blue_brain2 - 123seminarsonly.com
... functions of language, learning, memory and complex thought. The simulated neurons will be interconnected with rules the team has worked out about how the brain functions. ...
... functions of language, learning, memory and complex thought. The simulated neurons will be interconnected with rules the team has worked out about how the brain functions. ...
central mechanisms underlying short-term and long
... nerves and circulating hormones as their effector mechanisms. The vascular resistance in any particular region is influenced, to varying degrees depending on the region, by the activity of sympathetic vasomotor nerves, the level of circulating vasoactive hormones, and also by local factors, includin ...
... nerves and circulating hormones as their effector mechanisms. The vascular resistance in any particular region is influenced, to varying degrees depending on the region, by the activity of sympathetic vasomotor nerves, the level of circulating vasoactive hormones, and also by local factors, includin ...
AHF 2203 AVIATION HUMAN FACTORS
... circulation of blood arriving at the cells. • An arm or leg going to sleep because the blood flow has accidentally been shut off is one form of stagnant hypoxia. ...
... circulation of blood arriving at the cells. • An arm or leg going to sleep because the blood flow has accidentally been shut off is one form of stagnant hypoxia. ...
SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE
... Subarachnoid hematomas typically occur as a focal lesion usually in association with acute contusions of the cortex. They can occur at the base of the brain or over the convexity of the cerebral hemispheres. It is felt these lesions arise due to tears in a large vein or in an artery. On a rare occas ...
... Subarachnoid hematomas typically occur as a focal lesion usually in association with acute contusions of the cortex. They can occur at the base of the brain or over the convexity of the cerebral hemispheres. It is felt these lesions arise due to tears in a large vein or in an artery. On a rare occas ...
B. True or False/Edit
... sending nerve impulses to the brainstem region. Respiratory centers located in the medulla oblongata interpret this incoming sensory information and respond most vigorously to a rise in plasma carbon dioxide concentrations or a fall in acid-base or pH levels. Interestingly, your brain is more sensit ...
... sending nerve impulses to the brainstem region. Respiratory centers located in the medulla oblongata interpret this incoming sensory information and respond most vigorously to a rise in plasma carbon dioxide concentrations or a fall in acid-base or pH levels. Interestingly, your brain is more sensit ...
MS Word Version - Interactive Physiology
... Presynaptic inhibition is due to decreased _______ entering the terminal as a result of ____________________________________. ...
... Presynaptic inhibition is due to decreased _______ entering the terminal as a result of ____________________________________. ...
Disorders of Consciousness: Brain Death, Coma
... by hypoxic-ischemic injury (lack of blood flow and oxygen) is worse than that with injury caused by trauma. Common causes of hypoxic-ischemic injury are cardiac arrest and drowning. Patients with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage are very unlikely to recover any awareness after only three months in the ...
... by hypoxic-ischemic injury (lack of blood flow and oxygen) is worse than that with injury caused by trauma. Common causes of hypoxic-ischemic injury are cardiac arrest and drowning. Patients with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage are very unlikely to recover any awareness after only three months in the ...
International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science
... Here, instead of a central nervous system, there are decentralized nerve nets where sensory neurons communicate with motor neurons by electric signals. This communication can be seen as a logic circuit where some action is done if signals from a certain group of input sensory neurons are present. Th ...
... Here, instead of a central nervous system, there are decentralized nerve nets where sensory neurons communicate with motor neurons by electric signals. This communication can be seen as a logic circuit where some action is done if signals from a certain group of input sensory neurons are present. Th ...
No Slide Title
... • The activity of the upper airway muscles (nose, pharynx and larynx) also decreases during sleep. • The negative pressure during inspiration is normally counterbalanced by activity of the upper airway muscles that function to keep the upper airway open. • Inspiration tends to collapse the upper air ...
... • The activity of the upper airway muscles (nose, pharynx and larynx) also decreases during sleep. • The negative pressure during inspiration is normally counterbalanced by activity of the upper airway muscles that function to keep the upper airway open. • Inspiration tends to collapse the upper air ...
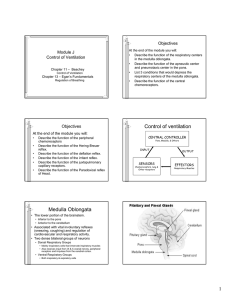
Control of ventilation Medulla Oblongata
... • Located in the medulla of the brain. • Responsive to H+ ions in the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF). • During hypoventilation, CO2 molecules readily diffuse across the blood brain barrier and enter the CSF. The blood brain barrier is impermeable to H+ ions but very permeable to CO2. • In the CSF: CO2 ...
... • Located in the medulla of the brain. • Responsive to H+ ions in the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF). • During hypoventilation, CO2 molecules readily diffuse across the blood brain barrier and enter the CSF. The blood brain barrier is impermeable to H+ ions but very permeable to CO2. • In the CSF: CO2 ...
PowerPoint Presentation - macomb
... • Located in the medulla of the brain. • Responsive to H+ ions in the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF). • During hypoventilation, CO2 molecules readily diffuse across the blood brain barrier and enter the CSF. The blood brain barrier is impermeable to H+ ions but very permeable to CO2. • In the CSF: CO2 ...
... • Located in the medulla of the brain. • Responsive to H+ ions in the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF). • During hypoventilation, CO2 molecules readily diffuse across the blood brain barrier and enter the CSF. The blood brain barrier is impermeable to H+ ions but very permeable to CO2. • In the CSF: CO2 ...
Blood Vessels
... • Measured as systemic arterial BP in large arteries near the heart • The pressure gradient provides the driving force that keeps blood moving from higher to lower pressure areas ...
... • Measured as systemic arterial BP in large arteries near the heart • The pressure gradient provides the driving force that keeps blood moving from higher to lower pressure areas ...
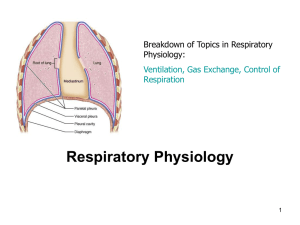
11 Respiratory physiology
... • Air has weight; atmospheric pressure is 760 mmHg at sea level (much less weight and pressure at high altitudes). • Since air will flow from higher pressure to lower pressure areas, to get the air to flow into our lungs, we need to have a lower pressure in our lungs. • We can decrease the pressure ...
... • Air has weight; atmospheric pressure is 760 mmHg at sea level (much less weight and pressure at high altitudes). • Since air will flow from higher pressure to lower pressure areas, to get the air to flow into our lungs, we need to have a lower pressure in our lungs. • We can decrease the pressure ...
Chapter 3 - Martinos Center
... Blood consists of a suspension of erythrocytes, leucocytes and platelets in plasma. Erythrocytes (RBCs) are about 7-9um in diameter. They are anuclear, and contain hemoglobin in solution within the cytosol. Since they contain no mitochondria, they obtain their metabolic energy through glycolysis. Th ...
... Blood consists of a suspension of erythrocytes, leucocytes and platelets in plasma. Erythrocytes (RBCs) are about 7-9um in diameter. They are anuclear, and contain hemoglobin in solution within the cytosol. Since they contain no mitochondria, they obtain their metabolic energy through glycolysis. Th ...
Viscoelastic Properties of the Rat Brain in the Horizontal Plane
... the rat brain in orthogonal planes [17, 18]. Traumatic brain injury events occur at rapid rates so the viscoelasticity of the tissue must be quantitatively described in finite element models of these events to produce accurate predictions of brain deformation and in ...
... the rat brain in orthogonal planes [17, 18]. Traumatic brain injury events occur at rapid rates so the viscoelasticity of the tissue must be quantitatively described in finite element models of these events to produce accurate predictions of brain deformation and in ...
Regulation or respiration2
... nervous signal that is transmitted to the • inspiratory muscles begins weakly & increases steadily in a ramp manner for about 2 seconds in normal respiration. Then it ceases abruptly for approximately the • next 3 seconds, which turns off the excitation of the diaphragm and allows elastic recoil of ...
... nervous signal that is transmitted to the • inspiratory muscles begins weakly & increases steadily in a ramp manner for about 2 seconds in normal respiration. Then it ceases abruptly for approximately the • next 3 seconds, which turns off the excitation of the diaphragm and allows elastic recoil of ...
PDF - 6 pages - Scholastic Heads Up
... waves. Hydrogen atoms in the water of tissues and bones absorb and then release the energy from the radio waves. A computer maps and measures these changes to create an image. Changes in the size of tissues (such as from diseases like cancer that cause tumors) can increase the amount of water in dif ...
... waves. Hydrogen atoms in the water of tissues and bones absorb and then release the energy from the radio waves. A computer maps and measures these changes to create an image. Changes in the size of tissues (such as from diseases like cancer that cause tumors) can increase the amount of water in dif ...
Brain Fun and Exploration for Kids
... Downloadable lesson plans and overheads, students create a giant synapse and act out communication at the neural level by behaving as vesicles, neurotransmitters, receptors, secondary messengers and transporters. http://teach.genetics.utah.edu/content/addiction/pompom.html Students visualize how an ...
... Downloadable lesson plans and overheads, students create a giant synapse and act out communication at the neural level by behaving as vesicles, neurotransmitters, receptors, secondary messengers and transporters. http://teach.genetics.utah.edu/content/addiction/pompom.html Students visualize how an ...
Arousal Systems
... • To produce stupor or coma in humans, • Disorder must damage or depress the function: • Both cerebral hemispheres or • Brainstem arousal system, • Paramedian region of the upper brainstem or • The diencephalon on both sides of the brain. ...
... • To produce stupor or coma in humans, • Disorder must damage or depress the function: • Both cerebral hemispheres or • Brainstem arousal system, • Paramedian region of the upper brainstem or • The diencephalon on both sides of the brain. ...
Physiologic changes of pregnancy lect 2
... Because large amounts of iron may not be available from body stores and may not be in the diet Supplementation is recommended to prevent iron deficiency anemia At term, Hemoglobin less than 10.0 is usually due to iron deficiency anemia rather than the hemodilution of pregnancy ...
... Because large amounts of iron may not be available from body stores and may not be in the diet Supplementation is recommended to prevent iron deficiency anemia At term, Hemoglobin less than 10.0 is usually due to iron deficiency anemia rather than the hemodilution of pregnancy ...
Heart
... Blood flow to the kidney decreases dramatically in response to sympathetic stimulation. If the kidney becomes ischemic, the kidney tubules can be damaged, resulting in acute renal failure and reduced urine production. increased blood urea nitrogen, increased blood levels of K+, and edema are indicat ...
... Blood flow to the kidney decreases dramatically in response to sympathetic stimulation. If the kidney becomes ischemic, the kidney tubules can be damaged, resulting in acute renal failure and reduced urine production. increased blood urea nitrogen, increased blood levels of K+, and edema are indicat ...
colloid osmotic pressures
... • The majority of body cells are not directly contact with the external environment , but these cells must make exchanges with this environment . e.g.O2 pickup and CO2 removal • Blood vessels is passageway of substance transportation and bring about the function of exchanging the substance • All blo ...
... • The majority of body cells are not directly contact with the external environment , but these cells must make exchanges with this environment . e.g.O2 pickup and CO2 removal • Blood vessels is passageway of substance transportation and bring about the function of exchanging the substance • All blo ...
Basic Parts and Organization of the Brain
... OBLONGATA, which contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor (blood vessel constriction) centers. It controls the nerves that effect the heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing. Damage here causes coma. Swelling from an injury causes pressure, which can damage this area, which can ca ...
... OBLONGATA, which contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor (blood vessel constriction) centers. It controls the nerves that effect the heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing. Damage here causes coma. Swelling from an injury causes pressure, which can damage this area, which can ca ...
The Nervous System
... – The actual mass of the human brain is about 1400 grams; however the net weight of the brain suspended in the CSF is equivalent to a mass of 25 grams. The brain therefore exists in neutral buoyancy, which allows the brain to maintain its density without being impaired by its own weight, which would ...
... – The actual mass of the human brain is about 1400 grams; however the net weight of the brain suspended in the CSF is equivalent to a mass of 25 grams. The brain therefore exists in neutral buoyancy, which allows the brain to maintain its density without being impaired by its own weight, which would ...
Intracranial pressure

Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure inside the skull and thus in the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF. CSF pressure has been shown to be influenced by abrupt changes in intrathoracic pressure during coughing (intraabdominal pressure), valsalva maneuver, and communication with the vasculature (venous and arterial systems). ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and, at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adult. Changes in ICP are attributed to volume changes in one or more of the constituents contained in the cranium. Intracranial hypertension, commonly abbreviated IH, IICP or raised ICP, is elevation of the pressure in the cranium. ICP is normally 7–15 mm Hg; at 20–25 mm Hg, the upper limit of normal, treatment to reduce ICP may be needed.