PowerPoint Presentation - The Atom: Chp 12 sect 2
... the same, • although the physical properties of some isotopes may be different. • Some isotopes are radioactivemeaning they "radiate" energy as they decay to a more stable form, • perhaps another element half-life: time required for half of the atoms of an element to decay into stable form. ...
... the same, • although the physical properties of some isotopes may be different. • Some isotopes are radioactivemeaning they "radiate" energy as they decay to a more stable form, • perhaps another element half-life: time required for half of the atoms of an element to decay into stable form. ...
Radioactivity Notes Day 1 and 2 Apr 23 and Apr 24
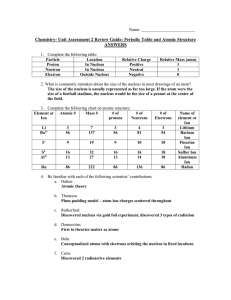
... Isotopes are different atoms of the same element, with the difference between the two atoms being the number of neutrons in the nucleus. o Eg. Carbon-12, Carbon-13, Carbon-14 o By having different numbers of neutrons, isotopes have different mass numbers. Isotopes of an element have the same sym ...
... Isotopes are different atoms of the same element, with the difference between the two atoms being the number of neutrons in the nucleus. o Eg. Carbon-12, Carbon-13, Carbon-14 o By having different numbers of neutrons, isotopes have different mass numbers. Isotopes of an element have the same sym ...
Chapter 4 The structure of the Atom
... Is a method of measuring the mass of an atom relative to the mass of the carbon-12 atom. Since C-12 has exactly six protons and six neutrons. Each of these particles was given an arbitrary value of one. 21. What is the atomic mass? It is the weighted average mass of the isotopes of an element. Secti ...
... Is a method of measuring the mass of an atom relative to the mass of the carbon-12 atom. Since C-12 has exactly six protons and six neutrons. Each of these particles was given an arbitrary value of one. 21. What is the atomic mass? It is the weighted average mass of the isotopes of an element. Secti ...
Nuclear Chemistry powerpoint
... ) and no charge ( ). Thus, it causes change in or numbers. Gamma rays almost accompany alpha and beta radiation. However, since there is effect on mass number or atomic number, they are usually from nuclear equations. ...
... ) and no charge ( ). Thus, it causes change in or numbers. Gamma rays almost accompany alpha and beta radiation. However, since there is effect on mass number or atomic number, they are usually from nuclear equations. ...
Chapter 28 for Chem
... isotopes. Elements with a HIGH atomic number that are unstable usually have too many neutrons. They decay by α decay, primarily until they reach 206Pb, which is a stable isotope of ...
... isotopes. Elements with a HIGH atomic number that are unstable usually have too many neutrons. They decay by α decay, primarily until they reach 206Pb, which is a stable isotope of ...
Atoms - Mrs. Carlyle`s Classroom
... Suppose you have a box containing two sizes of marbles. If 25% of the marbles have masses of 2.00 g each and 75% have masses of 3.00 g each, how is the weighted average calculated? Suppose you have 100 marbles. 25% of 100 = 25 marbles 75% of 100 = 75 marbles 25 marbles x 2.00 g = 50 g 75 marbles x 3 ...
... Suppose you have a box containing two sizes of marbles. If 25% of the marbles have masses of 2.00 g each and 75% have masses of 3.00 g each, how is the weighted average calculated? Suppose you have 100 marbles. 25% of 100 = 25 marbles 75% of 100 = 75 marbles 25 marbles x 2.00 g = 50 g 75 marbles x 3 ...
atomic structure - IGCSE STUDY BANK
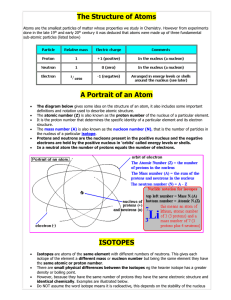
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. This gives each isotope of the element a different mass or nucleon number but being the same element they have the same atomic or proton number. There are small physical differences between the isotopes eg the heavier isotope ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. This gives each isotope of the element a different mass or nucleon number but being the same element they have the same atomic or proton number. There are small physical differences between the isotopes eg the heavier isotope ...
Chapter 3: The Structure of Matter
... compound are usually different from the elements that make it •Example: Liquid water is made up of hydrogen gas and oxygen gas ...
... compound are usually different from the elements that make it •Example: Liquid water is made up of hydrogen gas and oxygen gas ...
File - 7th Grade Science
... Average Atomic Mass • Average atomic mass – the average mass of the element’s isotopes, weighted according to the abundance of each isotope • For example: even though Carbon has mass numbers 12, 13, and 14 there’s more Carbon-12 on Earth, about 99% is Carbon-12 ...
... Average Atomic Mass • Average atomic mass – the average mass of the element’s isotopes, weighted according to the abundance of each isotope • For example: even though Carbon has mass numbers 12, 13, and 14 there’s more Carbon-12 on Earth, about 99% is Carbon-12 ...
Atoms - cloudfront.net
... Dalton’s indivisible atom has not been disregarded—it has been modified to explain new observations. Two important concepts, (1) All matter is composed of atoms and (2) Atoms of any one element differ in properties from atoms of another element, remain unchanged. ...
... Dalton’s indivisible atom has not been disregarded—it has been modified to explain new observations. Two important concepts, (1) All matter is composed of atoms and (2) Atoms of any one element differ in properties from atoms of another element, remain unchanged. ...
SL Topic 2 : Atomic structure
... A. Isotopes have the same molecular formula but a different structural formula. B. Isotopes have the same number of neutrons in atoms of the element C. Isotopes of atoms of the same element have the same electron configuration. D. Isotopes of atoms of the same element have the same mass number. ...
... A. Isotopes have the same molecular formula but a different structural formula. B. Isotopes have the same number of neutrons in atoms of the element C. Isotopes of atoms of the same element have the same electron configuration. D. Isotopes of atoms of the same element have the same mass number. ...
Learning About The Atom and Atomic Structure
... The Nucleus of an atom contains both protons and neutrons. Protons have a positive charge of 1+, while a neutron has no charge, but both have relatively the same mass. An electron, on the other hand, has a charge of 1- , and have a mass much lower than that of a proton or neutron (will give mass ...
... The Nucleus of an atom contains both protons and neutrons. Protons have a positive charge of 1+, while a neutron has no charge, but both have relatively the same mass. An electron, on the other hand, has a charge of 1- , and have a mass much lower than that of a proton or neutron (will give mass ...
Day 23 How Atoms Differ - WaylandHighSchoolChemistry
... Schrödinger and Heisenberg, and many, many more. Used their brains to venture in the realm of inner space and found the world of the atom was a weird and wondrous place. ...
... Schrödinger and Heisenberg, and many, many more. Used their brains to venture in the realm of inner space and found the world of the atom was a weird and wondrous place. ...
Atomic Structure
... from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. ...
... from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. ...
atoms = building blocks
... • Matter- the stuff that makes up everything in the universe • Element- A substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical or physical means ...
... • Matter- the stuff that makes up everything in the universe • Element- A substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical or physical means ...
20161013082744
... • Every atom of a given element DOES NOT have the same number of neutrons. • Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons and different mass numbers • Isotopes of an element have the same atomic number but different mass numbers because they have different number of ...
... • Every atom of a given element DOES NOT have the same number of neutrons. • Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons and different mass numbers • Isotopes of an element have the same atomic number but different mass numbers because they have different number of ...
Protons, electrons and neutrons worksheet
... Atomic symbol is the symbol you find for each element shown in the periodic table. Magnesium symbol is Mg Gold symbol is Au Potassium symbol is K Phosphorous symbol is P Note: First letter of the element is not always the symbol. Atomic number is the number on the top left of atomic symbol in period ...
... Atomic symbol is the symbol you find for each element shown in the periodic table. Magnesium symbol is Mg Gold symbol is Au Potassium symbol is K Phosphorous symbol is P Note: First letter of the element is not always the symbol. Atomic number is the number on the top left of atomic symbol in period ...
Chapter 4 Outline Onlevel 2013
... 2. The half - life, (T1/2 ) of a substance is the time it takes for ½ the nuclei in a radioactive sample to decay. 3. Carbon - 14 has a half life of 5730 years. 146C ==> 147N + 0-1e (Carbon 14 is produced when cosmic rays bombard nitrogen - 14.) Ex. If we had 100 carbon - 14 atoms, after 5730 years ...
... 2. The half - life, (T1/2 ) of a substance is the time it takes for ½ the nuclei in a radioactive sample to decay. 3. Carbon - 14 has a half life of 5730 years. 146C ==> 147N + 0-1e (Carbon 14 is produced when cosmic rays bombard nitrogen - 14.) Ex. If we had 100 carbon - 14 atoms, after 5730 years ...
General CHemistry Unit 2 Homework Notes
... The particles in a liquid stay relatively close together, but they can move around each other. Gas particles are far apart; they move rapidly and collide with each other and with the walls of the container. TOPIC FOUR: THE MOLE & STOICHIMETRY (PAGE 4) The sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom i ...
... The particles in a liquid stay relatively close together, but they can move around each other. Gas particles are far apart; they move rapidly and collide with each other and with the walls of the container. TOPIC FOUR: THE MOLE & STOICHIMETRY (PAGE 4) The sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom i ...
CHEM A Note Guides Unit 2
... •Type of decay caused by neutron to proton ratio --if too many neutrons (to protons), these decay by turning a neutron into a proton beta particle = Beta emission --if not enough neutrons (to protons), these increase stability by turning protons into neutrons --all nuclei that have an atomic number ...
... •Type of decay caused by neutron to proton ratio --if too many neutrons (to protons), these decay by turning a neutron into a proton beta particle = Beta emission --if not enough neutrons (to protons), these increase stability by turning protons into neutrons --all nuclei that have an atomic number ...
Document
... – Alpha particles are represented by the symbols: 2 protons and 2 neutrons make a mass number of 4 it has a charge of 2+ because of the protons Alpha particles are ____________ and penetrate materials much less than the other forms of radiation. A sheet of paper will stop an alpha particle. Th ...
... – Alpha particles are represented by the symbols: 2 protons and 2 neutrons make a mass number of 4 it has a charge of 2+ because of the protons Alpha particles are ____________ and penetrate materials much less than the other forms of radiation. A sheet of paper will stop an alpha particle. Th ...
File
... Isotopes are atoms of an element with identical chemical properties but with different a. numbers of protons. b. masses. c. numbers of electrons. d. atomic numbers. ...
... Isotopes are atoms of an element with identical chemical properties but with different a. numbers of protons. b. masses. c. numbers of electrons. d. atomic numbers. ...
Chem Unit 2 Review Guide ANSWERS
... Atomic mass unit. Equal to the mass of a proton or neutron. 14.) What is a radioactive isotope? An unstable atom which decay (break down) and give off radioactive energy. 15.) What makes an atom unstable? An imbalance in the ratio of protons to neutrons. The farther this ratio gets from 1:1, the mor ...
... Atomic mass unit. Equal to the mass of a proton or neutron. 14.) What is a radioactive isotope? An unstable atom which decay (break down) and give off radioactive energy. 15.) What makes an atom unstable? An imbalance in the ratio of protons to neutrons. The farther this ratio gets from 1:1, the mor ...
Nuclear Fission and Fusion Notes
... *Stars and Sun: Energy is produced when H nuclei combine *We need a large amount of energy to start a fusion reaction so that the H nuclei can be brought together and overcome the electric forces ...
... *Stars and Sun: Energy is produced when H nuclei combine *We need a large amount of energy to start a fusion reaction so that the H nuclei can be brought together and overcome the electric forces ...