In children
... • Weakness, tiredness, weight loss, nausea, intermittent vomiting, abdominal pain, general malaise, muscle cramps, and symptoms suggestive of postural hypotension • Psychiatric symptoms may occur in longstanding cases and include memory impairment, depression, and psychosis. • Patients may be inappr ...
... • Weakness, tiredness, weight loss, nausea, intermittent vomiting, abdominal pain, general malaise, muscle cramps, and symptoms suggestive of postural hypotension • Psychiatric symptoms may occur in longstanding cases and include memory impairment, depression, and psychosis. • Patients may be inappr ...
Document
... • Contralateral reflex - starts on one side of body and travels to opposite side • Ipsilateral reflex - stimulus and response are on same side of body ...
... • Contralateral reflex - starts on one side of body and travels to opposite side • Ipsilateral reflex - stimulus and response are on same side of body ...
Skill.
... visual aura but feelings of nausea. This is followed by a cluster headache in the head or face lasting about 2 hours. • These are more common in younger people and can be triggered by anxiety, fatigue, bright lights, food allergies, and hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle. ...
... visual aura but feelings of nausea. This is followed by a cluster headache in the head or face lasting about 2 hours. • These are more common in younger people and can be triggered by anxiety, fatigue, bright lights, food allergies, and hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle. ...
Disorders of the Nervous System
... -Contracoup injury: brain slams against cranium in one direction and then back in the other direction ...
... -Contracoup injury: brain slams against cranium in one direction and then back in the other direction ...
Development and Plasticity of the Brain
... 6-OHDA destroys axons that release dopamine on one side of the brain. Later amphetamine stimulates only the intact side of the brain because it cannot cause axons to release dopamine on the damaged side.Apomorphine stimulates the damaged side more strongly because it directly stimulates dopamine rec ...
... 6-OHDA destroys axons that release dopamine on one side of the brain. Later amphetamine stimulates only the intact side of the brain because it cannot cause axons to release dopamine on the damaged side.Apomorphine stimulates the damaged side more strongly because it directly stimulates dopamine rec ...
Brain Damage & Neuroplasticity
... - concussion (mild brain injury) - moderate to severe brain injury: classification dependent on the degree of post-traumatic amnesia (or anterograde amnesia – deficits in new learning) - Pathophysiology of TBI ~ focal damage (coupe & contra-coupe) ~ diffuse damage (shearing & tearing of axons referr ...
... - concussion (mild brain injury) - moderate to severe brain injury: classification dependent on the degree of post-traumatic amnesia (or anterograde amnesia – deficits in new learning) - Pathophysiology of TBI ~ focal damage (coupe & contra-coupe) ~ diffuse damage (shearing & tearing of axons referr ...
Using POCS Method of Problem
... The term exocytosis (Pinel pages 94-95) refers to the process of releasing a neurotransmitter. Neurotransmitter chemicals work a bit like keys in locks. In this case, the “locks” are special receptor sites in the dendrites of the receiving neuron. These sites accept only one kind of chemical. For th ...
... The term exocytosis (Pinel pages 94-95) refers to the process of releasing a neurotransmitter. Neurotransmitter chemicals work a bit like keys in locks. In this case, the “locks” are special receptor sites in the dendrites of the receiving neuron. These sites accept only one kind of chemical. For th ...
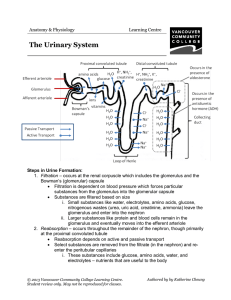
Urinary System - VCC Library - Vancouver Community College
... dilute because there is more water than normal. 3. If red blood cells or proteins were present in your urine, you should be concerned because a normally functioning kidney would not allow these large substances to enter into the glomerular capsule and end up in urine. 4. ACE inhibitor would prevent ...
... dilute because there is more water than normal. 3. If red blood cells or proteins were present in your urine, you should be concerned because a normally functioning kidney would not allow these large substances to enter into the glomerular capsule and end up in urine. 4. ACE inhibitor would prevent ...
NEUROTRANSMITTER TEST KIT (13 vials) - Life
... Involved in sleep-wake regulation, by increasing wakefulness and prevent sleep; also protects against the susceptibility to convulsion, drug sensitisation, denervation super-sensitivity, ischemic lesions and stress; may controls the mechanisms by which memories and learning are forgotten; may be inv ...
... Involved in sleep-wake regulation, by increasing wakefulness and prevent sleep; also protects against the susceptibility to convulsion, drug sensitisation, denervation super-sensitivity, ischemic lesions and stress; may controls the mechanisms by which memories and learning are forgotten; may be inv ...
coma
... differentiate intracranial diseases 、 systemic disease ( initial symptom 、 intracranial hypertension 、 focal signs ) intracranial diseases : type of onset (acute、subacute、 chronic) location sign ( focal lesion 、 meningeal irritation sign ) ...
... differentiate intracranial diseases 、 systemic disease ( initial symptom 、 intracranial hypertension 、 focal signs ) intracranial diseases : type of onset (acute、subacute、 chronic) location sign ( focal lesion 、 meningeal irritation sign ) ...
Heart Rate The interval between two successive R waves
... Blood pressure is most commonly measured by the indirect method. An inflatable rubber cuff attached to a manometer is placed around the upper arm of the sitting patient (Fig.15). This is inflated until the brachial artery is completely occluded (the radial pulse can no longer be felt). Now the press ...
... Blood pressure is most commonly measured by the indirect method. An inflatable rubber cuff attached to a manometer is placed around the upper arm of the sitting patient (Fig.15). This is inflated until the brachial artery is completely occluded (the radial pulse can no longer be felt). Now the press ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM Aids in remembering, thinking, moving
... Divides spinal cord into right and left halves ...
... Divides spinal cord into right and left halves ...
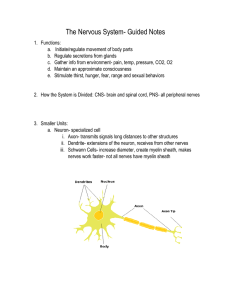
Nervous System Guided Notes
... 10. Sensory Somatic and Autonomic Systems: a. Autonomic: involuntary, controls internal environment of animal i. Two divisions: sympathetic and parasympathetic systems ii. Sympathetic= fight or flight iii. Sympathetic stimulation- HR and BP increases iv. Blood shift away from the skin and abdominal ...
... 10. Sensory Somatic and Autonomic Systems: a. Autonomic: involuntary, controls internal environment of animal i. Two divisions: sympathetic and parasympathetic systems ii. Sympathetic= fight or flight iii. Sympathetic stimulation- HR and BP increases iv. Blood shift away from the skin and abdominal ...
Chapter 11 - Central Nervous System
... cerebrum, also houses many cranial nerves Midbrain- between diencephalon and pons • Corpora quadrigemina- visual and auditory ...
... cerebrum, also houses many cranial nerves Midbrain- between diencephalon and pons • Corpora quadrigemina- visual and auditory ...
Permeability, Osmosis, and Edema
... Dr. Drummond’s teaching point is that in the periphery, any reduction in colloid has a significant osmotic effect, because only the colloid is impermeant. The other solutes, small molecules such as electrolytes, pass freely through the membranes and therefore do not have an osmotic effect. In the br ...
... Dr. Drummond’s teaching point is that in the periphery, any reduction in colloid has a significant osmotic effect, because only the colloid is impermeant. The other solutes, small molecules such as electrolytes, pass freely through the membranes and therefore do not have an osmotic effect. In the br ...
The Brain - Gordon State College
... The Brain Can Alter Its Neural Connections – Plasticity: the flexibility of the brain to alter its neural connections following injury – Hemispherectomy: a radical surgical procedure in which one of the cerebral hemispheres is removed to control life-threatening epileptic seizures. The remaining he ...
... The Brain Can Alter Its Neural Connections – Plasticity: the flexibility of the brain to alter its neural connections following injury – Hemispherectomy: a radical surgical procedure in which one of the cerebral hemispheres is removed to control life-threatening epileptic seizures. The remaining he ...
AV shunt
... •has two waves for every single carotid artery pulsation; make this comparison by gently palpating the carotid pulse on the opposite side of the neck; •falls with inspiration and rises with expiration (except where there is cardiac tamponade); •can be obliterated by pressing firmly but gently with t ...
... •has two waves for every single carotid artery pulsation; make this comparison by gently palpating the carotid pulse on the opposite side of the neck; •falls with inspiration and rises with expiration (except where there is cardiac tamponade); •can be obliterated by pressing firmly but gently with t ...
Lecture 7 Powerpoint file
... Intracranial and “single” Unit • Single electrodes may pick up action potentials from a single cell • An electrode may pick up the signals from several nearby cells – spike-sorting attempts to isolate individual cells ...
... Intracranial and “single” Unit • Single electrodes may pick up action potentials from a single cell • An electrode may pick up the signals from several nearby cells – spike-sorting attempts to isolate individual cells ...
ANTERIOR LEG MASSAGE 1 Session 11
... (indication of tight hamstrings) ii. Press down on client’s foot when moving into end ROM, and when giving resistance iii. Allow client to relax before repeating movement iv. Breathe v. Complete: when no further ROM is achieved e. Pressure points i. Apply pressure gradually ii. Hold for 6-10 seconds ...
... (indication of tight hamstrings) ii. Press down on client’s foot when moving into end ROM, and when giving resistance iii. Allow client to relax before repeating movement iv. Breathe v. Complete: when no further ROM is achieved e. Pressure points i. Apply pressure gradually ii. Hold for 6-10 seconds ...
Development of the Brain
... those similar to the mechanisms of brain development such as the new branching of axons and dendrites. ...
... those similar to the mechanisms of brain development such as the new branching of axons and dendrites. ...
Lec 8Aviation, High-Altitude by Prof. Saboohi
... • 1-Blood is centrifuged toward the lowermost part of the body. • The centrifugal acceleratory force is +5 G and • the person is in an immobilized standing position, • the pressure in the veins of the feet becomes greatly increased (to about 450 mm Hg) and nearly 300 mm Hg in the sitting position. ...
... • 1-Blood is centrifuged toward the lowermost part of the body. • The centrifugal acceleratory force is +5 G and • the person is in an immobilized standing position, • the pressure in the veins of the feet becomes greatly increased (to about 450 mm Hg) and nearly 300 mm Hg in the sitting position. ...
The Brain and Cranial Nerves The Brain
... into the fourth ventricle (5) The choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle adds more CSF (6) The CSF passes through lateral and medial apertures into the subarachnoid space and central canal of the spinal cord (7) The CSF is reabsorbed into veins through the arachnoid villi ...
... into the fourth ventricle (5) The choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle adds more CSF (6) The CSF passes through lateral and medial apertures into the subarachnoid space and central canal of the spinal cord (7) The CSF is reabsorbed into veins through the arachnoid villi ...
Intracranial pressure

Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure inside the skull and thus in the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF. CSF pressure has been shown to be influenced by abrupt changes in intrathoracic pressure during coughing (intraabdominal pressure), valsalva maneuver, and communication with the vasculature (venous and arterial systems). ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and, at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adult. Changes in ICP are attributed to volume changes in one or more of the constituents contained in the cranium. Intracranial hypertension, commonly abbreviated IH, IICP or raised ICP, is elevation of the pressure in the cranium. ICP is normally 7–15 mm Hg; at 20–25 mm Hg, the upper limit of normal, treatment to reduce ICP may be needed.