
Fe(H2O)63+ + H2O → ← H3O+ + Fe(H2O)5(OH)2+
... 51. If a reaction proceeding by the mechanism A + B → C + D occurs at a rate x, and if the concentrations of A and B are both doubled, what will be the new rate of reaction? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) ...
... 51. If a reaction proceeding by the mechanism A + B → C + D occurs at a rate x, and if the concentrations of A and B are both doubled, what will be the new rate of reaction? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) ...
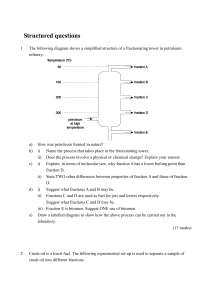
Structured questions
... ii) Write an equation to show the formation of acid rain from ONE of the pollutants named in (i). iii) The rainwater led to faster corrosion of buildings made of marble. (1) Name the major component of marble. (2) Explain, with the help of an ionic equation, why the buildings corroded much faster th ...
... ii) Write an equation to show the formation of acid rain from ONE of the pollutants named in (i). iii) The rainwater led to faster corrosion of buildings made of marble. (1) Name the major component of marble. (2) Explain, with the help of an ionic equation, why the buildings corroded much faster th ...
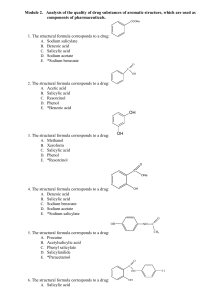
Chapter 1 questions
... An oxide of sulfur contains 40.0% by mass of sulfur. Calculate the empirical formula of the oxide. Q8. Analysis by mass has indicated the following percentage composition by mass of certain compounds. Calculate the empirical formula of each: a) carbon 75.0%, hydrogen 25.0% b) magnesium 60.3%, oxygen ...
... An oxide of sulfur contains 40.0% by mass of sulfur. Calculate the empirical formula of the oxide. Q8. Analysis by mass has indicated the following percentage composition by mass of certain compounds. Calculate the empirical formula of each: a) carbon 75.0%, hydrogen 25.0% b) magnesium 60.3%, oxygen ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... haven’t covered yet. Having the following skills will be essential to your success in AP Chemistry and I will expect that you already have a firm grasp on these topics as we start the year. The following assignment is to be completed over the summer and brought in COMPLETED on the first day of class ...
... haven’t covered yet. Having the following skills will be essential to your success in AP Chemistry and I will expect that you already have a firm grasp on these topics as we start the year. The following assignment is to be completed over the summer and brought in COMPLETED on the first day of class ...
E:\My Documents\sch4u\SCH4U review McKay answers.wpd
... a) Q = 2.15 /5.30 = 0.87 Q=K, thus the system is at equilibrium b) Q = 1.552/0.80 = 3.0 Q 2NH3;
...
... a) Q = 2.15 /5.30 = 0.87 Q=K, thus the system is at equilibrium b) Q = 1.552/0.80 = 3.0 Q
Chapter 16 Aqueous Ionic Equilibrium Lecture Presentation
... point and excess acid region. • The initial pH is determined using the Ka of the weak acid. • The pH in the excess acid region is determined as you would determine the pH of a buffer. • The pH at the equivalence point is determined using the Kb of the conjugate base of the weak acid. • The pH after ...
... point and excess acid region. • The initial pH is determined using the Ka of the weak acid. • The pH in the excess acid region is determined as you would determine the pH of a buffer. • The pH at the equivalence point is determined using the Kb of the conjugate base of the weak acid. • The pH after ...
A Plausible Simultaneous Synthesis of Amino Acids and Simple
... questions remain about their plausibility under prebiotic geochemical conditions.[4] In addition, concentrated salts, clays, and Cu2+ ions have been suggested as being important amino acid condensation reagents,[8] although these have not been demonstrated to be effective polymerization agents under ...
... questions remain about their plausibility under prebiotic geochemical conditions.[4] In addition, concentrated salts, clays, and Cu2+ ions have been suggested as being important amino acid condensation reagents,[8] although these have not been demonstrated to be effective polymerization agents under ...
CHAPTER-7 EQUILIBRIUM Equilibrium state- When
... Buffer solution :The solutions which resist change in pH on dilution or with the addition of small amounts of acid or alkali are called Buffer Solutions. common ion effect: It can be defined as a shift in equilibrium on adding a substance that provides more of an ionic species already present in ...
... Buffer solution :The solutions which resist change in pH on dilution or with the addition of small amounts of acid or alkali are called Buffer Solutions. common ion effect: It can be defined as a shift in equilibrium on adding a substance that provides more of an ionic species already present in ...
Homework Solutions Week 6
... 9-17 a) Why do many rivers in Box 9-1. lie on the line [HCO3-] = 2[Ca2+]? According to Box 9-1, the source of calcium in the rivers is the mineral calcite, which dissolves by reacting with carbon dioxide in the river waver according to the equation: CaCO3(s) + CO2(aq) + H2O < == > Ca2+ + 2 HCO3If th ...
... 9-17 a) Why do many rivers in Box 9-1. lie on the line [HCO3-] = 2[Ca2+]? According to Box 9-1, the source of calcium in the rivers is the mineral calcite, which dissolves by reacting with carbon dioxide in the river waver according to the equation: CaCO3(s) + CO2(aq) + H2O < == > Ca2+ + 2 HCO3If th ...
+ H 2 O
... 3) The oxidation state of oxygen in compounds is -2, except in peroxides, such as H2O2 where it is -1. 4) The oxidation state of hydrogen in compounds is +1, except in metal hydrides, like NaH, where it is -1. ...
... 3) The oxidation state of oxygen in compounds is -2, except in peroxides, such as H2O2 where it is -1. 4) The oxidation state of hydrogen in compounds is +1, except in metal hydrides, like NaH, where it is -1. ...
ChemChapter_7sec1_and_section2[1]FORMULA
... Writing Acid Formulas – in reverse! • Hydrogen will be listed first • The name will tell you the anion • Be sure the charges cancel out. • Starts with prefix hydro?- there is no oxygen, -ide ending for anion ...
... Writing Acid Formulas – in reverse! • Hydrogen will be listed first • The name will tell you the anion • Be sure the charges cancel out. • Starts with prefix hydro?- there is no oxygen, -ide ending for anion ...
Acid rain
Acid rain is a rain or any other form of precipitation that is unusually acidic, meaning that it possesses elevated levels of hydrogen ions (low pH). It can have harmful effects on plants, aquatic animals and infrastructure. Acid rain is caused by emissions of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide, which react with the water molecules in the atmosphere to produce acids. Governments have made efforts since the 1970s to reduce the release of sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere with positive results. Nitrogen oxides can also be produced naturally by lightning strikes and sulfur dioxide is produced by volcanic eruptions. The chemicals in acid rain can cause paint to peel, corrosion of steel structures such as bridges, and erosion of stone statues.





















![ChemChapter_7sec1_and_section2[1]FORMULA](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000546743_1-278f96ccbbfd49e292510ec017e27124-300x300.png)