Document
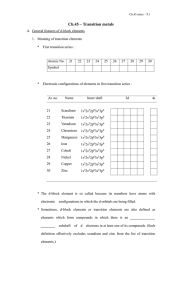
... first transition series react to form compounds, they can form ions of roughly the ___________________ by losing different numbers of electrons. * The higher oxidation states arise through ____________ bonding with more electronegative elements such as fluorine, chlorine and oxygen, as in TiCl4 , ...
... first transition series react to form compounds, they can form ions of roughly the ___________________ by losing different numbers of electrons. * The higher oxidation states arise through ____________ bonding with more electronegative elements such as fluorine, chlorine and oxygen, as in TiCl4 , ...
REACTIONS OF IRON(II)
... When iron reacts with acids it gives rise to iron(II) (ferrous) salts. Aqueous solutions of such salts contain the pale green, octahedral hexaaquairon(II) ion ...
... When iron reacts with acids it gives rise to iron(II) (ferrous) salts. Aqueous solutions of such salts contain the pale green, octahedral hexaaquairon(II) ion ...
Chapter 2 - U of L Class Index
... field splitting. Fe(OH2)63+ and Fe(C2O4)33- are both complexes of Fe3+ but Fe(OH2)63+ is red-orange while Fe(C2O4)33- is green. A spectrophotometer measures the amount of light absorbed by a complex. When analyzing a green complex, it is therefore necessary to look at the absorption of light other t ...
... field splitting. Fe(OH2)63+ and Fe(C2O4)33- are both complexes of Fe3+ but Fe(OH2)63+ is red-orange while Fe(C2O4)33- is green. A spectrophotometer measures the amount of light absorbed by a complex. When analyzing a green complex, it is therefore necessary to look at the absorption of light other t ...
Pdf - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... particular salt, so it is not a typical iron salt or copper salt or any other metal salt, but it is colored. So, colored salts we all know what is particular salt can be colored, it cannot be potassium chloride, it cannot be sodium chloride, so definitely it is a typical salt, which can give rise to ...
... particular salt, so it is not a typical iron salt or copper salt or any other metal salt, but it is colored. So, colored salts we all know what is particular salt can be colored, it cannot be potassium chloride, it cannot be sodium chloride, so definitely it is a typical salt, which can give rise to ...
Chapter 4 - profpaz.com
... This relationship is valid because the product of molarity times volume on each side equals the moles of solute, which remains constant during dilution. Molarity and volume, however, are inversely proportional during the dilution process. ...
... This relationship is valid because the product of molarity times volume on each side equals the moles of solute, which remains constant during dilution. Molarity and volume, however, are inversely proportional during the dilution process. ...