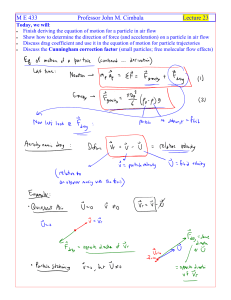
The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
... The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to know both the momentum and the position of a particle at the same time. This limitation is critical when dealing with small particles such as electrons. But it does not matter for ordinary- ...
... The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to know both the momentum and the position of a particle at the same time. This limitation is critical when dealing with small particles such as electrons. But it does not matter for ordinary- ...
2.8 Matter in Extremely Intense Laser Pulses
... numbers that play a role here. The approach developed in Ref. [5] above yrast. yields approximate analytical expressions for the total and partial level densities and allows the semiquantitative study of the competition between photon absorption, photon-induced nucleon emission, and neutron evaporat ...
... numbers that play a role here. The approach developed in Ref. [5] above yrast. yields approximate analytical expressions for the total and partial level densities and allows the semiquantitative study of the competition between photon absorption, photon-induced nucleon emission, and neutron evaporat ...
Physics 8805: Nuclear Few- and Many-Body Physics
... Overview of exercises and discussion questions. The problems here range from basic (and generally quick) to quite sophisticated (quick and not so quick) and are organized according to the lecture schedule. Comments on the pedagogy: • The underlying philosophy is that students learn most effectively ...
... Overview of exercises and discussion questions. The problems here range from basic (and generally quick) to quite sophisticated (quick and not so quick) and are organized according to the lecture schedule. Comments on the pedagogy: • The underlying philosophy is that students learn most effectively ...
14. Elementary Particles
... A strange quark (s) was also required. And then a fourth quark called the charmed quark (c) was proposed to explain some additional discrepancies in the lifetimes of some of the known particles. A new quantum number called charm C was introduced so that the new quark would have C = +1 while its anti ...
... A strange quark (s) was also required. And then a fourth quark called the charmed quark (c) was proposed to explain some additional discrepancies in the lifetimes of some of the known particles. A new quantum number called charm C was introduced so that the new quark would have C = +1 while its anti ...
Measurements and Physics of Single Event Effects in
... balloon and low orbit experiments. Accelerator application like those at LHC where radiation on electronics is extreme even by space tech standards ...
... balloon and low orbit experiments. Accelerator application like those at LHC where radiation on electronics is extreme even by space tech standards ...
CERN PARTICLE ACCELERATOR
... • This is a circular path which is 628 metres in circumference • The proton beam passes through the PS for 1.2 seconds • During this time, it is accelerated to 99.9% of the speed of light, where they have approached the limiting speed of light • In the PS, the particles reach their point of transiti ...
... • This is a circular path which is 628 metres in circumference • The proton beam passes through the PS for 1.2 seconds • During this time, it is accelerated to 99.9% of the speed of light, where they have approached the limiting speed of light • In the PS, the particles reach their point of transiti ...
high-energy emission and cosmic rays from gamma
... paper (Gialis & Pelletier 2004), we have proposed a Fermi acceleration process resulting from scattering off relativistic hydromagnetic fronts at the very beginning of the internal shock phase. The efficiency of this process, as shown by numerical simulation, is sufficient to generate a sizeable fra ...
... paper (Gialis & Pelletier 2004), we have proposed a Fermi acceleration process resulting from scattering off relativistic hydromagnetic fronts at the very beginning of the internal shock phase. The efficiency of this process, as shown by numerical simulation, is sufficient to generate a sizeable fra ...
atom unit review key 10
... The atomic number assures us that there are 12 protons. Since it is a neutral atom, it also must have 12 electrons. With a mass of 24 amu, that means the remaining mass comes from its 12 neutrons. ...
... The atomic number assures us that there are 12 protons. Since it is a neutral atom, it also must have 12 electrons. With a mass of 24 amu, that means the remaining mass comes from its 12 neutrons. ...
Overview Acceleration with RF fields Bunches Phase
... A particle enters the cavity from the left. For acceleration, it needs to have the correct phase in the electric field. Assume that particle 1 travels at time t0 = 0 ns through cavity 1 – it will be accelerated by 1 MV. A particle that travels through the cavity at another time will be accelerated l ...
... A particle enters the cavity from the left. For acceleration, it needs to have the correct phase in the electric field. Assume that particle 1 travels at time t0 = 0 ns through cavity 1 – it will be accelerated by 1 MV. A particle that travels through the cavity at another time will be accelerated l ...
Magnetic Lenses, Interactions of Electrons with Matter
... Absorption Penetration depth/mean free path determines depth of specimen sampled Varies with keV and material, but typically shorter than for x-rays ...
... Absorption Penetration depth/mean free path determines depth of specimen sampled Varies with keV and material, but typically shorter than for x-rays ...
DESY
The Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron (english German Electron Synchrotron) commonly referred to by the abbreviation DESY, is a national research center in Germany that operates particle accelerators used to investigate the structure of matter. It conducts a broad spectrum of inter-disciplinary scientific research in three main areas: particle and high energy physics; photon science; and the development, construction and operation of particle accelerators. Its name refers to its first project, an electron synchrotron. DESY is publicly financed by the Federal Republic of Germany, the States of Germany, and the German Research Foundation (DFG). DESY is a member of the Helmholtz Association and operates at sites in Hamburg and Zeuthen.