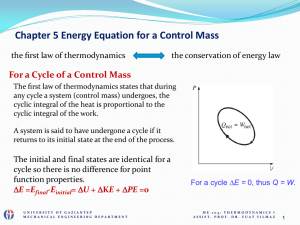
ME 204 Thermodynamics I
... The Constant–Volume and Constant–Pressure Specific Heats Consider a homogeneous phase of a substance of constant composition. It may be a solid, a liquid, or a gas, but no change of phase will occur. Specific heat at constant volume, cv: The energy required to raise the temperature of the unit mass ...
... The Constant–Volume and Constant–Pressure Specific Heats Consider a homogeneous phase of a substance of constant composition. It may be a solid, a liquid, or a gas, but no change of phase will occur. Specific heat at constant volume, cv: The energy required to raise the temperature of the unit mass ...
lecture1423183006
... The law states that ”The total change of heat in a chemical reaction is same irrespective whether it occurs in a single step or in multiple steps provided that the reaction must be isothermal or isobaric or isochoric.” ...
... The law states that ”The total change of heat in a chemical reaction is same irrespective whether it occurs in a single step or in multiple steps provided that the reaction must be isothermal or isobaric or isochoric.” ...
Introduction NOTES AND PROBLEM SET 1
... However the setup above is not always possible. When the ’tail’ takes too much volume, such as when there is more than one ’tail’, then the closed structures are not possible and instead we get bilayers: ...
... However the setup above is not always possible. When the ’tail’ takes too much volume, such as when there is more than one ’tail’, then the closed structures are not possible and instead we get bilayers: ...
chem 155 trial questions
... 34. An isolated system is best described by which one of the following statements? a. Neither matter nor heat can pass into or out of the system b. The system has a boundary which allows heat to be transferred but does not allow material to pass into or out of the system c. The system has a diatherm ...
... 34. An isolated system is best described by which one of the following statements? a. Neither matter nor heat can pass into or out of the system b. The system has a boundary which allows heat to be transferred but does not allow material to pass into or out of the system c. The system has a diatherm ...