attack (what battle)? What country had controlled most of ...
... What historical event led to the rise of fascism in Italy and German, and totalitarianism in the Soviet Union? Chapter 24 Section 2 After Hitler invaded Czechoslovakia, where was his next target? Where did the British hold out from the German attack (what battle)? What country had controlled most of ...
Chapters 30-31: The Great Depression, World War II
... The Soviet Union Because its economy was independent and did not depend on external trade, the Soviet Union had few economic troubles during the 1930s. ...
... The Soviet Union Because its economy was independent and did not depend on external trade, the Soviet Union had few economic troubles during the 1930s. ...
Allies of World War II

The Allies of World War II, called the United Nations from the 1 January 1942 declaration, were the countries that opposed the Axis powers together during the Second World War (1939–1945). The Allies promoted the alliance as seeking to stop German, Japanese and Italian aggression.The anti-German coalition at the start of the war (1 September 1939) consisted of France, Poland and Great Britain, soon to be joined by the British Commonwealth (Canada, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa). Poland was a minor factor after its defeat in 1939; France was a minor factor after its defeat in 1940. After first having cooperated with Germany in partitioning Poland whilst remaining neutral in the Allied-Axis conflict, the Soviet Union perforce joined the Allies in June 1941 after being invaded by Germany. The United States provided war material and money all along, and officially joined in December 1941 after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. As of 1942, the ""Big Three"" leaders of the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, and the United States controlled Allied policy; relations between the UK and the U.S. were especially close. China had been already at war with Japan since 1937 but officially joined the Allies in 1941. The Big Three and China were referred as a ""trusteeship of the powerful"", then were recognized as the Allied ""Big Four"" in Declaration by United Nations and later the ""Four Policemen"" of ""United Nations"" for the Allies. Other key Allies included British India, the Netherlands, and Yugoslavia as well as Free France; there were numerous others. Together they called themselves the ""United Nations"" and in 1945 created the modern UN.