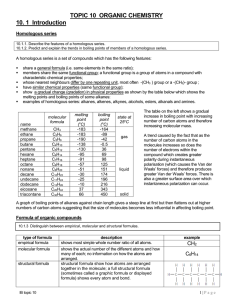
A2 Module 2814: Chains, Rings and Spectroscopy
... Generally the +2 oxidation will be common as this corresponds to the removal of the element’s two 4s electrons. Higher oxidation states than +2 mean that 3d electrons (close in energy to the 4s) have also been removed. Copper is the only transition metal to form a significant number of compounds in ...
... Generally the +2 oxidation will be common as this corresponds to the removal of the element’s two 4s electrons. Higher oxidation states than +2 mean that 3d electrons (close in energy to the 4s) have also been removed. Copper is the only transition metal to form a significant number of compounds in ...
Electronic Structure of Metals The “Sea of Electrons”
... Demo: Oxidation States of Vanadium Different colors are due to different numbers of electrons in the highest-occupied MOs of each Vcontaining polyatomic ion. V +4 is the most common oxidation state. V +5 is easily converted to V+4 by the mild reducing agent NaHSO3(aq). An excess of the stronger ...
... Demo: Oxidation States of Vanadium Different colors are due to different numbers of electrons in the highest-occupied MOs of each Vcontaining polyatomic ion. V +4 is the most common oxidation state. V +5 is easily converted to V+4 by the mild reducing agent NaHSO3(aq). An excess of the stronger ...
KORT INTRODUKTION TIL
... number-prefix. In such cases the terms bis-, tris-, tetrakis-, pentakis- … are used. F Different ligands in the same coordination compound are given in strictly alphabetic order of the ligands (number-prefixes has no influence on that) G Bridging ligands (between two central atoms) is given the pref ...
... number-prefix. In such cases the terms bis-, tris-, tetrakis-, pentakis- … are used. F Different ligands in the same coordination compound are given in strictly alphabetic order of the ligands (number-prefixes has no influence on that) G Bridging ligands (between two central atoms) is given the pref ...
Introduction to nomenclature of coordination compounds
... number-prefix. In such cases the terms bis-, tris-, tetrakis-, pentakis- … are used. F Different ligands in the same coordination compound are given in strictly alphabetic order of the ligands (number-prefixes has no influence on that) G Bridging ligands (between two central atoms) is given the pref ...
... number-prefix. In such cases the terms bis-, tris-, tetrakis-, pentakis- … are used. F Different ligands in the same coordination compound are given in strictly alphabetic order of the ligands (number-prefixes has no influence on that) G Bridging ligands (between two central atoms) is given the pref ...
Rare Oxidation-State Combinations and Unusual Structural Motifs in
... produced in situ from the metal-assisted hydrolytic deoximation and nucleophilic attack of H2O to the ketone group that forms, followed by single deprotonation, as has already been observed in Mn chemistry.14 The cation of 3 (Figure 3)10 contains three MnII (Mn2, Mn4, and Mn6) and three MnIII (Mn1, ...
... produced in situ from the metal-assisted hydrolytic deoximation and nucleophilic attack of H2O to the ketone group that forms, followed by single deprotonation, as has already been observed in Mn chemistry.14 The cation of 3 (Figure 3)10 contains three MnII (Mn2, Mn4, and Mn6) and three MnIII (Mn1, ...
Coordination Chemistry and Organo Metallics
... neutral molecules. These are stable in solid state as well as in dissolved state i.e., The constituent is not retained in solutions. For example NiCl 2 4NH3 is stable in solid state as well as in aqueous solution. Its aqueous solution does not give test for Ni ++ or Cl- and NH4. It is also defined ...
... neutral molecules. These are stable in solid state as well as in dissolved state i.e., The constituent is not retained in solutions. For example NiCl 2 4NH3 is stable in solid state as well as in aqueous solution. Its aqueous solution does not give test for Ni ++ or Cl- and NH4. It is also defined ...
Preparation of Mn(acac)
... reduced to Mn(acac)3– (–0.06 V vs SCE) in acetonitrile solution (0.1 M tetraethylamonium perchlorate). It has been shown that many electron transfer reactions like those above are ligandcentered rather than metal-centered.3 This implies that in many transition metal complexes electron transfer react ...
... reduced to Mn(acac)3– (–0.06 V vs SCE) in acetonitrile solution (0.1 M tetraethylamonium perchlorate). It has been shown that many electron transfer reactions like those above are ligandcentered rather than metal-centered.3 This implies that in many transition metal complexes electron transfer react ...
Name: (1 of 2) Math Set # 13 Protons,
... now has a charge. For example, if a hydrogen atom has one proton (+) and one electron (-‐) the two charges cancel each other out. When the electron is lost the hydrogen atom is only a ...
... now has a charge. For example, if a hydrogen atom has one proton (+) and one electron (-‐) the two charges cancel each other out. When the electron is lost the hydrogen atom is only a ...