Chapter 4 notes - Sussex Regional High School
... • Teacher‐ summarized results of his experiments and those of others. • Elements are substances that can’t be broken down • In Dalton’s Atomic Theory • Combined idea of elements with that of atoms. 1. All matter is made of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are id ...
... • Teacher‐ summarized results of his experiments and those of others. • Elements are substances that can’t be broken down • In Dalton’s Atomic Theory • Combined idea of elements with that of atoms. 1. All matter is made of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are id ...
Chapter 4 Review ans.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... c. calcium d. cadmium S – 16 P – 15 Ca – 20 Cd - 48 19. Two isotopes of oxygen are oxygen – 16 and oxygen – 18. Write the nuclear symbol for each. ...
... c. calcium d. cadmium S – 16 P – 15 Ca – 20 Cd - 48 19. Two isotopes of oxygen are oxygen – 16 and oxygen – 18. Write the nuclear symbol for each. ...
Mass Defect - Lamont High
... Dealing with numbers such as 9.11 x 10-31 kg is a little cumbersome. For this reason, scientists that work with the nucleus deal in terms of atomic mass units (u). These are defined as exactly 1/12 of the mass of carbon-12 1u = 1.66x10-27 kg= 931.5 MeV/c2 See your data table for mass of the ...
... Dealing with numbers such as 9.11 x 10-31 kg is a little cumbersome. For this reason, scientists that work with the nucleus deal in terms of atomic mass units (u). These are defined as exactly 1/12 of the mass of carbon-12 1u = 1.66x10-27 kg= 931.5 MeV/c2 See your data table for mass of the ...
Chapter 25 Nuclear Chemistry
... All nuclei contain protons and neutrons (exception - hydrogen-1 has no neutrons). Since protons are positively charged, it would be expected that they would repel and separate, but this does not occur. A force holds them together. The nuclear force is an attractive force that acts between all nuclea ...
... All nuclei contain protons and neutrons (exception - hydrogen-1 has no neutrons). Since protons are positively charged, it would be expected that they would repel and separate, but this does not occur. A force holds them together. The nuclear force is an attractive force that acts between all nuclea ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
... contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
4.1 Early Theories of Matter The Philosophers Democritus – Greek
... Refined the idea of the nucleus by working with hydrogen Discovered that each element contains a unique positive charge that occurs in a whole number ratio to that of hydrogen Developed the idea of atomic number in terms of this positive charge The amount of positive charge would later be de ...
... Refined the idea of the nucleus by working with hydrogen Discovered that each element contains a unique positive charge that occurs in a whole number ratio to that of hydrogen Developed the idea of atomic number in terms of this positive charge The amount of positive charge would later be de ...
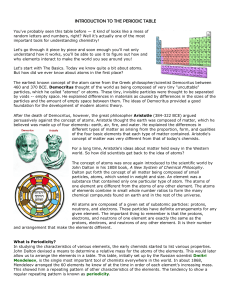
INTRODUCTION TO THE PERIODIC TABLE
... why elements interact to make the world you see around you! Let's start with The Basics. Today we know quite a bit about atoms. But how did we ever know about atoms in the first place? The earliest known concept of the atom came from the Greek philosopher/scientist Democritus between 460 and 370 BCE ...
... why elements interact to make the world you see around you! Let's start with The Basics. Today we know quite a bit about atoms. But how did we ever know about atoms in the first place? The earliest known concept of the atom came from the Greek philosopher/scientist Democritus between 460 and 370 BCE ...
2010 Physical Science Comprehensive Test REVIEW Ch 0.3 Sig
... 38. Be able to identify the atomic number, mass number, and stable isotopes. Your periodic table will not have a key on it. Such as: What is the atomic number of phosphorus? Such as: What is the mass number of K-41? Such as: K-41 is stable, but K-40 is not 42. Many models have been developed to expl ...
... 38. Be able to identify the atomic number, mass number, and stable isotopes. Your periodic table will not have a key on it. Such as: What is the atomic number of phosphorus? Such as: What is the mass number of K-41? Such as: K-41 is stable, but K-40 is not 42. Many models have been developed to expl ...
unit 3 - structure, history of the atom, density
... Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined or rearranged. However, atoms of one element ARE NOT changed into atoms of another element by a chemical reaction. (only by nuclear reactions) About 100 years ago, 2 of the 3 main subatomic particles were discovered. (5) J. J. THOMSON discov ...
... Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined or rearranged. However, atoms of one element ARE NOT changed into atoms of another element by a chemical reaction. (only by nuclear reactions) About 100 years ago, 2 of the 3 main subatomic particles were discovered. (5) J. J. THOMSON discov ...
Unit 3 Study Guide: Atomic Structure and Nuclear
... For each item in Column A, write the letter of the matching item in Column B. Column A ...
... For each item in Column A, write the letter of the matching item in Column B. Column A ...
Chemical Element
... The mass number of an element, A, is the number of nucleons (protons and neutrons) in the atomic nucleus. Different isotopes of a given element are distinguished by their mass numbers, which are conventionally written as a super-index on the left hand side of the atomic symbol (e.g., 238U). The rela ...
... The mass number of an element, A, is the number of nucleons (protons and neutrons) in the atomic nucleus. Different isotopes of a given element are distinguished by their mass numbers, which are conventionally written as a super-index on the left hand side of the atomic symbol (e.g., 238U). The rela ...
Section 12.1 - CPO Science
... 12.1 How atoms of various elements are different Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. The mass number of an isotope tells you the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. How are these carbon isotopes different? ...
... 12.1 How atoms of various elements are different Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. The mass number of an isotope tells you the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. How are these carbon isotopes different? ...
12.1 Structure of the Atom - appleg8
... 12.1 How atoms of various elements are different Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. The mass number of an isotope tells you the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. How are these carbon isotopes different? ...
... 12.1 How atoms of various elements are different Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. The mass number of an isotope tells you the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. How are these carbon isotopes different? ...
1 - College of Arts and Sciences
... What is an ALPHA particle? An Particle is the Helium nucleus ...
... What is an ALPHA particle? An Particle is the Helium nucleus ...
1 - College of Arts and Sciences
... Avogadro’s number is chosen so that 1 mole of 12C atoms has a mass of exactly 12 grams. 6 protons x 1.66 x 10-24 grams = 9.96 x 10-24 6 neutrons x 1.66 x 10-24 grams = 9.96 x 10-24 So 12 C weighs 19.92 x 10 -24 grams ...
... Avogadro’s number is chosen so that 1 mole of 12C atoms has a mass of exactly 12 grams. 6 protons x 1.66 x 10-24 grams = 9.96 x 10-24 6 neutrons x 1.66 x 10-24 grams = 9.96 x 10-24 So 12 C weighs 19.92 x 10 -24 grams ...
Practice exam Part 3 Name 1) A Ca 2+ ion differs from a Ca0 atom in
... 9) How many protons are in the nucleus of an atom of beryllium? a) 2 b) 4 c) 9 ...
... 9) How many protons are in the nucleus of an atom of beryllium? a) 2 b) 4 c) 9 ...
File 15-16unit 6
... Modern Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made up of very tiny particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are chemically alike. 3. Individual atoms of an element may not all have the same mass. However, the atoms of an element have a definite average mass that is characteristic of the element ...
... Modern Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made up of very tiny particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are chemically alike. 3. Individual atoms of an element may not all have the same mass. However, the atoms of an element have a definite average mass that is characteristic of the element ...
ib atomic and nuclear physics definitions and concepts
... NUCLEON NUMBER, A: The number of nucleons in the nucleus. PROTON NUMBER, Z: The number of protons in the nucleus. NEUTRON NUMBER, N: duh! N=A-Z RADIOACTIVE DECAY: A random and spontaneous process in which unstable nuclei emit a particle (disintegrate). The rate decreases exponentially with time. NAT ...
... NUCLEON NUMBER, A: The number of nucleons in the nucleus. PROTON NUMBER, Z: The number of protons in the nucleus. NEUTRON NUMBER, N: duh! N=A-Z RADIOACTIVE DECAY: A random and spontaneous process in which unstable nuclei emit a particle (disintegrate). The rate decreases exponentially with time. NAT ...
Physical Science EOCT Review Domain 1: Chemistry
... have different numbers of neutrons. • Thus, different mass numbers. • These are called isotopes. ...
... have different numbers of neutrons. • Thus, different mass numbers. • These are called isotopes. ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.