Kinetic investigation of low-pH Fe(II) oxidation and development of a
... emitted from environmental facilities and industrial processes such as petroleum refineries, paper manufacturing, anaerobic digestion processes etc. The removal of H2S from gaseous streams is required for the health of the general public, occupational safety and for operational reasons. The Liquid R ...
... emitted from environmental facilities and industrial processes such as petroleum refineries, paper manufacturing, anaerobic digestion processes etc. The removal of H2S from gaseous streams is required for the health of the general public, occupational safety and for operational reasons. The Liquid R ...
Multiple Choice
... bonding pairs H2O (2) < NH3 (1) < CH4 (0). Acids contain the COOH functional group (B) (a is a ketone, c is an alcohol, and d is an ether) 4-methylpentane is the same as 2-methylpentane because # 4 C = # 2 (left to right vs. right to left). C1H3–C2C3H: C1 is sp3, C2 is sp, C3 is sp Both are non ...
... bonding pairs H2O (2) < NH3 (1) < CH4 (0). Acids contain the COOH functional group (B) (a is a ketone, c is an alcohol, and d is an ether) 4-methylpentane is the same as 2-methylpentane because # 4 C = # 2 (left to right vs. right to left). C1H3–C2C3H: C1 is sp3, C2 is sp, C3 is sp Both are non ...
Chemistry
... (idea of s-p mixing and orbital interaction to be given). Formal charge, Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR), shapes of the following simple molecules and ions containing lone pairs and bond pairs of electrons: H2O, NH3, PCl3, PCl5, SF6, ClF3, I3-, BrF2+, PCl6-, ICl2ICl4- and SO42-. ...
... (idea of s-p mixing and orbital interaction to be given). Formal charge, Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR), shapes of the following simple molecules and ions containing lone pairs and bond pairs of electrons: H2O, NH3, PCl3, PCl5, SF6, ClF3, I3-, BrF2+, PCl6-, ICl2ICl4- and SO42-. ...
Chemistry 11 Final Examination Review
... a) Electrons can absorb or emit energy only in whole numbers of photons. b) Atoms have a central positively charged nucleus. c) Electrons move around the nucleus as planets orbit the sun. d) Most of the volume of an atom is empty space. 10. Which of the following orbitals is spherical in shape? a) 3 ...
... a) Electrons can absorb or emit energy only in whole numbers of photons. b) Atoms have a central positively charged nucleus. c) Electrons move around the nucleus as planets orbit the sun. d) Most of the volume of an atom is empty space. 10. Which of the following orbitals is spherical in shape? a) 3 ...
Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
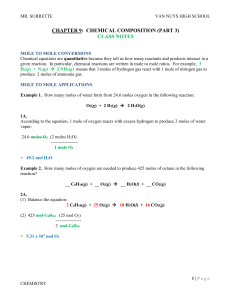
... • One mole of molecules or formula units contains Avogadro’s number times the number of atoms or ions of each element in the compound Stoichiometry ...
... • One mole of molecules or formula units contains Avogadro’s number times the number of atoms or ions of each element in the compound Stoichiometry ...
SCH3U: Final Exam Review
... What is molar volume? State the molar volume (including the units) of any gas at STP. Calculate the volume that is occupied by 5.05 mol of hydrogen chloride, HCl, gas at STP. What is the pressure of 6.7 mol of carbon dioxide gas, in 35.0 L at 30°C? Calculate the volume of water vapour that is produc ...
... What is molar volume? State the molar volume (including the units) of any gas at STP. Calculate the volume that is occupied by 5.05 mol of hydrogen chloride, HCl, gas at STP. What is the pressure of 6.7 mol of carbon dioxide gas, in 35.0 L at 30°C? Calculate the volume of water vapour that is produc ...
CHEMICAL AND PROCESS DESIGN HANDBOOK
... are manufactured by industrial processes influence what we do and how we do it. This book offers descriptions and process details of the most popular of those chemicals. The manufacture of chemicals involves many facets of chemistry and engineering which are exhaustively treated in a whole series of ...
... are manufactured by industrial processes influence what we do and how we do it. This book offers descriptions and process details of the most popular of those chemicals. The manufacture of chemicals involves many facets of chemistry and engineering which are exhaustively treated in a whole series of ...
Liquid–liquid extraction

Liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) consists in transferring one (or more) solute(s) contained in a feed solution to another immiscible liquid (solvent). The solvent that is enriched in solute(s) is called extract. The feed solution that is depleted in solute(s) is called raffinate.Liquid–liquid extraction also known as solvent extraction and partitioning, is a method to separate compounds based on their relative solubilities in two different immiscible liquids, usually water and an organic solvent. It is an extraction of a substance from one liquid into another liquid phase. Liquid–liquid extraction is a basic technique in chemical laboratories, where it is performed using a variety of apparatus, from separatory funnels to countercurrent distribution equipment. This type of process is commonly performed after a chemical reaction as part of the work-up.The term partitioning is commonly used to refer to the underlying chemical and physical processes involved in liquid–liquid extraction, but on another reading may be fully synonymous with it. The term solvent extraction can also refer to the separation of a substance from a mixture by preferentially dissolving that substance in a suitable solvent. In that case, a soluble compound is separated from an insoluble compound or a complex matrix.Solvent extraction is used in nuclear reprocessing, ore processing, the production of fine organic compounds, the processing of perfumes, the production of vegetable oils and biodiesel, and other industries.Liquid–liquid extraction is possible in non-aqueous systems: In a system consisting of a molten metal in contact with molten salts, metals can be extracted from one phase to the other. This is related to a mercury electrode where a metal can be reduced, the metal will often then dissolve in the mercury to form an amalgam that modifies its electrochemistry greatly. For example, it is possible for sodium cations to be reduced at a mercury cathode to form sodium amalgam, while at an inert electrode (such as platinum) the sodium cations are not reduced. Instead, water is reduced to hydrogen. A detergent or fine solid can be used to stabilize an emulsion, or third phase.