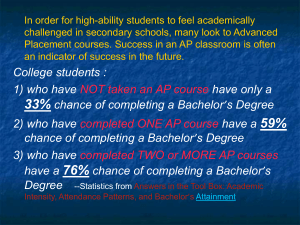
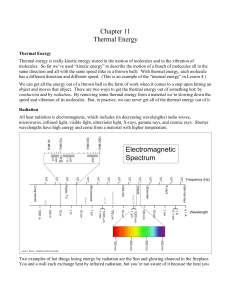
3.1 Thermal concepts (PPT)
... Thermal energy is a term often confused with that of heat. Simply put, heat is the flow of thermal energy. Thermal energy is the total internal energy of the system. This has to do with the kinetic and potential energies of the molecules, i.e. how fast the molecules are vibrating and their chemical ...
... Thermal energy is a term often confused with that of heat. Simply put, heat is the flow of thermal energy. Thermal energy is the total internal energy of the system. This has to do with the kinetic and potential energies of the molecules, i.e. how fast the molecules are vibrating and their chemical ...
Chapter 2-C
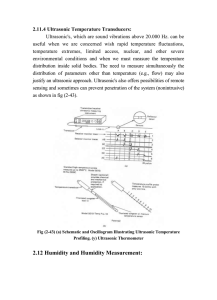
... A typical electrolytic hygrometer as shown in Fig (2-45) can cover a range of from 0 to 2,000 ppm with an accuracy of 5% of the reading, which is more than adequate for most industrial applications. The transducer is suitable for most inert elemental gases and organic and inorganic gas compounds t ...
... A typical electrolytic hygrometer as shown in Fig (2-45) can cover a range of from 0 to 2,000 ppm with an accuracy of 5% of the reading, which is more than adequate for most industrial applications. The transducer is suitable for most inert elemental gases and organic and inorganic gas compounds t ...
Fundamental Concepts, Definitions and Zeroth
... Q. 4: Explain thermodynamic system, surrounding and universe. Differentiate among open system, closed system and an isolated system. Give two suitable examples of each system. (Dec. 03) Or Define and explain a thermodynamic system. Differentiate between various types of thermodynamic systems and giv ...
... Q. 4: Explain thermodynamic system, surrounding and universe. Differentiate among open system, closed system and an isolated system. Give two suitable examples of each system. (Dec. 03) Or Define and explain a thermodynamic system. Differentiate between various types of thermodynamic systems and giv ...
Lecture August 28
... that has a very large size The macroscopic system under consideration can change its state as a result of its contact to the bath ☛ but the state of the bath does not change due to interaction with a much smaller system For example ☛ thermometer measuring temperature of body can be considered as sys ...
... that has a very large size The macroscopic system under consideration can change its state as a result of its contact to the bath ☛ but the state of the bath does not change due to interaction with a much smaller system For example ☛ thermometer measuring temperature of body can be considered as sys ...
Thermodynamics: Notes
... In thermodynamics we confine our attention to a particular part of the universe which we call our system. The rest of the universe outside our system we call the surroundings. The system and the surroundings are separated by a boundary or a wall. They may, in general, exchange energy and matter, dep ...
... In thermodynamics we confine our attention to a particular part of the universe which we call our system. The rest of the universe outside our system we call the surroundings. The system and the surroundings are separated by a boundary or a wall. They may, in general, exchange energy and matter, dep ...
Microwave-Specific Enhancement of the Carbon−Carbon Dioxide
... Thermal. For flow reactions carried out under thermal conditions, a reaction tube of the same diameter and having the same mass of carbon, spread out over a quartz frit, is brought up to the desired temperature in a Lindberg tube furnace packed with quartz wool to insulate the tube. After the system ...
... Thermal. For flow reactions carried out under thermal conditions, a reaction tube of the same diameter and having the same mass of carbon, spread out over a quartz frit, is brought up to the desired temperature in a Lindberg tube furnace packed with quartz wool to insulate the tube. After the system ...
Physics - WordPress.com
... The international system of units is based on seven independent units known as Fundamental or Basic Units. These are given below: 1. Meter (m): length, distance, height (l) 2. Kilogram (kg): mass (m) 3. Second (s): time (t) 4. Ampere (A): electric current (I) 5. Kelvin (K): temperature (T) 6. Mole ( ...
... The international system of units is based on seven independent units known as Fundamental or Basic Units. These are given below: 1. Meter (m): length, distance, height (l) 2. Kilogram (kg): mass (m) 3. Second (s): time (t) 4. Ampere (A): electric current (I) 5. Kelvin (K): temperature (T) 6. Mole ( ...
Disability accessible Draft Guide - Fermi Gamma
... black hole, an object more massive than the Sun, time and space are warped to the yet concentrated into a volume extreme, and nothing – not even millions of times smaller – literally light – can escape the pull of their a puncture in the fabric of the cosferocious gravity. Black holes once mos. The ...
... black hole, an object more massive than the Sun, time and space are warped to the yet concentrated into a volume extreme, and nothing – not even millions of times smaller – literally light – can escape the pull of their a puncture in the fabric of the cosferocious gravity. Black holes once mos. The ...
THERMODYNAMICS LECTURE NOTES
... that is at a different temperature, heat is transferred from the body at higher temperature to the one at lower temperature until both bodies attain the same temperature as shown in figure 1.6. At that point, the heat transfer stops, and the two bodies are said to have reached thermal equilibrium. T ...
... that is at a different temperature, heat is transferred from the body at higher temperature to the one at lower temperature until both bodies attain the same temperature as shown in figure 1.6. At that point, the heat transfer stops, and the two bodies are said to have reached thermal equilibrium. T ...
Thermochemistry
... the number of cycles that pass an observer in a second. The unit of frequency is the Hertz (1Hz=one oscillation per second). The product of wavelength and frequency for an individual wave is equal to the speed of light (speed is distance divided by time): c = λ × f . From this equation one can see t ...
... the number of cycles that pass an observer in a second. The unit of frequency is the Hertz (1Hz=one oscillation per second). The product of wavelength and frequency for an individual wave is equal to the speed of light (speed is distance divided by time): c = λ × f . From this equation one can see t ...
Black body
A black body (also blackbody) is an idealized physical body that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation, regardless of frequency or angle of incidence. A white body is one with a ""rough surface [that] reflects all incident rays completely and uniformly in all directions.""A black body in thermal equilibrium (that is, at a constant temperature) emits electromagnetic radiation called black-body radiation. The radiation is emitted according to Planck's law, meaning that it has a spectrum that is determined by the temperature alone (see figure at right), not by the body's shape or composition.A black body in thermal equilibrium has two notable properties:It is an ideal emitter: at every frequency, it emits as much energy as – or more energy than – any other body at the same temperature.It is a diffuse emitter: the energy is radiated isotropically, independent of direction.An approximate realization of a black surface is a hole in the wall of a large enclosure (see below). Any light entering the hole is reflected indefinitely or absorbed inside and is unlikely to re-emerge, making the hole a nearly perfect absorber. The radiation confined in such an enclosure may or may not be in thermal equilibrium, depending upon the nature of the walls and the other contents of the enclosure.Real materials emit energy at a fraction—called the emissivity—of black-body energy levels. By definition, a black body in thermal equilibrium has an emissivity of ε = 1.0. A source with lower emissivity independent of frequency often is referred to as a gray body.Construction of black bodies with emissivity as close to one as possible remains a topic of current interest.In astronomy, the radiation from stars and planets is sometimes characterized in terms of an effective temperature, the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total flux of electromagnetic energy.