* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II p. 430
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Tora! Tora! Tora! wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Pearl Harbor (film) wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Britain (film) wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
The War That Came Early wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
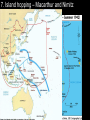
p. 443 - 457 I. Leaders A. Axis 1. Adolf Hitler – Germany (did already) 2. Benito Mussolini – Italy (did already) 3. Emperor Hirohito – (1901-1989) Japan a. The emperor was regarded as divine by Japanese. Reality little power. b. Reluctantly supported invasion of Manchuria & war with China. “Asia for Asians. (Panay Incident???) c. Attempted to encourage cooperation with Britain and the USA. d. had no choice but to approve the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. e. Despite lack of enthusiasm to go to war, was pleased with the Japanese military & naval successes. f. After the atomic bomb attacks, wants Japan to surrender. g. August 15, 1945, makes a radio broadcast announcing the end of the war (first time the people of Japan had heard the voice of their emperor.) h. Some Allied leaders want to try him as war criminal. B. Allies 1. Joseph Stalin – USSR – (already did) 2. Franklin D. Roosevelt – USA – a. Guided US through Depression b. Initially kept America out of World War Two c. Provided financial assistance and equipment to Britain and its allies. d. Devoted time to the planning of the post-war workload, (UN). 3. Harry Truman – USA – took FDR’s place when he died, decided to drop atomic bomb. 4. Winston Churchill – Great Britain a. May 13, 1940 became Prime Minister – later fall of France b. To parliament -“I have nothing to offer but blood, toil, tears and sweat” c. Led G.B. through the Battle of Britain d. “Give us the tools and we'll finish the job” - asks US for supplies e. We shall defend our island, whatever the cost may be, we shall fight on the beaches, we shall fight on the landing grounds, we shall fight in the fields and in the streets, we shall fight in the hills; we shall never surrender. f. “Never in the field of human conflict was so much owed by so many to so few.” Battle of Britain g. “If Hitler invaded hell I would make at least a favorable reference to the devil in the House of Commons.” Following Germany’s attack on USSR 5. Big Three – Churchill, Roosevelt, and Stalin a. Decide the plans of WW2 and the future. II. Generals A. Axis 1. Wilhelm Keitel – German #1 general - Hitler's chief military advisor, completely loyal to Hitler. 2. Erwin Rommel – Desert Fox – a. blitzkrieg, famous for attack on France and exploits in N. Africa. b. “He outwitted, bluffed, deceived, cheated the enemy. It was said that his greatest pleasure was to trick his opponents into premature and often quite needless surrender.” David Irving c. Not given enough supplies to win d. Committed suicide when falsely accused of plotting against Hitler. 2. Heinz Guderian - Regarded as one of the leading pioneers of modern mechanized warfare. 3. Alfred Jodl, Chief of the Operations Staff during the war. Hitler's first adviser on strategic and operations matters. 2. Hideki Tojo – Japan - Axis a. led his country's war efforts after the attack on the U.S. base at Pearl Harbor, December 7, 1941, b. under his direction smashing victories were initially scored throughout Southeast Asia and the Pacific. c. was tried for war crimes and was found guilty, hanged. 3. Admiral Isoruku Yamamoto – a. led attack on Pearl Harbor – b. "I'm afraid we have awakened a sleeping giant and filled it with terrible resolve," c. Plane shot down B. Bernard Montgomery – British – Monty – beat Rommel C. Dwight Eisenhower – US – In charge of European theater D. Douglas Macarthur – US – Pacific theater of war – island hopping E. George Patton – US – famous tank commander – “Old blood and guts” F. Admiral Chester Nimitz – US – Pacific fleet commander G. Georgi Konstantinovich Zhukov – USSR – a. took charge of the defense of Stalingrad where b. oversaw the encirclement and surrender of the German 6th Army. c. coordinated the Soviet armies at the Battle of Kursk, the largest tank battle in history, the defeat of the Germans at Kursk was the turning point of the war. d. Zhukov led the final Soviet assault on Germany in 1945, capturing Berlin in April and becoming a world famous figure III. Inventions A. B. C. D. E. F. Jets - Messerschmitt Me 262 , Me163 Komet rocket fighters Radar Sonar Missles – V1 flying bomb “Buzz Bomb”, V2 ballistic missile Aircraft carriers Assault weapons – MP 44 Submachine gun G. Napalm H. penicillin I. Synthetic rubber J. Magnetron which is now used in microwave ovens k. Atomic bomb – Little boy Hiroshima, Fat Man Nagasaki L. SPAM M. Helicopters N. Operational Battle Tanks O. Synthetic motor oil P. Aluminum Tanks IV. Main Battles/Events A. European Theater – After Poland invasion 1. Phony War – Sitzkrieg 2. USSR under Stalin takes – Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Finland 3. Apr. 9, 1939 Hitler takes Den and Norway 4. May 1940 Hitler takes low countries more 5. France - Maginot Line - Dunkirk -France Surrenders on June 22 - Occupied France and Vichy France - Charles deGaulle Now Britain Is All Alone! 6. U. S. Lend-Lease Act, 1941 Great Britain.........................$31 billion Soviet Union..........................$11 billion France..................................$3 billion China..................................$1.5 billion Other European......................$500 million South America.......................$400 million The amount totaled: $48,601,365,000 Lend-Lease Battle of Britain: The “Blitz” 7. Great Britain – - Germans assemble - Luftwaffe vs. RAF - Battle of Britain / Blitz - Radar allows GB to maximize the RAF Date:July 1940 to May 1941 (with main daylight battles taking place in August to October) Location:United Kingdom airspace, mostly over southern England Result:British strategic victory Combatants United Kingdom Germany Commanders Hugh Dowding, Hermann Göring Strength approx 700 fighters (at the beginning)1,260 bombers; 320 dive-bombers; 1,090 fighters (at the beginning) Casualties1,550 aircraft; Civilian: 27,450 dead, 32,140 wounded1,890 aircraft 8. Axis invasion - Fall 1940 Italy invades Eg & Greece - Apr. 1941 Ger. Invades Yugo - May 1941 Ger invades Greece - June 1941 Ger signs Turkey - June 22, 1941 Ger invades USSR (Barbarossa) - Stalingrad (0 – 48) – Turning point - sniper - (US and Pearl Harbor) 9. The Atlantic Charter Roosevelt and Churchill sign treaty of friendship in August 1941. Solidifies alliance. Fashioned after Wilson’s 14 Points. Calls for League of Nations type organization. 10. North Africa –Nov. 1942 - Rommel 11. “Soft Underbelly” – Sept. 1943 - Anzio 12. “Round the Clock Bombing” (0-2 min) Little Friends 13. D-day/Normandy/Operation Overlord Band (3 min – end) 14. Battle of the Bulge - December 16, 1944 to January 25, 1945 15. May 8, 1945 Ger. Surrenders (V E Day) WW2 Pwpt 2 Europe theatre Pwpt. B. Pacific Theatre 1. 1931 Japan attacks China – 1st belligerent action. 2. Panay incident -Japanese attack on the United States Navy gunboat Panay Dec. 12, 1937 3. Dec. 7,1941 – Pearl Harbor and … (data) a. Gen. Yamamoto b. Dec. 8 – “This day will live in infamy” FDR c. Other US and British military installations attacked also d. Bataan Death March - 72,000 prisoners taken together, killing rate of one in four up to two in seven (25% to 28.5%) 4. Doolittle Raids - April 18, 1942. Left from carrier Hornet, Doolittle led a flight of 16 B-25 bombers on a daring raid over Japan, hitting targets in Tokyo, Yokohama, and other cities, scoring a moral huge victory. (start at 3) 5. Battle of Coral Sea - May 4-8, 1942 - air and naval engagement between the US, Australians and Japanese on May 7-8, 1942. • stopped the Japanese advance to Australia. • first naval battle fought without the opposing ships making contact, 6. Battle of Midway - June 4-7, 1942, effectively destroyed Japan’s naval strength when the US destroyed four of its aircraft carriers. Japan’s navy never recovered and it was on the defensive after this battle. US on offense. Chester W. Nimitz Yamamoto Isoroku 3 carriers, ~25 support ships, 233 carrier aircraft, 127 land-based aircraft 4 carriers, 2 battleships, ~15 support ships (heavy and light cruisers, destroyers), 248[2] carrier aircraft, 16 floatplanes Did not participate in battle: 2 light carriers, 5 battleships, ~41 support ships (Yamamoto "Main Body", Kondo "Strike Force" plus "Escort" and "Occupation Support Force") carrier sunk, 1 destroyer sunk, 98 aircraft destroyed[citation needed], 307 killed[3] 4 carriers sunk, 1 cruiser sunk, 248 carrier aircraft destroyed, 3,057 killed 7. Island hopping – Macarthur and Nimitz • • • • • • January 1943, New Guinea Invaded Tarawa invaded, Nov. 20, 1943 Marianas secured on June 19, 20, 1944 Battle of Leyte Gulf, October 25, 1944 Iwo Jima, February 19, 1945 Okinawa, April 1, 1945 • Kamikaze • Banzai Charge 8. Japanese atrocities – Rape of Nanking, Philippines, testing disease, experimenting on soldiers, prisoners of war. (US interned Japanese civilians) 9. Atomic bombing of Japan – Warned??? a. Hiroshima Aug. 6, 1945 – 140,000 b. Nagasaki Aug. 9, 1945 – 80,000 10. V-J Day – Aug. 14, 1945 – Some don’t sur.. VI. Conference - Feb. 4–11, 1945 A. Yalta – Big 3 met to met at Yalta in the Crimea to plan the final defeat and occupation of Nazi Germany. Germany was to be divided into zones - U.S., British, French, & Soviets. Allies stated they had no duty to Germans except minimum subsistence, German military industry would be abolished or confiscated, and major war criminals to be tried at an international court, which subsequently presided at Nuremberg. More details on UN. Eastern Eur. would hold elections to determine new gov’t. USSR would help with Japan. Unconditional surrender was goal. • B. Potsdam - July 17 to August 2, 1945 - topics administration of defeated Germany, the demarcation of the boundaries of Poland, the occupation of Austria, the definition of the Soviet Union’s role in eastern Europe, the determination of reparations, and the further prosecution of the war against Japan. The good will characterized former wartime conferences was missing at Potsdam, each nation was most concerned with its own self-interest, and Churchill was suspicious of Stalin. Stalin will reverse on many of the earlier agreements. WW II Casualties: Europe Each symbol indicates 100,000 dead in the appropriate theater of operations WW II Casualties: Asia Each symbol indicates 100,000 dead in the appropriate theater of operations Country Men in war Battle deaths Wounded Australia 1,000,000 26,976 180,864 Austria 800,000 280,000 350,117 Belgium 625,000 8,460 55,5131 40,334 943 4,222 339,760 6,671 21,878 Canada 1,086,3437 42,0427 53,145 China3 17,250,521 1,324,516 1,762,006 Czechoslovakia — 6,6834 8,017 Denmark — 4,339 — Finland 500,000 79,047 50,000 France — 201,568 400,000 20,000,000 3,250,0004 7,250,000 Greece — 17,024 47,290 Hungary — 147,435 89,313 India 2,393,891 32,121 64,354 Italy 3,100,000 149,4964 66,716 Japan 9,700,000 1,270,000 140,000 Netherlands 280,000 6,500 2,860 New Zealand 194,000 11,6254 17,000 75,000 2,000 — — 664,000 530,000 650,0005 350,0006 — 410,056 2,473 — — 6,115,0004 14,012,000 5,896,000 357,1164 369,267 16,112,566 291,557 670,846 3,741,000 305,000 425,000 Brazil2 Bulgaria Germany Norway Poland Romania South Africa U.S.S.R. United Kingdom United States Yugoslavia WW II Casualties 1. Civilians only. 2. Army and navy figures. 3. Figures cover period July 7, 1937 to Sept. 2, 1945, and concern only Chinese regular troops. They do not include casualties suffered by guerrillas and local military corps. 4. Deaths from all causes. 5. Against Soviet Russia; 385,847 against Nazi Germany. 6. Against Soviet Russia; 169,822 against Nazi Germany. 7. National Defense Ctr., Canadian Forces Hq., Director of History. Massive Human Dislocations The U.S. & the U.S.S.R. Emerged as the Two Superpowers of the later 20c The Bi-Polarization of Europe: The Beginning of the Cold War The Division of Germany: 1945 - 1990 The Creation of the U. N. The Nuremberg War Trials: Crimes Against Humanity Japanese War Crimes Trials General Hideki Tojo Bio-Chemical Experiments 7 Future American Presidents Served in World War II The Race for Space Early Computer Technology Came Out of WW II Colossus, 1941 Mark I, 1944 Admiral Grace Hooper, 1944-1992 COBOL language The Emergence of Third World Nationalist Movements The De-Colonization of European Empires Was the US justified in dropping the Atomic Bomb on Hiroshima? 1. Yes 2. No 50% 1 50% 2 Nagasaki? 1. Yes 2. No 3. Should have waited/given more time. 33% 1 33% 2 33% 3 Which of the following dictators would you least like to live under? 1. 2. 3. 4. Hitler Mussolini Hirohito Stalin 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 After looking at WWII, who would you least like to be attacked by? (no Abomb) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Germany USSR Japan Italy USA 20% 1 20% 20% 2 3 20% 4 20% 5