Whole Package - Math.utah.edu
... (a) If you got 1, read what I wrote above. (b) If you got 1, read what I wrote above. (c) Parens tell you what to do before squaring. (d) Evaluate the whole numerator and whole denominator (with proper order of operations) first. Then reduce the resulting fraction. No cancelling until you’ve done al ...
... (a) If you got 1, read what I wrote above. (b) If you got 1, read what I wrote above. (c) Parens tell you what to do before squaring. (d) Evaluate the whole numerator and whole denominator (with proper order of operations) first. Then reduce the resulting fraction. No cancelling until you’ve done al ...
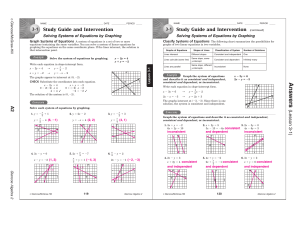
Solving Addition and Subtraction Equations
... The Giants scored 13 points in a game against Dallas. They scored 7 points for a touchdown and the rest of their points for field goals. How many points did they score on field goals? Let f represent the field goal points. ...
... The Giants scored 13 points in a game against Dallas. They scored 7 points for a touchdown and the rest of their points for field goals. How many points did they score on field goals? Let f represent the field goal points. ...
The First Law of Thermodynamics
... Chapter 18: Thermal Properties of Matter Ideal Gas Law For an ideal gas the pressure P , the volume V , and the absolute temperature T are related by the ideal gas law P V = nRT where n is the number of moles of the gas, and R is the ideal gas constant. In the MKS system, R = 8.314 J/mole-K. If pres ...
... Chapter 18: Thermal Properties of Matter Ideal Gas Law For an ideal gas the pressure P , the volume V , and the absolute temperature T are related by the ideal gas law P V = nRT where n is the number of moles of the gas, and R is the ideal gas constant. In the MKS system, R = 8.314 J/mole-K. If pres ...
Lecture 2 Intro to Heat Flow
... as a function of the curvature of the temperature gradient (perhaps more intuitive than the previous equation): ...
... as a function of the curvature of the temperature gradient (perhaps more intuitive than the previous equation): ...