- Pcpolytechnic
... It is a system of fixed mass and no heat or work energy cross its boundary. In other words, an isolated system does not have transfer of either mass or energy(heat or work) with the surrounding. A open system with its surroundings (known as universe) is an example of an isolated system. ...
... It is a system of fixed mass and no heat or work energy cross its boundary. In other words, an isolated system does not have transfer of either mass or energy(heat or work) with the surrounding. A open system with its surroundings (known as universe) is an example of an isolated system. ...
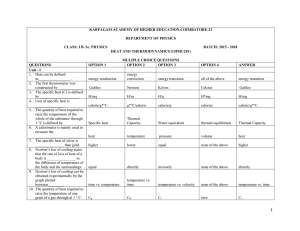
Heat and Thermodynamics 300 MCQ
... 44. Extension property of a system is one whose value 45. Work done in a free expansion process is 46. The statement that molecular weights of all gases occupy the same volume is known as 47. If a gas is heated against a pressure keeping the volume ...
... 44. Extension property of a system is one whose value 45. Work done in a free expansion process is 46. The statement that molecular weights of all gases occupy the same volume is known as 47. If a gas is heated against a pressure keeping the volume ...
Temperature
... a. Describe two different types of thermometer. What physical properties do they rely on? b. Give examples of when you might use these methods. c. Why do you always have to hold the thermometer under your tongue for what seems like hours (but is usually about 30 seconds) when you have your temperatu ...
... a. Describe two different types of thermometer. What physical properties do they rely on? b. Give examples of when you might use these methods. c. Why do you always have to hold the thermometer under your tongue for what seems like hours (but is usually about 30 seconds) when you have your temperatu ...
Document
... temperature and chemical composition of stars • Identified the spectral sequence as a temperature sequence and correctly concluded that the large variations in absorption lines seen in stars is due to ionization and not abundances • Found abundances of silicon, carbon, etc on sun similar to earth • ...
... temperature and chemical composition of stars • Identified the spectral sequence as a temperature sequence and correctly concluded that the large variations in absorption lines seen in stars is due to ionization and not abundances • Found abundances of silicon, carbon, etc on sun similar to earth • ...
Document
... The number of collisions is pr20vNT where N is the number of perturbers per unit volume, T is the interval of the collisions. If we set T = Dt0, the average length of an uninterupted segment a photon will travel. Over this length the number of ...
... The number of collisions is pr20vNT where N is the number of perturbers per unit volume, T is the interval of the collisions. If we set T = Dt0, the average length of an uninterupted segment a photon will travel. Over this length the number of ...
Michell, Laplace and the Origin of the Black Hole Concept
... proportion to its vis inertiae, with other bodies, all light emitted from such a body would be made to return towards it, by its own proper gravity. (Michell, 1784: ...
... proportion to its vis inertiae, with other bodies, all light emitted from such a body would be made to return towards it, by its own proper gravity. (Michell, 1784: ...
File
... 6. It is impossible by a cyclic process to transfer heat from a low temperature region to a high temperature region without at the same time converting same work into heat. 7. It is impossible to obtain work by cooling a body below the lowest temperature of the system. 8. There exists a function ‘S’ ...
... 6. It is impossible by a cyclic process to transfer heat from a low temperature region to a high temperature region without at the same time converting same work into heat. 7. It is impossible to obtain work by cooling a body below the lowest temperature of the system. 8. There exists a function ‘S’ ...
Atmospheric Thermodynamics
... with cpd=7/2 Rd=1004.7 J kg-1 K-1 the heat capacity for dry air at constant pressure, as obtained from (14) and (3). The enthalpy is the preferred state function in meteorology as it uses pressure as dependent variable, and simplifies for isentropic transformations. Furthermore, the enthalpy is also ...
... with cpd=7/2 Rd=1004.7 J kg-1 K-1 the heat capacity for dry air at constant pressure, as obtained from (14) and (3). The enthalpy is the preferred state function in meteorology as it uses pressure as dependent variable, and simplifies for isentropic transformations. Furthermore, the enthalpy is also ...
Black body
A black body (also blackbody) is an idealized physical body that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation, regardless of frequency or angle of incidence. A white body is one with a ""rough surface [that] reflects all incident rays completely and uniformly in all directions.""A black body in thermal equilibrium (that is, at a constant temperature) emits electromagnetic radiation called black-body radiation. The radiation is emitted according to Planck's law, meaning that it has a spectrum that is determined by the temperature alone (see figure at right), not by the body's shape or composition.A black body in thermal equilibrium has two notable properties:It is an ideal emitter: at every frequency, it emits as much energy as – or more energy than – any other body at the same temperature.It is a diffuse emitter: the energy is radiated isotropically, independent of direction.An approximate realization of a black surface is a hole in the wall of a large enclosure (see below). Any light entering the hole is reflected indefinitely or absorbed inside and is unlikely to re-emerge, making the hole a nearly perfect absorber. The radiation confined in such an enclosure may or may not be in thermal equilibrium, depending upon the nature of the walls and the other contents of the enclosure.Real materials emit energy at a fraction—called the emissivity—of black-body energy levels. By definition, a black body in thermal equilibrium has an emissivity of ε = 1.0. A source with lower emissivity independent of frequency often is referred to as a gray body.Construction of black bodies with emissivity as close to one as possible remains a topic of current interest.In astronomy, the radiation from stars and planets is sometimes characterized in terms of an effective temperature, the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total flux of electromagnetic energy.