2006 natl fx fnd abstract - University of Illinois Archives
... Bill, you’ve got 1 word to spare. I pasted your old version below so if I dropped any important ideas you can try to put them back. Good luck! Also, do you mind if my name goes before Robert’s? ...
... Bill, you’ve got 1 word to spare. I pasted your old version below so if I dropped any important ideas you can try to put them back. Good luck! Also, do you mind if my name goes before Robert’s? ...
SHEEP BRAIN DISSECTION GUIDE
... The Visual System Retinothalamic Projections and Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Light enters the eye through the lens and strikes the retina at the back of the eye. Photoreceptors in the retina transmit light information to other retinal neurons which process the information and send the output to ...
... The Visual System Retinothalamic Projections and Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Light enters the eye through the lens and strikes the retina at the back of the eye. Photoreceptors in the retina transmit light information to other retinal neurons which process the information and send the output to ...
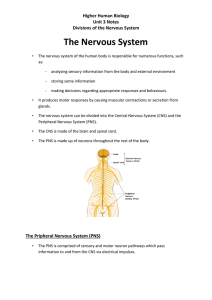
The Nervous System - Cathkin High School
... The sympathetic system is involved in the ‘fight or flight’ response, whilst the parasympathetic system is involved in the ‘rest and digest’ response. ...
... The sympathetic system is involved in the ‘fight or flight’ response, whilst the parasympathetic system is involved in the ‘rest and digest’ response. ...
1 CREATIVE DEMONSTRATIVE EVIDENCE: “ADDING THE MIDAS
... injury. You can effectively use videos and photographs of the patient taken in the hospital to show the plaintiff’s state immediately after the injury and contrast it to the plaintiff’s appearance at trial (which can be markedly better, especially with mild to moderate brain injuries). You may also ...
... injury. You can effectively use videos and photographs of the patient taken in the hospital to show the plaintiff’s state immediately after the injury and contrast it to the plaintiff’s appearance at trial (which can be markedly better, especially with mild to moderate brain injuries). You may also ...
BOX 42.1 HOW DO WE LEARN ABOUT BRAIN EVOLUTION? There
... about the bones of our ancestors, but much less about everything else. Of course one can infer much about some soft tissues, such as muscles, from their effects on bones, and this is true for brains as well. The brains of mammals fill the skull tightly, and thus the skull cavity of fossils (the endo ...
... about the bones of our ancestors, but much less about everything else. Of course one can infer much about some soft tissues, such as muscles, from their effects on bones, and this is true for brains as well. The brains of mammals fill the skull tightly, and thus the skull cavity of fossils (the endo ...
Overview of brain anatomy
... Ventricles and cerebrospinal fluid The brain has hollow fluid-filled cavities called ventricles . Inside the ventricles is a ribbon-like structure called the choroid plexus that makes clear colorless cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF flows within and around the brain and spinal cord to help cushion it ...
... Ventricles and cerebrospinal fluid The brain has hollow fluid-filled cavities called ventricles . Inside the ventricles is a ribbon-like structure called the choroid plexus that makes clear colorless cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF flows within and around the brain and spinal cord to help cushion it ...
Brain Anatomy Overview
... Ventricles and cerebrospinal fluid The brain has hollow fluid-filled cavities called ventricles . Inside the ventricles is a ribbon-like structure called the choroid plexus that makes clear colorless cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF flows within and around the brain and spinal cord to help cushion it ...
... Ventricles and cerebrospinal fluid The brain has hollow fluid-filled cavities called ventricles . Inside the ventricles is a ribbon-like structure called the choroid plexus that makes clear colorless cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF flows within and around the brain and spinal cord to help cushion it ...
Objectives 53 - u.arizona.edu
... to enhance dissolution of clots and restore profusion of the brain; risk includes hemorrhage in brain (after 3 hours, risk is to great to administer thrombolytic agents) - new techniques involve infusing thrombolytic agents at site of clot by catheter through arterial system; future of anti-necrotic ...
... to enhance dissolution of clots and restore profusion of the brain; risk includes hemorrhage in brain (after 3 hours, risk is to great to administer thrombolytic agents) - new techniques involve infusing thrombolytic agents at site of clot by catheter through arterial system; future of anti-necrotic ...
SECTION 3 VASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Ⅰ. Functional properties of
... vasoconstriction of skin, splanchnic and renal vessels, but vasodilation in skeletal ...
... vasoconstriction of skin, splanchnic and renal vessels, but vasodilation in skeletal ...
06 trauma
... stretched out and the brain has additional space for movement, accounting for the higher rate of subdural hematomas in these patients, even after relatively minor head trauma • Infants are also susceptible to subdural hematomas because their bridging veins are thin-walled ...
... stretched out and the brain has additional space for movement, accounting for the higher rate of subdural hematomas in these patients, even after relatively minor head trauma • Infants are also susceptible to subdural hematomas because their bridging veins are thin-walled ...
Traumatic Brain Injury in the War Zone
... typically cause damage to nerve axons in many areas of the brain. Although it is unclear what initiates axonal damage, it begins within minutes after the injury occurs, develops over a period of hours to a few days, and leads to the degeneration of some axons' distal projections and to diffuse loss ...
... typically cause damage to nerve axons in many areas of the brain. Although it is unclear what initiates axonal damage, it begins within minutes after the injury occurs, develops over a period of hours to a few days, and leads to the degeneration of some axons' distal projections and to diffuse loss ...
Introduction to Body Function
... the decreased drop in blood pressure the body uses mechanisms to increase blood pressure. Do these mechanisms use positive or negative feedback processes? Describe how the body responds to correct this situation. Correction of blood pressure in this situation is an example of a negative feedback pro ...
... the decreased drop in blood pressure the body uses mechanisms to increase blood pressure. Do these mechanisms use positive or negative feedback processes? Describe how the body responds to correct this situation. Correction of blood pressure in this situation is an example of a negative feedback pro ...
Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology, 3rd
... Non-threshold substances pass through the glomerular membrane into the filtrate and are not reabsorbed, regardless of their plasma concentration. Creatinine is an example of a non-threshold substance. 8. A. The descending loop of Henle is freely permeable to water and moderately permeable to most ion ...
... Non-threshold substances pass through the glomerular membrane into the filtrate and are not reabsorbed, regardless of their plasma concentration. Creatinine is an example of a non-threshold substance. 8. A. The descending loop of Henle is freely permeable to water and moderately permeable to most ion ...
Neuroanatomy 6-12
... o Myelin Sheath: The yellow part of the neuron picture. Its main purpose is to increase the speed of signals that travel across the axon. The signal is sent from the dendrite through the nucleus, to the axon, and then goes to the axon terminal. • Sheep Brain Dissection o Explain where the forebrain, ...
... o Myelin Sheath: The yellow part of the neuron picture. Its main purpose is to increase the speed of signals that travel across the axon. The signal is sent from the dendrite through the nucleus, to the axon, and then goes to the axon terminal. • Sheep Brain Dissection o Explain where the forebrain, ...
Lecture notes for Chapter 12
... CSF is filtered from plexus at constant rate Ependymal cells use ion pumps to control composition of CSF and help cleanse CSF by removing wastes Cilia of ependymal cells help to keep CSF in motion Normal adult CSF volume of ~150 ml is replaced every 8 hours ...
... CSF is filtered from plexus at constant rate Ependymal cells use ion pumps to control composition of CSF and help cleanse CSF by removing wastes Cilia of ependymal cells help to keep CSF in motion Normal adult CSF volume of ~150 ml is replaced every 8 hours ...
The Bio-Psychology Dictionary - Windsor C
... protects the brain and spinal cord, and is also found throughout the ventricle (brain cavities and tunnels). CSF cushions the brain and spinal cord from jolts. This fluid circulates through the brain and the spinal canal. cerebrum - the largest and most complex portion of the brain. It controls thou ...
... protects the brain and spinal cord, and is also found throughout the ventricle (brain cavities and tunnels). CSF cushions the brain and spinal cord from jolts. This fluid circulates through the brain and the spinal canal. cerebrum - the largest and most complex portion of the brain. It controls thou ...
(Renal haemodynamic and GFR).
... • Factors governing filtration rate at the capillary bed are: – Total surface area available for filtration – Filtration membrane permeability – Net filtration pressure • GFR is directly proportional to the NFP • Changes in GFR normally result from changes in glomerular blood pressure ...
... • Factors governing filtration rate at the capillary bed are: – Total surface area available for filtration – Filtration membrane permeability – Net filtration pressure • GFR is directly proportional to the NFP • Changes in GFR normally result from changes in glomerular blood pressure ...
33 Pleura
... abdominal muscles. Simultaneously the elastic tissue within the lungs recoils increasing the pressure within the lungs forcing air out of the lungs. Control of Respiratory Rate The primary respiratory center for regulating respiration is located in the reticular formation of the medulla (rostral ven ...
... abdominal muscles. Simultaneously the elastic tissue within the lungs recoils increasing the pressure within the lungs forcing air out of the lungs. Control of Respiratory Rate The primary respiratory center for regulating respiration is located in the reticular formation of the medulla (rostral ven ...
Regulation of systemic circulation
... Role of rennin–angiotensin-aldosteron system in regulation of vessel tone Uxta glomerular cells of kidney produce enzyme rennin as the answer of decrease of kidneys perfusion or increase of influences of sympathetic nervous system. It convert angiotensinogen, which produced in liver, in Angiotensin ...
... Role of rennin–angiotensin-aldosteron system in regulation of vessel tone Uxta glomerular cells of kidney produce enzyme rennin as the answer of decrease of kidneys perfusion or increase of influences of sympathetic nervous system. It convert angiotensinogen, which produced in liver, in Angiotensin ...
Ascolot Lesson #5 - 2015 Brain-Machine
... signals from and transmitting them to neurons. Long the McGuffins of science fiction, from The Terminal Man to The Matrix, brain chips are now being used or tested as treatments for epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, paralysis, blindness and other disorders. Decades ago Delgado carried out experiments t ...
... signals from and transmitting them to neurons. Long the McGuffins of science fiction, from The Terminal Man to The Matrix, brain chips are now being used or tested as treatments for epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, paralysis, blindness and other disorders. Decades ago Delgado carried out experiments t ...
SEMINAR ON BLUE BRAIN
... The uploading is possible by the use of small robots known as the nanobots. These robots are small enough to travel through out our circulatory system. Traveling into the spine and brain, they will be able to monitor the activity and structure of our central nervous system. They will be able t ...
... The uploading is possible by the use of small robots known as the nanobots. These robots are small enough to travel through out our circulatory system. Traveling into the spine and brain, they will be able to monitor the activity and structure of our central nervous system. They will be able t ...
Blood Pressure - bloodhounds Incorporated
... B. The amount of blood in the ventricles at the end of diastole would be greater C. The amount of blood in the ventricles at the end of systole would be greater D. The stroke volume would decrease ...
... B. The amount of blood in the ventricles at the end of diastole would be greater C. The amount of blood in the ventricles at the end of systole would be greater D. The stroke volume would decrease ...
Understanding Traumatic Brain Injury
... homonymous hemianopia is the loss of half of the field of view on the same side in both eyes. It occurs frequently in traumatic brain injuries, because of the manner in which the nasal nerve fibers from each eye cross as they pass to the back of the brain. The visual images that we see to the right ...
... homonymous hemianopia is the loss of half of the field of view on the same side in both eyes. It occurs frequently in traumatic brain injuries, because of the manner in which the nasal nerve fibers from each eye cross as they pass to the back of the brain. The visual images that we see to the right ...
A Piece of Your Mind: Brain Anatomy
... divided into two major parts, the thalamus and hypothalamus. The thalamus is associated with transmitting sensory impulses and the hypothalamus is associated with maintaining homeostasis (balance) in the body by controlling temperature, sleep, appetite, and some emotions. (#7 in the diagram) ...
... divided into two major parts, the thalamus and hypothalamus. The thalamus is associated with transmitting sensory impulses and the hypothalamus is associated with maintaining homeostasis (balance) in the body by controlling temperature, sleep, appetite, and some emotions. (#7 in the diagram) ...
Intracranial pressure

Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure inside the skull and thus in the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF. CSF pressure has been shown to be influenced by abrupt changes in intrathoracic pressure during coughing (intraabdominal pressure), valsalva maneuver, and communication with the vasculature (venous and arterial systems). ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and, at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adult. Changes in ICP are attributed to volume changes in one or more of the constituents contained in the cranium. Intracranial hypertension, commonly abbreviated IH, IICP or raised ICP, is elevation of the pressure in the cranium. ICP is normally 7–15 mm Hg; at 20–25 mm Hg, the upper limit of normal, treatment to reduce ICP may be needed.