Solutes
... • Solvent – substance present in the largest amount • Solutes – substance present in the smallest amount • Aqueous solution – solutions with water as the solvent • Concentration – the amount of solute in a given volume of solution • Concentrated – large amount of solute dissolved in solvent • Dilute ...
... • Solvent – substance present in the largest amount • Solutes – substance present in the smallest amount • Aqueous solution – solutions with water as the solvent • Concentration – the amount of solute in a given volume of solution • Concentrated – large amount of solute dissolved in solvent • Dilute ...
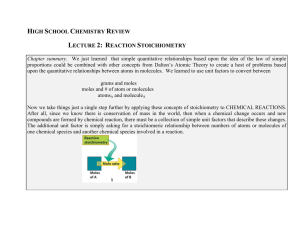
HIGH SCHOOL CHEMISTRY REVIEW LECTURE 2: REACTION
... If you follow these two rules for balancing equations, solving every equation will be a snap---unless the rules don’t apply. Then you are on your own and will wish you’d practiced more. Look, everyone can balance equations. It is just a matter of how much time it takes: practice a lot and solve your ...
... If you follow these two rules for balancing equations, solving every equation will be a snap---unless the rules don’t apply. Then you are on your own and will wish you’d practiced more. Look, everyone can balance equations. It is just a matter of how much time it takes: practice a lot and solve your ...
Aqueous Solutions
... Figure 4.3: (a) The ethanol molecule contains a polar O—H bond similar to those in the water molecule. (b) The polar water molecule interacts strongly with the polar O—H bond in ethanol. This is a case of "like dissolving like." ...
... Figure 4.3: (a) The ethanol molecule contains a polar O—H bond similar to those in the water molecule. (b) The polar water molecule interacts strongly with the polar O—H bond in ethanol. This is a case of "like dissolving like." ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... eg. when table salt is mixed with water, it seems to disappear, or become a liquid - the composition can vary from one sample to another. Pure substances have constant composition. Salt water samples from different seas or lakes have different amounts of salt ...
... eg. when table salt is mixed with water, it seems to disappear, or become a liquid - the composition can vary from one sample to another. Pure substances have constant composition. Salt water samples from different seas or lakes have different amounts of salt ...
〈541〉 TITRIMETRY
... substituted for the calomel electrode. The silver-silver chloride electrode is more rugged, and its use helps to eliminate toxic mercury salts from the laboratory. Generally, a salt bridge may be used to circumvent interference by silver ion. The more useful systems for titration in nonaqueous solve ...
... substituted for the calomel electrode. The silver-silver chloride electrode is more rugged, and its use helps to eliminate toxic mercury salts from the laboratory. Generally, a salt bridge may be used to circumvent interference by silver ion. The more useful systems for titration in nonaqueous solve ...
chromatographic study of photolysis of aqueous cyanocobalamin
... photoproducts are either fluorescent (365 nm) or quench fluorescence (254 nm), the sensitivity of detection is very high and even trace amounts of the photoproducts can be detected. In certain cases (e.g. photolysed solutions of cyanocobalamin and riboflavin), some minor unknown products of riboflav ...
... photoproducts are either fluorescent (365 nm) or quench fluorescence (254 nm), the sensitivity of detection is very high and even trace amounts of the photoproducts can be detected. In certain cases (e.g. photolysed solutions of cyanocobalamin and riboflavin), some minor unknown products of riboflav ...
Chapter 2 power point File
... electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions (between a metal and non metal) pure ionic bond - electrons are transferred. Ionic compounds cannot form molecules because each atom has a chemical bond with the atom next to it as well as an associated bond with the elements around it An i ...
... electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions (between a metal and non metal) pure ionic bond - electrons are transferred. Ionic compounds cannot form molecules because each atom has a chemical bond with the atom next to it as well as an associated bond with the elements around it An i ...
Signs of Reaction - Calderglen High School
... IDE means that the compound is made up of the TWO elements obvious from the name. Except: Hydroxide (something + H + 0) and ...
... IDE means that the compound is made up of the TWO elements obvious from the name. Except: Hydroxide (something + H + 0) and ...
Chapter 3 Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation by Heterogeneous
... quantum calculations and only consists of the two σ bond and π bond parameters. Details of the CBHLC scheme are given in the Supporting Information. All calculations were performed using the Jaguar 6.0 package [24]. QM calculations were carried out using DFT with X3LYP. X3LYP is an extended hybrid d ...
... quantum calculations and only consists of the two σ bond and π bond parameters. Details of the CBHLC scheme are given in the Supporting Information. All calculations were performed using the Jaguar 6.0 package [24]. QM calculations were carried out using DFT with X3LYP. X3LYP is an extended hybrid d ...
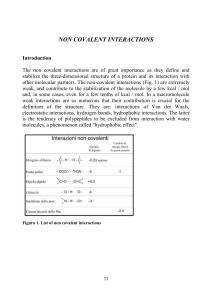
i principi di base - Structural Biology
... The hydrogen bond occurs between a donor and an acceptor of hydrogen atoms. When the interaction takes place between charged groups it is often referred to as salt bridge and it has properties typical either of an electrostatic interaction either of an hydrogen bond. The weak bonds between atoms wit ...
... The hydrogen bond occurs between a donor and an acceptor of hydrogen atoms. When the interaction takes place between charged groups it is often referred to as salt bridge and it has properties typical either of an electrostatic interaction either of an hydrogen bond. The weak bonds between atoms wit ...
Paper chromatography
... Solutes dissolve into solvents that have similar properties. (Like dissolves like) This allows different solutes to be separated by different combinations of solvents. Separation of components depends on both their solubility in the mobile phase and their differential affinity to the mobile phas ...
... Solutes dissolve into solvents that have similar properties. (Like dissolves like) This allows different solutes to be separated by different combinations of solvents. Separation of components depends on both their solubility in the mobile phase and their differential affinity to the mobile phas ...
lab-6-chrmatography
... of similar properties, isomers for example, may not separate. A sample that results in many spots after development is a confirmation of a mixture of different compounds. In that sense, TCL can also be used to determine the number of components in a mixture. Are these compounds identical? TLC can ...
... of similar properties, isomers for example, may not separate. A sample that results in many spots after development is a confirmation of a mixture of different compounds. In that sense, TCL can also be used to determine the number of components in a mixture. Are these compounds identical? TLC can ...
File
... dissolve? Dissolving Covalent Compounds • C12H22O11 (s) C12H22O11 (aq) • NO dissociation because NO ions • Sucrose dissolves in water because sugar is polar (-OH group), but dissociation does not occur. Sucrose molecules are simply separated from each other. No ions are formed ...
... dissolve? Dissolving Covalent Compounds • C12H22O11 (s) C12H22O11 (aq) • NO dissociation because NO ions • Sucrose dissolves in water because sugar is polar (-OH group), but dissociation does not occur. Sucrose molecules are simply separated from each other. No ions are formed ...
Computers_in_chemistry - University of St Andrews
... Also, a balls-and-springs model lacks the quantum mechanics needed to simulate a chemical reaction. Nonetheless, molecular dynamics is very important for understanding shape changes, interactions and energetics of large molecules. ...
... Also, a balls-and-springs model lacks the quantum mechanics needed to simulate a chemical reaction. Nonetheless, molecular dynamics is very important for understanding shape changes, interactions and energetics of large molecules. ...
Compulsory textbook Recommended textbooks Topics of the first
... and some function of the analyte on the vertical axis; the equivalence point can be read off the titration curve; it can either be sigmoidal or linear segment curve. Indicators – they are added to the analyte solution to produce a visually observable physical change (usually colour change) at or ver ...
... and some function of the analyte on the vertical axis; the equivalence point can be read off the titration curve; it can either be sigmoidal or linear segment curve. Indicators – they are added to the analyte solution to produce a visually observable physical change (usually colour change) at or ver ...
Analytical Chemistry
... Calculate the molar concentration of Ag+ in a solution having a pAg of 6.372 . pAg = - log[Ag+] = 6.372 log[Ag+] = -6.372 = - 7.oo + 0.628 [Ag+] = antilog ( -7 ) * antilog ( 0.628) = 10-7*4.246 ...
... Calculate the molar concentration of Ag+ in a solution having a pAg of 6.372 . pAg = - log[Ag+] = 6.372 log[Ag+] = -6.372 = - 7.oo + 0.628 [Ag+] = antilog ( -7 ) * antilog ( 0.628) = 10-7*4.246 ...
Introduction to Computational Chemistry Laboratory
... The good side of ab-initio methods is that they eventually converge to the exact solution, once all of the approximations are made sufficiently small in magnitude. However, this convergence is not monotonic. Sometimes, more approximate calculation gives better result for a given property, than a mor ...
... The good side of ab-initio methods is that they eventually converge to the exact solution, once all of the approximations are made sufficiently small in magnitude. However, this convergence is not monotonic. Sometimes, more approximate calculation gives better result for a given property, than a mor ...
Chapter 3 – Stoichiometry of Formulas and Equations This chapter
... atomic and macroscopic levels and 2) the number relationship between reacting species. 3.1 The Mole You were introduced briefly to the atomic mass unit in the previous chapter as a convenient way of discussing the masses of atoms and subatomic particles. As you have already surmised, on the macrosco ...
... atomic and macroscopic levels and 2) the number relationship between reacting species. 3.1 The Mole You were introduced briefly to the atomic mass unit in the previous chapter as a convenient way of discussing the masses of atoms and subatomic particles. As you have already surmised, on the macrosco ...
homework_#1_10
... Interpret the balanced equation in terms of relative numbers of moles, volumes of gases at STP and masses of reactants and products. 2C2H2(g) + 5O2 (g) ...
... Interpret the balanced equation in terms of relative numbers of moles, volumes of gases at STP and masses of reactants and products. 2C2H2(g) + 5O2 (g) ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Separate the reactions into oxidation and reduction processes Work with one (ox or red) first Balance number of non-oxygen, non-hydrogen atoms first. Then balance oxygen with water Then balance hydrogen with H+ Then balance charge with electrons. Then balance other half-reaction using steps 3 throug ...
... Separate the reactions into oxidation and reduction processes Work with one (ox or red) first Balance number of non-oxygen, non-hydrogen atoms first. Then balance oxygen with water Then balance hydrogen with H+ Then balance charge with electrons. Then balance other half-reaction using steps 3 throug ...
Section 5
... will depend on the polarity of the H-X bond (in most Brønsted acids, X = N, O, or a halogen) Electron-withdrawing groups attached to X will increase the quantity of partial positive charge on the H-atom, making it more susceptible to nucleophilic attack by a solvent (inductive effect) ...
... will depend on the polarity of the H-X bond (in most Brønsted acids, X = N, O, or a halogen) Electron-withdrawing groups attached to X will increase the quantity of partial positive charge on the H-atom, making it more susceptible to nucleophilic attack by a solvent (inductive effect) ...
File
... An atom is an extremely small particle of matter that retains its identity during chemical reactions. An atom consists of a nucleus and electrons surrounding the nucleus. The nucleus, the core of the atom, has the majority of the mass of the atom, and a positive charge. An electron is a very light p ...
... An atom is an extremely small particle of matter that retains its identity during chemical reactions. An atom consists of a nucleus and electrons surrounding the nucleus. The nucleus, the core of the atom, has the majority of the mass of the atom, and a positive charge. An electron is a very light p ...
Carbene Singlets, Triplets, and the Physics that
... while knowing a set of rules for writing them allows them to be consistent with experiments in cases where there are no extremely similar energy levels in the interaction diagram, they are not suitable for discerning numerical results. However, as will be shown in more detail later, these molecular ...
... while knowing a set of rules for writing them allows them to be consistent with experiments in cases where there are no extremely similar energy levels in the interaction diagram, they are not suitable for discerning numerical results. However, as will be shown in more detail later, these molecular ...
Computers in Chemistry - University of St Andrews
... Also, a balls-and-springs model lacks the quantum mechanics needed to simulate a chemical reaction. Nonetheless, molecular dynamics is very important for understanding shape changes, interactions and energetics of large molecules. ...
... Also, a balls-and-springs model lacks the quantum mechanics needed to simulate a chemical reaction. Nonetheless, molecular dynamics is very important for understanding shape changes, interactions and energetics of large molecules. ...
Solvent models
Within the field of computational chemistry, solvent models are a variety of methods to account for the behavior of solvated condensed phases. Solvent models allow simulations and calculations of reactions and processes which take place in solvated phases. These include biological, chemical and environmental processes. Such calculation can lead to predictions and improved understanding of the physical processes occurring. Such models have been extensively tested and reviewed in scientific literature. The various models have their own pros and cons. Implicit models are generally computationally efficient and can provide a reasonable description of the solvent behaviour, but fail to account for the local fluctuations in solvent density around a solute molecule. The density fluctuation behaviour is due to solvent ordering around a solute and is particularly prevalent when one is considering water as the solvent. Explicit models are often less computationally economical, but can provide a physical spatially resolved description of the solvent. However, many of these explicit models are computaionally demanding and can fail to reproduce some experimental results, often due to certain fitting methods and parametrization. Hybrid methodologies are another option. These methods incorporate aspects of implicit and explicit aiming to minimse computational cost whist retaining at least some spatial resolution of the solvent. These methods can require more experience to use them correctly and often contain post calculation correction terms.