Experiment 1 - Melting Points - NAU jan.ucc.nau.edu web server
... in a simple distillation; richer in cyclohexane than in toluene, but by no means pure cyclohexane. Then, as more cyclohexane and toluene boil, the temperature of these vapors is higher than that of the first portion of the mixture, because the portion contains less cyclohexane and more toluene. Thes ...
... in a simple distillation; richer in cyclohexane than in toluene, but by no means pure cyclohexane. Then, as more cyclohexane and toluene boil, the temperature of these vapors is higher than that of the first portion of the mixture, because the portion contains less cyclohexane and more toluene. Thes ...
File - Roden`s AP Chemistry
... (pure water) vapor pressure because alcohol is a volaThe molar solubility of silver bromide is diminished by tile solute and contributes substantially to the vapor of the addition of a small amount of solid potassium bro- the solution. The higher the vapor pressure, the lower mide to a saturated sol ...
... (pure water) vapor pressure because alcohol is a volaThe molar solubility of silver bromide is diminished by tile solute and contributes substantially to the vapor of the addition of a small amount of solid potassium bro- the solution. The higher the vapor pressure, the lower mide to a saturated sol ...
Chapter 9: Non-aqueous media
... A protic solvent undergoes self-ionization (see Section 7.2) to provide protons which are solvated. If it undergoes selfionization, an aprotic solvent does so without the formation of protons. ...
... A protic solvent undergoes self-ionization (see Section 7.2) to provide protons which are solvated. If it undergoes selfionization, an aprotic solvent does so without the formation of protons. ...
SAMPLE EXAMINATION IV Section I – Multiple Choice
... the limiting reactant is consumed and a maximum quantity of product is formed. However, in actual practice, many reaction systems reach a condition in which some quantity of each reactant remains in contact with some quantity of each product and that no further change appears to occur. The system ha ...
... the limiting reactant is consumed and a maximum quantity of product is formed. However, in actual practice, many reaction systems reach a condition in which some quantity of each reactant remains in contact with some quantity of each product and that no further change appears to occur. The system ha ...
Test 4: Equations and Math of Equations Review Name: Tuesday
... Acid rain is a problem in industrialized countries around the world. Oxides of sulfur and nitrogen are formed when various fuels are burned. These oxides dissolve in atmospheric water droplets that fall to earth as acid rain or acid snow. While normal rain has a pH between 5.0 and 6.0 due to the pre ...
... Acid rain is a problem in industrialized countries around the world. Oxides of sulfur and nitrogen are formed when various fuels are burned. These oxides dissolve in atmospheric water droplets that fall to earth as acid rain or acid snow. While normal rain has a pH between 5.0 and 6.0 due to the pre ...
Solubility and Solubility Equilibrium
... First things first, you have to memorize the basic solubility rules in order to (1) know which salts dissociate (break apart) in solution and (2) which ions combine to form precipitates when you mix solutions. The other part of this is that if you are given the name of a compound, you have to know t ...
... First things first, you have to memorize the basic solubility rules in order to (1) know which salts dissociate (break apart) in solution and (2) which ions combine to form precipitates when you mix solutions. The other part of this is that if you are given the name of a compound, you have to know t ...
Coordination and Chemistry of Stable Cu (II) Complexes in the Gas
... A mixture of argon as a carrier gas and a solvent undergoes supersonic expansion through a pulsed conical nozzle. For ammonia, carbon dioxide, and ethene, high-pressure cylinders containing 99% Ar and 1% solvent were used to produce the required mixture of gases. For the remainder of solvents studie ...
... A mixture of argon as a carrier gas and a solvent undergoes supersonic expansion through a pulsed conical nozzle. For ammonia, carbon dioxide, and ethene, high-pressure cylinders containing 99% Ar and 1% solvent were used to produce the required mixture of gases. For the remainder of solvents studie ...
Test 1 w/answers
... 1. _______ 2. _______ 3. _______ 4. _______ 5. _______ 6. _______ 7. _______ ...
... 1. _______ 2. _______ 3. _______ 4. _______ 5. _______ 6. _______ 7. _______ ...
Solution Chemistry and the Hydrosphere
... hydrazine produces enough energy that the substance is used as a rocket fuel. Identify the species oxidized, the species reduced, the oxidizing agent, the reducing agent, and the number of electrons transferred in the balanced ...
... hydrazine produces enough energy that the substance is used as a rocket fuel. Identify the species oxidized, the species reduced, the oxidizing agent, the reducing agent, and the number of electrons transferred in the balanced ...
Here`s - Sonlight
... Common Prefixes Used in the Metric System Prefix micro (µ) milli (m) centi (c) ...
... Common Prefixes Used in the Metric System Prefix micro (µ) milli (m) centi (c) ...
〈541〉 TITRIMETRY
... Relatively neutral solvents of low dielectric constant such as benzene, toluene, chloroform, or dioxane may be used in conjunction with any acidic or basic solvent in order to increase the sensitivity of the titration end-points. 2 In titrant. ...
... Relatively neutral solvents of low dielectric constant such as benzene, toluene, chloroform, or dioxane may be used in conjunction with any acidic or basic solvent in order to increase the sensitivity of the titration end-points. 2 In titrant. ...
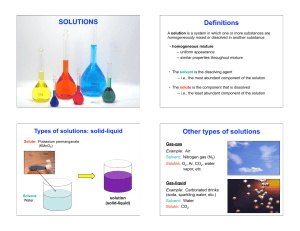
What is a solution
... amount as solvent, while those constituents – one or more – present in relatively small amounts are called the solutes. The distinction between solvent and solute is an arbitrary one, nothing fundamental distinguishes them. It is not possible to classify the two constituents of a binary solution int ...
... amount as solvent, while those constituents – one or more – present in relatively small amounts are called the solutes. The distinction between solvent and solute is an arbitrary one, nothing fundamental distinguishes them. It is not possible to classify the two constituents of a binary solution int ...
Chapter 4: Reactions in Aqueous Solution
... 2) Many reactions take place in aqueous solution. The term aqueous means dissolved in water. 3) Hydration of solids in Water A) Solid dissolves (falls apart) through interaction of ions with water. B) Newly formed ions are now “FREE TO MOVE”. C) “Like Dissolves Like” i) polar materials dissolve in p ...
... 2) Many reactions take place in aqueous solution. The term aqueous means dissolved in water. 3) Hydration of solids in Water A) Solid dissolves (falls apart) through interaction of ions with water. B) Newly formed ions are now “FREE TO MOVE”. C) “Like Dissolves Like” i) polar materials dissolve in p ...
Design and Analysis of Chain and Network Structures from Organic
... groups cap the faces of the ring. The angle between aniline moieties is 151°. The larger cluster, [Mo12O46(AsC6H4-4NH3+)4], is known from the literature and has been described as an “inverse-Keggin” cluster in which the heteroatoms are located on the surface of the cluster, as opposed to the interio ...
... groups cap the faces of the ring. The angle between aniline moieties is 151°. The larger cluster, [Mo12O46(AsC6H4-4NH3+)4], is known from the literature and has been described as an “inverse-Keggin” cluster in which the heteroatoms are located on the surface of the cluster, as opposed to the interio ...
FM 10-67-2 Chapter 7
... Petroleum laboratory technicians must create solutions for many of the chemical tests they do. It is important that they understand the factors that effect solubility, so they perform their job efficiently. The solubility of a solute and solvent depends on the following factors: • The nature of the ...
... Petroleum laboratory technicians must create solutions for many of the chemical tests they do. It is important that they understand the factors that effect solubility, so they perform their job efficiently. The solubility of a solute and solvent depends on the following factors: • The nature of the ...
Solutes
... • Solvent – substance present in the largest amount • Solutes – substance present in the smallest amount • Aqueous solution – solutions with water as the solvent • Concentration – the amount of solute in a given volume of solution • Concentrated – large amount of solute dissolved in solvent • Dilute ...
... • Solvent – substance present in the largest amount • Solutes – substance present in the smallest amount • Aqueous solution – solutions with water as the solvent • Concentration – the amount of solute in a given volume of solution • Concentrated – large amount of solute dissolved in solvent • Dilute ...
AP Chemistry Standards and Benchmarks
... These descriptive facts, including chemistry involved in environmental and societal issues, should not be isolated form the principles being studied but should be taught throughout the course to illustrate and illuminate the principles. The following areas should be covered: • chemical reactivity an ...
... These descriptive facts, including chemistry involved in environmental and societal issues, should not be isolated form the principles being studied but should be taught throughout the course to illustrate and illuminate the principles. The following areas should be covered: • chemical reactivity an ...
A Model For the Calculation of Solvent ... Reaction Rates for Process Design Purposes
... parameters that describe its polarity as well as the geometric distribution of its charges. To calculate solvent effects on a specific reaction, the reaction fingerprint parameters are regressed from experimental kinetic data in at least three solvents. With these parameters, the Gibbs' free energy ...
... parameters that describe its polarity as well as the geometric distribution of its charges. To calculate solvent effects on a specific reaction, the reaction fingerprint parameters are regressed from experimental kinetic data in at least three solvents. With these parameters, the Gibbs' free energy ...
CHAPTER 4: CHEMICAL QUANTITIES and AQUEOUS REACTIONS
... the least no. of product will be limiting reactant. 5. Calculate the mass of the product from the Limiting reactant. That will be the theoretical yield. Example: Methanol (CH3OH) is produced form 1.00 g H2 and 6.44 g CO. Which is the limiting reactant? What is the Limiting reactant and theoretical y ...
... the least no. of product will be limiting reactant. 5. Calculate the mass of the product from the Limiting reactant. That will be the theoretical yield. Example: Methanol (CH3OH) is produced form 1.00 g H2 and 6.44 g CO. Which is the limiting reactant? What is the Limiting reactant and theoretical y ...
Solutions
... (we will use subscript m, from mixture), 'solute' (we will use subscript s, from solute) and 'solvent' (we will use subscript dis, from dissolve); the standard labelling of '1' for solute and '2' for solvent, may be unclear when one wants to distinguish between solvent and solution. To give an idea ...
... (we will use subscript m, from mixture), 'solute' (we will use subscript s, from solute) and 'solvent' (we will use subscript dis, from dissolve); the standard labelling of '1' for solute and '2' for solvent, may be unclear when one wants to distinguish between solvent and solution. To give an idea ...
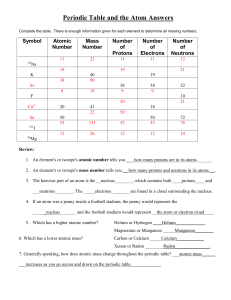
Periodic Table and the Atom Answers
... b) Arrange the pH in increasing order of hydrogen ion comcentration. 2) Define the term "pH"; what does" pH" stand for? Answer: The term "pH" is defined as the negative logarithm of H+ ion concentration of a given solution; the concentration being expressed as moles per litre. Mathematically pH = - ...
... b) Arrange the pH in increasing order of hydrogen ion comcentration. 2) Define the term "pH"; what does" pH" stand for? Answer: The term "pH" is defined as the negative logarithm of H+ ion concentration of a given solution; the concentration being expressed as moles per litre. Mathematically pH = - ...
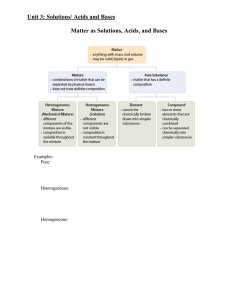
Outline for Unit 1 Solutions, Acid/Base, and Gases
... 1. Nature of solute and solvent – like dissolves like 2. Agitation – solute dissolves more rapidly since fresh solvent is brought into contact with the solute. Only affects the rate not amount of solute that dissolves. 3. Temperature – at higher temp kinetic energy of the solvent is higher so more c ...
... 1. Nature of solute and solvent – like dissolves like 2. Agitation – solute dissolves more rapidly since fresh solvent is brought into contact with the solute. Only affects the rate not amount of solute that dissolves. 3. Temperature – at higher temp kinetic energy of the solvent is higher so more c ...
Solvent models
Within the field of computational chemistry, solvent models are a variety of methods to account for the behavior of solvated condensed phases. Solvent models allow simulations and calculations of reactions and processes which take place in solvated phases. These include biological, chemical and environmental processes. Such calculation can lead to predictions and improved understanding of the physical processes occurring. Such models have been extensively tested and reviewed in scientific literature. The various models have their own pros and cons. Implicit models are generally computationally efficient and can provide a reasonable description of the solvent behaviour, but fail to account for the local fluctuations in solvent density around a solute molecule. The density fluctuation behaviour is due to solvent ordering around a solute and is particularly prevalent when one is considering water as the solvent. Explicit models are often less computationally economical, but can provide a physical spatially resolved description of the solvent. However, many of these explicit models are computaionally demanding and can fail to reproduce some experimental results, often due to certain fitting methods and parametrization. Hybrid methodologies are another option. These methods incorporate aspects of implicit and explicit aiming to minimse computational cost whist retaining at least some spatial resolution of the solvent. These methods can require more experience to use them correctly and often contain post calculation correction terms.