Discovery of the Higgs Particle
... important ingredient (though not the only one) is a property called spin―a kind of angular momentum carried by a single particle. All electrons (and protons, quarks, and muons) carry the same amount of spin: ½ times Planck’s constant, which has units of length times momentum, or angular momentum. Al ...
... important ingredient (though not the only one) is a property called spin―a kind of angular momentum carried by a single particle. All electrons (and protons, quarks, and muons) carry the same amount of spin: ½ times Planck’s constant, which has units of length times momentum, or angular momentum. Al ...
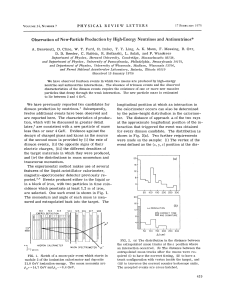
Observation of New-Particle Production by High
... characteristics of the dimuon events require the existence of one or more new massive particles that decay through the weak interaction. The new particle mass is estimated to lie between 2 and 4 GeV. ...
... characteristics of the dimuon events require the existence of one or more new massive particles that decay through the weak interaction. The new particle mass is estimated to lie between 2 and 4 GeV. ...
Anticipating New Physics at the LHC
... mediates SUSY breaking – 5 free parameters at high energies Squark and Gluino mass reach is 2.5-3.0 TeV @ 300 fb-1 ...
... mediates SUSY breaking – 5 free parameters at high energies Squark and Gluino mass reach is 2.5-3.0 TeV @ 300 fb-1 ...
Beyond the Standard Model - Southampton High Energy Physics
... (super)string theory: extra space-time dimensions? ...
... (super)string theory: extra space-time dimensions? ...
Chapter Fourteen Radiation by Moving Charges
... emit radiation only if it is accelerated. Hence the two terms are interpreted as the non-radiation and radiation parts respectively. From these results when β̇ = 0, we should be able to recover the results for the fields of a uniformly moving charge which we derived in chapter 11 (Jackson Eq. 11.15 ...
... emit radiation only if it is accelerated. Hence the two terms are interpreted as the non-radiation and radiation parts respectively. From these results when β̇ = 0, we should be able to recover the results for the fields of a uniformly moving charge which we derived in chapter 11 (Jackson Eq. 11.15 ...
KS4 The Atom
... • This means that when we react atoms of an element we are using a mixture of atoms with different mass numbers. • The relative atomic mass given in the periodic table takes account of this. E.g.. For 100 atoms of chlorine: Mass of 75 atoms of Chlorine 35: 75 x 35 =2625 Mass of 25 atoms of Chlorine ...
... • This means that when we react atoms of an element we are using a mixture of atoms with different mass numbers. • The relative atomic mass given in the periodic table takes account of this. E.g.. For 100 atoms of chlorine: Mass of 75 atoms of Chlorine 35: 75 x 35 =2625 Mass of 25 atoms of Chlorine ...
No Slide Title - WordPress.com
... • This means that when we react atoms of an element we are using a mixture of atoms with different mass numbers. • The relative atomic mass given in the periodic table takes account of this. E.g.. For 100 atoms of chlorine: Mass of 75 atoms of Chlorine 35: 75 x 35 =2625 Mass of 25 atoms of Chlorine ...
... • This means that when we react atoms of an element we are using a mixture of atoms with different mass numbers. • The relative atomic mass given in the periodic table takes account of this. E.g.. For 100 atoms of chlorine: Mass of 75 atoms of Chlorine 35: 75 x 35 =2625 Mass of 25 atoms of Chlorine ...
The Role of Secondary Electrons in Low
... Results of the simulations In our simulations we monitored the secondary electrons and products from the ionizing collisions of secondary electrons with neutrals (their trajectories and collisions) in accordance with model assumptions in the some way as other plasma charged particles. The influence ...
... Results of the simulations In our simulations we monitored the secondary electrons and products from the ionizing collisions of secondary electrons with neutrals (their trajectories and collisions) in accordance with model assumptions in the some way as other plasma charged particles. The influence ...
R measurement and QCD study in the full BEPCII energy region
... Study of high mass charmonia in 3.84.6 GeV; QCD studies: ...
... Study of high mass charmonia in 3.84.6 GeV; QCD studies: ...
Preliminary analysis of the hypothetical ring system in the inner
... The Earth was exposed by numerous impacts of comets and asteroids during all its history. In the midst of example, we can cite the meteoroid’s craters in the Arizona. The model suggestS a stratospheric cloud of debris that could reduce extremely the solar action (Fawcett & Boslough, 2000). One of ...
... The Earth was exposed by numerous impacts of comets and asteroids during all its history. In the midst of example, we can cite the meteoroid’s craters in the Arizona. The model suggestS a stratospheric cloud of debris that could reduce extremely the solar action (Fawcett & Boslough, 2000). One of ...
double-slit worksheet
... accelerated by a potential difference of 5 x 104 m/s V. Do the following calculations nonrelativistically. (Details can be found at http://www.hqrd.hitachi.co.jp/em/doubleslit.cfm.) a) How fast were these electrons moving? b) How fast is that compared to the speed of light? 42 %. c) How long would t ...
... accelerated by a potential difference of 5 x 104 m/s V. Do the following calculations nonrelativistically. (Details can be found at http://www.hqrd.hitachi.co.jp/em/doubleslit.cfm.) a) How fast were these electrons moving? b) How fast is that compared to the speed of light? 42 %. c) How long would t ...
Talk1_Nardi
... • Effective theory : small-x gluons are described as the classical colour fields radiated by colour sources at higher rapidity. • This effective theory describes the saturated gluons (slow partons) as a Coulor Glass Condensate. ...
... • Effective theory : small-x gluons are described as the classical colour fields radiated by colour sources at higher rapidity. • This effective theory describes the saturated gluons (slow partons) as a Coulor Glass Condensate. ...
Requirements for ion sources
... As ion sources are the driver of other processes or experiments, it is clear that high reliability is desirable. In general, there will be a trade-off between the other performance factors of the source. For example, high-intensity sources (in particular, if they run at a high duty factor) can suffe ...
... As ion sources are the driver of other processes or experiments, it is clear that high reliability is desirable. In general, there will be a trade-off between the other performance factors of the source. For example, high-intensity sources (in particular, if they run at a high duty factor) can suffe ...
DESY
The Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron (english German Electron Synchrotron) commonly referred to by the abbreviation DESY, is a national research center in Germany that operates particle accelerators used to investigate the structure of matter. It conducts a broad spectrum of inter-disciplinary scientific research in three main areas: particle and high energy physics; photon science; and the development, construction and operation of particle accelerators. Its name refers to its first project, an electron synchrotron. DESY is publicly financed by the Federal Republic of Germany, the States of Germany, and the German Research Foundation (DFG). DESY is a member of the Helmholtz Association and operates at sites in Hamburg and Zeuthen.