Clusters
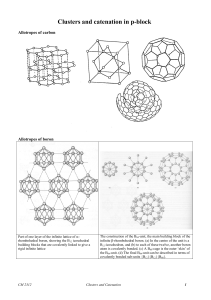
... It is possible to convert a borane into a carborane cluster by replacing a {BH−} by a {CH} unit because both fragments possess the same frontier orbital properties. The two sets of MOs have the same symmetry characteristics, are of approximately the same energy, and contain the same number of electr ...
... It is possible to convert a borane into a carborane cluster by replacing a {BH−} by a {CH} unit because both fragments possess the same frontier orbital properties. The two sets of MOs have the same symmetry characteristics, are of approximately the same energy, and contain the same number of electr ...
Electronic Structure of Metals The “Sea of Electrons”
... What are some aspects of coordination compounds we ...
... What are some aspects of coordination compounds we ...
chemistry 2.1
... Ionic compounds are formed by positive and negative ions combining. The formula of an ionic compound is obtained by balancing the charges of the ions so that the overall charge of the compound is zero. The formula represents the simplest unit or empirical formula of the compound. The term molecule s ...
... Ionic compounds are formed by positive and negative ions combining. The formula of an ionic compound is obtained by balancing the charges of the ions so that the overall charge of the compound is zero. The formula represents the simplest unit or empirical formula of the compound. The term molecule s ...
- Catalyst
... Ni(en)32+(aq) + 2 Hdmg(EtOH) + 2 H2O(l) → Ni(dmg)2(s) + 3 en(EtOH) + 2 H3O+(aq) (octahedral) (square planar) Note: If any green precipitate forms, it is Ni(OH)2(s). ...
... Ni(en)32+(aq) + 2 Hdmg(EtOH) + 2 H2O(l) → Ni(dmg)2(s) + 3 en(EtOH) + 2 H3O+(aq) (octahedral) (square planar) Note: If any green precipitate forms, it is Ni(OH)2(s). ...
Coordination compounds :
... possess more than one set of lone pair electrons, but only one of these pairs can coordinate with a central ion. Such ligands are said to be monodentate (―one tooth‖.) Larger ligands may contain more than one atom capable of coordinating with a single central ion, and are described as polydentate. T ...
... possess more than one set of lone pair electrons, but only one of these pairs can coordinate with a central ion. Such ligands are said to be monodentate (―one tooth‖.) Larger ligands may contain more than one atom capable of coordinating with a single central ion, and are described as polydentate. T ...
Click
... i.e. Ni→CO π-bond in Ni(CO)4 form by overlap between filled dz2 or dx2-y2 on Ni atom and empty π* molecular orbital on CO molecule. M→CO π-bond form by overlapping with filled dxy, dyz or dxz orbital of M with empty π* molecular orbital on CO molecule. Out of six CO, three are linked by M←CO σ-bond ...
... i.e. Ni→CO π-bond in Ni(CO)4 form by overlap between filled dz2 or dx2-y2 on Ni atom and empty π* molecular orbital on CO molecule. M→CO π-bond form by overlapping with filled dxy, dyz or dxz orbital of M with empty π* molecular orbital on CO molecule. Out of six CO, three are linked by M←CO σ-bond ...
Click here to Ch 06.2 Covalent Bonding_Lewis Structures
... electrons, and for those that can fit more than eight electrons, into their outermost orbital. • Hydrogen forms bonds in which it is surrounded by only two electrons. • Boron has just three valence electrons, so it tends to form bonds in which it is surrounded by six electrons. ...
... electrons, and for those that can fit more than eight electrons, into their outermost orbital. • Hydrogen forms bonds in which it is surrounded by only two electrons. • Boron has just three valence electrons, so it tends to form bonds in which it is surrounded by six electrons. ...
Chem+174–Lecture+12a..
... for aryl, dialkylamino and alkoxy phosphines The extreme cases are PCl3 and PF3, which is equivalent to CO in its p-acidity because more electronegative elements on the phosphorous atom stabilize the s-bond and lower the energy of the s*-orbital (see diagram) The contribution of the phosphorus a ...
... for aryl, dialkylamino and alkoxy phosphines The extreme cases are PCl3 and PF3, which is equivalent to CO in its p-acidity because more electronegative elements on the phosphorous atom stabilize the s-bond and lower the energy of the s*-orbital (see diagram) The contribution of the phosphorus a ...
Oxidation of benzoin with anchored vanadyl and
... carried out in the absence of catalyst, was very slow and low yields of benzil were obtained even when the reaction was allowed to proceed for a longer time (up to 32 h). Experiments were carried out using (i) the organic polymer without ligand and metal complex and (ii) the organic polymer function ...
... carried out in the absence of catalyst, was very slow and low yields of benzil were obtained even when the reaction was allowed to proceed for a longer time (up to 32 h). Experiments were carried out using (i) the organic polymer without ligand and metal complex and (ii) the organic polymer function ...
Biomimetic oxidation of catechol employing complexes formed in
... the oxidation of catechols. But with different rates which vary from 0,0635µmol.L−1.min−1 for the complex arising from ligand L3 and metallic salt ZnCl2 (weak catalyst) to 18,9219 µmol.L−1.min−1 for the complex formed from ligand L4 and the metallic salt Cu(CH3COO)2 (best catalyst). This can be rela ...
... the oxidation of catechols. But with different rates which vary from 0,0635µmol.L−1.min−1 for the complex arising from ligand L3 and metallic salt ZnCl2 (weak catalyst) to 18,9219 µmol.L−1.min−1 for the complex formed from ligand L4 and the metallic salt Cu(CH3COO)2 (best catalyst). This can be rela ...
Transition Metals Complexes
... A ligand may be an atom, an ion or a molecule. N.B. Ligands, nucleophiles and Lewis bases are all defined as electron pair donors. Since the ligand donates both of the electrons it shares with the central metal ion, a coordinate bond is formed. The co-ordination number is the number of atoms bonded ...
... A ligand may be an atom, an ion or a molecule. N.B. Ligands, nucleophiles and Lewis bases are all defined as electron pair donors. Since the ligand donates both of the electrons it shares with the central metal ion, a coordinate bond is formed. The co-ordination number is the number of atoms bonded ...
Chemistry 1000 Lecture 23: Introduction to transition metal chemistry
... A given metal ion in a given oxidation state typically has a preferred coordination number found in most of its compounds. I ...
... A given metal ion in a given oxidation state typically has a preferred coordination number found in most of its compounds. I ...
Answer - Assignment Expert
... Name: pentaamminechloroplatinum(IV) bromide Solution: The complex ion is a cation, the counter anion is the 3 bromides. The charge of the complex ion must be +3 since it bonds with 3 bromides. The NH3 are neutral molecules while the chloride carries - 1 charge. Therefore, the oxidation number of pla ...
... Name: pentaamminechloroplatinum(IV) bromide Solution: The complex ion is a cation, the counter anion is the 3 bromides. The charge of the complex ion must be +3 since it bonds with 3 bromides. The NH3 are neutral molecules while the chloride carries - 1 charge. Therefore, the oxidation number of pla ...























