Physics of Polarized Protons/Electrons in Accelerators
... The closer the vertical tune towards 0.7, the lower the beam polarization ...
... The closer the vertical tune towards 0.7, the lower the beam polarization ...
Operational Status and Power Upgrade Prospects of the
... energies, up to about s = 35 GeV [3]. The pion-pion cross section cannot be measured directly, and has been extracted from data only at very low energies near threshold [4]. The theoretical description of elastic scattering has been based so far only on phenomenological models. Even the simplest ver ...
... energies, up to about s = 35 GeV [3]. The pion-pion cross section cannot be measured directly, and has been extracted from data only at very low energies near threshold [4]. The theoretical description of elastic scattering has been based so far only on phenomenological models. Even the simplest ver ...
SU(3) - Physics
... “Can we describe the known physics with just a few building blocks ?” Historically the answer has been yes. Elements of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table (chemistry) nucleus of atom made of protons, neutrons proton and neutron really same “particle” (different isotopic spin) By 1950’s there was evidence ...
... “Can we describe the known physics with just a few building blocks ?” Historically the answer has been yes. Elements of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table (chemistry) nucleus of atom made of protons, neutrons proton and neutron really same “particle” (different isotopic spin) By 1950’s there was evidence ...
ModPhys III Lecture 5 - University of San Francisco
... Stretching the tube requires more and more energy At some distance it is energetically more favorable to pull a qq pair out of the vacuum than to increase the tubelength. ...
... Stretching the tube requires more and more energy At some distance it is energetically more favorable to pull a qq pair out of the vacuum than to increase the tubelength. ...
High angle neutron-proton scattering
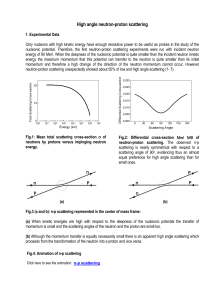
... Within the Standard Model the corresponding process of transmutation implies: (a) the interchange of quarks between colliding proton and neutron, or (b) the transmutation of quarks. (a) However the interchange of quarks cannot be retained since quarks are tightly confined and the bonding strength (f ...
... Within the Standard Model the corresponding process of transmutation implies: (a) the interchange of quarks between colliding proton and neutron, or (b) the transmutation of quarks. (a) However the interchange of quarks cannot be retained since quarks are tightly confined and the bonding strength (f ...
Irradiation of silicon particle detectors with MeV-protons
... In particle detection, the most common semiconductor detector material is clearly silicon. The advantages for using this second most abundant element in the earth’s crust are obvious. Not only are availability and affordability important, but the mechanical properties of silicon are also favourable, ...
... In particle detection, the most common semiconductor detector material is clearly silicon. The advantages for using this second most abundant element in the earth’s crust are obvious. Not only are availability and affordability important, but the mechanical properties of silicon are also favourable, ...
New discoveries at the LHC
... largest currently known centre-of-mass energy collisions, it is enabling researchers to probe new physics at a level of 10-19 m and recreate conditions similar to those a picosecond after the Big Bang at temperatures eight orders of magnitude higher than the core of the sun. With such a powerful mac ...
... largest currently known centre-of-mass energy collisions, it is enabling researchers to probe new physics at a level of 10-19 m and recreate conditions similar to those a picosecond after the Big Bang at temperatures eight orders of magnitude higher than the core of the sun. With such a powerful mac ...
CERN Summer Vacation
... the border between Switzerland and France, near Geneva Switzerland. • It is home to the Large Hadron Collider as well as many additional particle physics experiments (ATLAS, CMS, LHCb, etc.) • 2014 marks the 60th anniversary of CERN. Various celebrations are taking place all year long. ...
... the border between Switzerland and France, near Geneva Switzerland. • It is home to the Large Hadron Collider as well as many additional particle physics experiments (ATLAS, CMS, LHCb, etc.) • 2014 marks the 60th anniversary of CERN. Various celebrations are taking place all year long. ...
Core Problem - Max-Planck
... For the magnetic radius, the researchers now obtain 0.87 ± 0.06 femtometers. This value is currently still so imprecise that the two controversial values of the charge radius fit with it. “What is important is that we actually determined the magnetic radius using spectroscopy of muonic hydrogen in t ...
... For the magnetic radius, the researchers now obtain 0.87 ± 0.06 femtometers. This value is currently still so imprecise that the two controversial values of the charge radius fit with it. “What is important is that we actually determined the magnetic radius using spectroscopy of muonic hydrogen in t ...
Holographic thermalization of quark gluon plazma
... sNN 4.75 GeV sNN 17.2 GeV sNN 200 GeV sNN 2.76 TeV ...
... sNN 4.75 GeV sNN 17.2 GeV sNN 200 GeV sNN 2.76 TeV ...
Fe Particles or Protons on Fixed-ratio Operant
... For training and testing, the rats were maintained on a mild food deprivation schedule in which they were provided with 14 g/day of food. If the rats did not press the lever enough to obtain this amount of food, they were given additional food to bring their total to 14 g. For acquisition of the lev ...
... For training and testing, the rats were maintained on a mild food deprivation schedule in which they were provided with 14 g/day of food. If the rats did not press the lever enough to obtain this amount of food, they were given additional food to bring their total to 14 g. For acquisition of the lev ...
DESY
The Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron (english German Electron Synchrotron) commonly referred to by the abbreviation DESY, is a national research center in Germany that operates particle accelerators used to investigate the structure of matter. It conducts a broad spectrum of inter-disciplinary scientific research in three main areas: particle and high energy physics; photon science; and the development, construction and operation of particle accelerators. Its name refers to its first project, an electron synchrotron. DESY is publicly financed by the Federal Republic of Germany, the States of Germany, and the German Research Foundation (DFG). DESY is a member of the Helmholtz Association and operates at sites in Hamburg and Zeuthen.