
Chapter 17: Amines and Amides
... Their effect may be felt within 20 minutes. Barbiturates are used medically to relieve anxiety, tension, insomnia, epilepsy and hypertension. People using barbiturates should be aware of the extreme danger they are in if they combine alcohol and barbiturates. The barbiturate and alcohol combination ...
... Their effect may be felt within 20 minutes. Barbiturates are used medically to relieve anxiety, tension, insomnia, epilepsy and hypertension. People using barbiturates should be aware of the extreme danger they are in if they combine alcohol and barbiturates. The barbiturate and alcohol combination ...
Crystallization and Determination of Melting and Boiling Points
... Chromatography is a laboratory method based on selective adsorption by which components in complex mixtures can be separated for identification or purification purposes. (Adsorption is the binding of molecules to the surface of another substance.) The utilization of a moving (or mobile) phase and a ...
... Chromatography is a laboratory method based on selective adsorption by which components in complex mixtures can be separated for identification or purification purposes. (Adsorption is the binding of molecules to the surface of another substance.) The utilization of a moving (or mobile) phase and a ...
Organic Chemistry - Madison Public Schools
... Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten ...
... Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten ...
Organic Compounds: Alkanes
... ORGANIC COMPOUNDS ALKANES Methane is the simplest hydrocarbon; the molecule is approximately spherical, as is shown in the space-filling model: In the ammonia molecule, for example, the nitrogen atom normally has three unpaired p electrons, but by mixing the 2s and 3p orbitals, we can create four sp ...
... ORGANIC COMPOUNDS ALKANES Methane is the simplest hydrocarbon; the molecule is approximately spherical, as is shown in the space-filling model: In the ammonia molecule, for example, the nitrogen atom normally has three unpaired p electrons, but by mixing the 2s and 3p orbitals, we can create four sp ...
Chapter 12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids
... Reactions of aldehydes and ketones: Aldehydes are generally more reactive than ketones in nucleophilic addition reactions due to steric and electronic reasons (or inductive effect). Electronic Effect: Relative reactivities of aldehydes and ketones in nucleophilic addition reactions is due the positi ...
... Reactions of aldehydes and ketones: Aldehydes are generally more reactive than ketones in nucleophilic addition reactions due to steric and electronic reasons (or inductive effect). Electronic Effect: Relative reactivities of aldehydes and ketones in nucleophilic addition reactions is due the positi ...
Propolis (bee glue): an unusual mordant for gilding in Italian
... hive product containing material collected by bees from buds or other plant exudates, volatile substances and beeswax. It is used by bees as a sealant and to protect the nest against microorganisms. Both Aristotle and Pliny give accounts of propolis – mentioning its medicinal properties. Interest in ...
... hive product containing material collected by bees from buds or other plant exudates, volatile substances and beeswax. It is used by bees as a sealant and to protect the nest against microorganisms. Both Aristotle and Pliny give accounts of propolis – mentioning its medicinal properties. Interest in ...
Answers
... oxidized further to the caboxylic acid while propanone is not easily oxidized. The Tollens’ Test for aldehydes makes use of this difference in properties. (Tollens’ reagent is made by adding sodium hydroxide to silver nitrate solution to give a precipitate of silver hydroxide and then redissolving t ...
... oxidized further to the caboxylic acid while propanone is not easily oxidized. The Tollens’ Test for aldehydes makes use of this difference in properties. (Tollens’ reagent is made by adding sodium hydroxide to silver nitrate solution to give a precipitate of silver hydroxide and then redissolving t ...
Organometallic Compounds: Alkyllithium Reagent
... Grignard reagents react with formaldehyde to give a primary alcohol ...
... Grignard reagents react with formaldehyde to give a primary alcohol ...
Alcohols and Thiols
... 3) Alcohols arising from Carbon-Carbon Bond Forming Reactions: The addition of Grignard reagents, alkyllithiums, vinyllithium or acetylides (which I will designate as RM)to carbonyl groups forms alcohols, in addition to new carbon-carbon bonds. These sorts of reactions can be classified both by the ...
... 3) Alcohols arising from Carbon-Carbon Bond Forming Reactions: The addition of Grignard reagents, alkyllithiums, vinyllithium or acetylides (which I will designate as RM)to carbonyl groups forms alcohols, in addition to new carbon-carbon bonds. These sorts of reactions can be classified both by the ...
Naming Compounds - Kowenscience.com
... Always remember atoms are trying to complete their outer shell! The number of electrons the atoms needs is the total number of bonds they can make. Ex. … H? O? F? N? Cl? C? one two one three one four ...
... Always remember atoms are trying to complete their outer shell! The number of electrons the atoms needs is the total number of bonds they can make. Ex. … H? O? F? N? Cl? C? one two one three one four ...
Boiling Point of Liquids Procedures:
... The boiling point (bp) is an important physical property of a substance and can be used to help identify it or, if known, offer information about its purity. Pure substances have a narrow boiling point range while mixtures may show multiple or broad ranged boiling temperatures. A number of definitio ...
... The boiling point (bp) is an important physical property of a substance and can be used to help identify it or, if known, offer information about its purity. Pure substances have a narrow boiling point range while mixtures may show multiple or broad ranged boiling temperatures. A number of definitio ...
unit 12 aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids
... adequately represented by >C=O, nor by the alternative >C+-O-. The real structure or resonance hybrid lies somewhere between the following structure: ...
... adequately represented by >C=O, nor by the alternative >C+-O-. The real structure or resonance hybrid lies somewhere between the following structure: ...
Formose reaction controlled by boronic acid - Beilstein
... contains a number of signals in a wide range of elution time, indicative for the formation of a complicated mixture. On the other hand, the HPLC chart for SPB indicates a broad signal in the region of smaller carbon numbers (Figure 2c), and the chart for pVPB/NaSS exhibits signals in the region of l ...
... contains a number of signals in a wide range of elution time, indicative for the formation of a complicated mixture. On the other hand, the HPLC chart for SPB indicates a broad signal in the region of smaller carbon numbers (Figure 2c), and the chart for pVPB/NaSS exhibits signals in the region of l ...
Recognize the functional group and give a characteristic of this
... A group of covalently bonded elements that when bonded to a carbon chain give it a unique quality. Compounds with similar functional groups will have similar qualities and properties. ...
... A group of covalently bonded elements that when bonded to a carbon chain give it a unique quality. Compounds with similar functional groups will have similar qualities and properties. ...
Carbonyl Compounds notes
... The salts of the long-chain fatty acids are known as soaps. They are extremely useful as they help oil and water mix together. Glycerol is a useful by-product of this reaction as it can be used to make pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. So the alkaline hydrolysis of fats and oils produces soap, which us ...
... The salts of the long-chain fatty acids are known as soaps. They are extremely useful as they help oil and water mix together. Glycerol is a useful by-product of this reaction as it can be used to make pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. So the alkaline hydrolysis of fats and oils produces soap, which us ...
Chapter 15 Carboxylic Acids and Esters
... CARBOXYLIC ACIDS IUPAC NOMENCLATURE • Find the longest carbon chain that contains the –COOH group. • Drop the –e from the end of the hydrocarbon name and substitute –oic acid. • Number the longest chain. Carbon number 1 is the carboxyl carbon. • Name and number other substituents. ...
... CARBOXYLIC ACIDS IUPAC NOMENCLATURE • Find the longest carbon chain that contains the –COOH group. • Drop the –e from the end of the hydrocarbon name and substitute –oic acid. • Number the longest chain. Carbon number 1 is the carboxyl carbon. • Name and number other substituents. ...
Ch14 Lecture
... • Aldehydes are further oxidized to carboxylic acids (RCOOH), replacing 1 C—H with 1 C—O. ...
... • Aldehydes are further oxidized to carboxylic acids (RCOOH), replacing 1 C—H with 1 C—O. ...
aldehyde group - Imperial Valley College Faculty Websites
... In the presence of excess alcohol and a strong acid such as dry HCl, aldehydes or hemiacetals react with a second molecule of the alcohol to yield an acetal. ...
... In the presence of excess alcohol and a strong acid such as dry HCl, aldehydes or hemiacetals react with a second molecule of the alcohol to yield an acetal. ...
INTRODUCTION - Open Access Repository of Indian Theses
... temperature in excellent yields is described. The 1,4-addition of thiols to α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds leading to synthesis of keto sulfides and keto ethers is very important transformation as they are key intermediates in synthesis of various natural products as well as in organic synthesi ...
... temperature in excellent yields is described. The 1,4-addition of thiols to α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds leading to synthesis of keto sulfides and keto ethers is very important transformation as they are key intermediates in synthesis of various natural products as well as in organic synthesi ...
Chapter 9
... • The most common reaction of aromatic compounds • This reaction is characteristic of all aromatic rings ...
... • The most common reaction of aromatic compounds • This reaction is characteristic of all aromatic rings ...
Chemistry 11 – Functional Groups Notes
... Chemistry 11 – Functional Groups Notes So far we have investigated hydrocarbon alkanes and have found that this particular group has limited uses and properties. If all organic molecules were alkanes, then organic chemistry would be useless and boring! Luckily, specific groups of atoms are found on ...
... Chemistry 11 – Functional Groups Notes So far we have investigated hydrocarbon alkanes and have found that this particular group has limited uses and properties. If all organic molecules were alkanes, then organic chemistry would be useless and boring! Luckily, specific groups of atoms are found on ...
[1] Ans1.Dows-proc - Sacred Heart School Moga,Best ICSE School
... pair of electrons. Since N is less electronegative than oxygen, therefore lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom is more easily available for bond formation. In other hand, nucleophillic attack occurs through N and hence silver nitrite predominantly gives nitro compounds. Q9. Explain, why the t ...
... pair of electrons. Since N is less electronegative than oxygen, therefore lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom is more easily available for bond formation. In other hand, nucleophillic attack occurs through N and hence silver nitrite predominantly gives nitro compounds. Q9. Explain, why the t ...
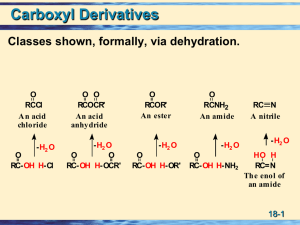
08.Carboxylic acids. Functional derivates of carboxylic acids
... derivatives of carboxylic acids, rather than as carboxyl derivatives of alcohols. We have seen earlier that hydroxyl groups take precedence over double bonds, and double bonds take precedence over halogens and alkyl groups, in naming compounds. Carboxylic acids outrank all the common groups we have ...
... derivatives of carboxylic acids, rather than as carboxyl derivatives of alcohols. We have seen earlier that hydroxyl groups take precedence over double bonds, and double bonds take precedence over halogens and alkyl groups, in naming compounds. Carboxylic acids outrank all the common groups we have ...
Carboxylic Acids
... Condensations of Acids with Amines ( Amides) Although the acid chloride/amine reaction generates amides, it is also possible (and cheaper) to synthesize amides directly from carboxylic acids. The direct reaction of an amine and a carboxylic acid initially forms a carboxylate anion and an ammonium c ...
... Condensations of Acids with Amines ( Amides) Although the acid chloride/amine reaction generates amides, it is also possible (and cheaper) to synthesize amides directly from carboxylic acids. The direct reaction of an amine and a carboxylic acid initially forms a carboxylate anion and an ammonium c ...
Phenols

In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol, which is also called carbolic acid C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.Synonyms are arenols or aryl alcohols.Phenolic compounds are synthesized industrially; they also are produced by plants and microorganisms, with variation between and within species.Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12).Loss of a positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides, although the term aryloxides is preferred according to the IUPAC Gold Book. Phenols can have two or more hydroxy groups bonded to the aromatic ring(s) in the same molecule. The simplest examples are the three benzenediols, each having two hydroxy groups on a benzene ring.Organisms that synthesize phenolic compounds do so in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research.ref name=Klepacka Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants. Others possess estrogenic or endocrine disrupting activity.




















![[1] Ans1.Dows-proc - Sacred Heart School Moga,Best ICSE School](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015878975_1-55791b331e05591620375059b6f74bac-300x300.png)

