Solutions
... Solutions have one or more solutes (dissolvee) and a solvent (dissolver). When a substance dissolves it is soluble Liquids that mix are miscible, those that don't are immiscible ...
... Solutions have one or more solutes (dissolvee) and a solvent (dissolver). When a substance dissolves it is soluble Liquids that mix are miscible, those that don't are immiscible ...
Chemistry 121 Mines PS13-1
... solids and liquids, which are only significantly dependent on temperature). It is most clear to see the effects of each if you start out with a system at dynamic equilibrium at a given T and P and then imagine how the “opposing” rates are affected by either a T change or a P change. Temperature effe ...
... solids and liquids, which are only significantly dependent on temperature). It is most clear to see the effects of each if you start out with a system at dynamic equilibrium at a given T and P and then imagine how the “opposing” rates are affected by either a T change or a P change. Temperature effe ...
State briefly the meaning of and
... the definition of a potential function, or a description of the terms by which the particles in the simulation will interact. This is usually referred to as a force field. Potentials may be defined at many levels of physical accuracy; those most commonly used in chemistry are based on molecular mech ...
... the definition of a potential function, or a description of the terms by which the particles in the simulation will interact. This is usually referred to as a force field. Potentials may be defined at many levels of physical accuracy; those most commonly used in chemistry are based on molecular mech ...
Document
... 5. The elements that make up a compound and the exact number of atoms of each element in a unit of the compound can be shown in a __________________. 6. A chemical bond that occurs when atoms share electrons is a(n) ________________ bond. 7. What is the correct name of the following chemical formula ...
... 5. The elements that make up a compound and the exact number of atoms of each element in a unit of the compound can be shown in a __________________. 6. A chemical bond that occurs when atoms share electrons is a(n) ________________ bond. 7. What is the correct name of the following chemical formula ...
Metathesis Problems (and Some Solutions) Identified Through
... dissolved substance than a saturated solution does • Sodium acetate and many other ionic compounds more soluble in hot water than in cold water – If a saturated solution is prepared at high temperature, and then the temperature is slowly lowered, the solution may become supersaturated – Introduction ...
... dissolved substance than a saturated solution does • Sodium acetate and many other ionic compounds more soluble in hot water than in cold water – If a saturated solution is prepared at high temperature, and then the temperature is slowly lowered, the solution may become supersaturated – Introduction ...
Solutions Foldable
... Pure Substances: when component parts of a mixture can no longer be physically separated into simpler substances. Pure substances are either compounds or elements. a. Compounds – can be decomposed by a chemical change. (Two or more elements bonded.) b. Elements – cannot be decomposed by a chemical c ...
... Pure Substances: when component parts of a mixture can no longer be physically separated into simpler substances. Pure substances are either compounds or elements. a. Compounds – can be decomposed by a chemical change. (Two or more elements bonded.) b. Elements – cannot be decomposed by a chemical c ...
solutions and molarity for votech
... A mixture in which the composition is uniform throughout May be solids, liquids and/or gases Also called a solution Salt and water Ice tea mix and water ...
... A mixture in which the composition is uniform throughout May be solids, liquids and/or gases Also called a solution Salt and water Ice tea mix and water ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... to compute the reduction potentials of biomolecules in a medium. The explicit solvent method involves quantum mechanical/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) treatment of the solvated moiety followed by a Monte–Carlo (MC) simulation of the primary solvent layer. The QM task for considerably large biomolecule ...
... to compute the reduction potentials of biomolecules in a medium. The explicit solvent method involves quantum mechanical/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) treatment of the solvated moiety followed by a Monte–Carlo (MC) simulation of the primary solvent layer. The QM task for considerably large biomolecule ...
7A SCIENCE FINAL REVIEW - MERRICK 7th SCIENCE REVIEW
... ___ Describe the difference between atoms and molecules. ___ Define elements, compounds, and mixtures. ___ Recognize elements from compounds if given the chemical symbol or a model. ___ Describe the difference between a chemical and physical property of matter, give examples of each. ___ Describe th ...
... ___ Describe the difference between atoms and molecules. ___ Define elements, compounds, and mixtures. ___ Recognize elements from compounds if given the chemical symbol or a model. ___ Describe the difference between a chemical and physical property of matter, give examples of each. ___ Describe th ...
Ch1-2
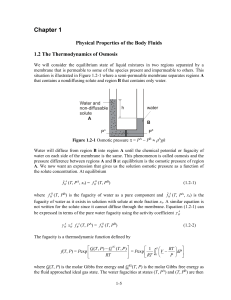
... The term osmole is defined as one mole of a nondiffusing and nondissociating substance. One mole of a dissociating substance such as NaCl is equivalent to two osmoles. The number of osmoles per liter of solution is called osmolarity. For physiological solutions, it is convenient to work in terms of ...
... The term osmole is defined as one mole of a nondiffusing and nondissociating substance. One mole of a dissociating substance such as NaCl is equivalent to two osmoles. The number of osmoles per liter of solution is called osmolarity. For physiological solutions, it is convenient to work in terms of ...
Solute
... Element – substances made up of only one kind of atom Every element has a unique atomic number Atomic number – number of protons in the nucleus ...
... Element – substances made up of only one kind of atom Every element has a unique atomic number Atomic number – number of protons in the nucleus ...
Development of Methods for Predicting Solvation and
... charge model, called charge model 3 (CM3). The CM3 charge model uses a semiempirical charge-mapping scheme that is a function of the Mayer bond orders in the molecule. This scheme systematically corrects errors in bond dipoles calculated from low-level charges, such as Löwdin population analysis cha ...
... charge model, called charge model 3 (CM3). The CM3 charge model uses a semiempirical charge-mapping scheme that is a function of the Mayer bond orders in the molecule. This scheme systematically corrects errors in bond dipoles calculated from low-level charges, such as Löwdin population analysis cha ...
Science Notes on Physical and Chemical Properties
... The appearance may change, but you still have the same substance as before – can be reversed and no energy is produced Example – Tear a piece of paper into 10-15 pieces. The shape and size have changed, but its still paper Example – Change of state = physical change…add energy to ice and you get a l ...
... The appearance may change, but you still have the same substance as before – can be reversed and no energy is produced Example – Tear a piece of paper into 10-15 pieces. The shape and size have changed, but its still paper Example – Change of state = physical change…add energy to ice and you get a l ...
Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. Examples
... Density is the mass per unit of volume. It is affected by a change in temperature. Formula: Density = mass D=m Volume V ...
... Density is the mass per unit of volume. It is affected by a change in temperature. Formula: Density = mass D=m Volume V ...
File
... composition that is uniform throughout, all the way down to the molecular level. • Hydrocarbon-any molecule consisting of only hydrogen and carbon atoms, typically fossil fuels and other compounds derived from them. • Ion- a charged atom, it has either gained or lost an electron. • Isotope-any varie ...
... composition that is uniform throughout, all the way down to the molecular level. • Hydrocarbon-any molecule consisting of only hydrogen and carbon atoms, typically fossil fuels and other compounds derived from them. • Ion- a charged atom, it has either gained or lost an electron. • Isotope-any varie ...
Unit 14: Solutions
... b) ex: oil will not dissolve in water because oil is nonpolar and water is polar ...
... b) ex: oil will not dissolve in water because oil is nonpolar and water is polar ...
Solid - burgess
... 3. the properties of the compound are different from the properties of the elements that make up the compound 4. can be separated only by a chemical reaction 5. two types of compounds a. ionic i. formed by the attraction between two or more elements that transfer electrons known as ions ...
... 3. the properties of the compound are different from the properties of the elements that make up the compound 4. can be separated only by a chemical reaction 5. two types of compounds a. ionic i. formed by the attraction between two or more elements that transfer electrons known as ions ...
Characterization of Alcohol Solvents by the Empirical Polarity
... Table II presents some new Z and ET(30) values preferred for the following reasons: (i) ET(30) vafor ethanol differently substituted in 2-position and lues are obtained more easily and more rapidly than for some alkylated alcohols. It is obvious that Z inAN values, (ii) a greater chemical stability ...
... Table II presents some new Z and ET(30) values preferred for the following reasons: (i) ET(30) vafor ethanol differently substituted in 2-position and lues are obtained more easily and more rapidly than for some alkylated alcohols. It is obvious that Z inAN values, (ii) a greater chemical stability ...
Molar Heat of Reaction
... This shows the quantity of energy involved in dissolving one mole of solute in the solvent (which is usually water) Expressed in kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) of dissolved solute In this reaction heat can be either released or absorbed ...
... This shows the quantity of energy involved in dissolving one mole of solute in the solvent (which is usually water) Expressed in kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) of dissolved solute In this reaction heat can be either released or absorbed ...
Monitoring Reactions by TLC The fastest and most commonly used
... component and ethyl acetate (EtOAc, bp 77-78 °C) as the polar component. The choice of solvents with similar boiling points assures that their ratio will not change dramatically over short periods of time due to differential evaporation. • For carboxylic acids that tend to "tail": Diethyl ether (2 m ...
... component and ethyl acetate (EtOAc, bp 77-78 °C) as the polar component. The choice of solvents with similar boiling points assures that their ratio will not change dramatically over short periods of time due to differential evaporation. • For carboxylic acids that tend to "tail": Diethyl ether (2 m ...
Chapter 13 Reading Guide Section 13.1 Define the following terms
... What are the two main factors that determine the ability of substances to form solutions? ...
... What are the two main factors that determine the ability of substances to form solutions? ...
std 6 review12ans
... 3. A teaspoon of dry coffee crystals dissolves when mixed in a cup of hot water. This process produces a coffee solution. The original crystals are classified as a A solute. B solvent. C reactant. D product. ...
... 3. A teaspoon of dry coffee crystals dissolves when mixed in a cup of hot water. This process produces a coffee solution. The original crystals are classified as a A solute. B solvent. C reactant. D product. ...
Solvent models
Within the field of computational chemistry, solvent models are a variety of methods to account for the behavior of solvated condensed phases. Solvent models allow simulations and calculations of reactions and processes which take place in solvated phases. These include biological, chemical and environmental processes. Such calculation can lead to predictions and improved understanding of the physical processes occurring. Such models have been extensively tested and reviewed in scientific literature. The various models have their own pros and cons. Implicit models are generally computationally efficient and can provide a reasonable description of the solvent behaviour, but fail to account for the local fluctuations in solvent density around a solute molecule. The density fluctuation behaviour is due to solvent ordering around a solute and is particularly prevalent when one is considering water as the solvent. Explicit models are often less computationally economical, but can provide a physical spatially resolved description of the solvent. However, many of these explicit models are computaionally demanding and can fail to reproduce some experimental results, often due to certain fitting methods and parametrization. Hybrid methodologies are another option. These methods incorporate aspects of implicit and explicit aiming to minimse computational cost whist retaining at least some spatial resolution of the solvent. These methods can require more experience to use them correctly and often contain post calculation correction terms.