doc - EECS: www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu
... Consider a 100-Mbps optical link with a length of 10km. Assume the link transmits packets of 10000 bits. (The speed of light is 2x108 m/sec). From the start of a packet transmission until the last bit of the packet arrives at the receiver, it takes how much time? Latency = TransmitTime + Propagation ...
... Consider a 100-Mbps optical link with a length of 10km. Assume the link transmits packets of 10000 bits. (The speed of light is 2x108 m/sec). From the start of a packet transmission until the last bit of the packet arrives at the receiver, it takes how much time? Latency = TransmitTime + Propagation ...
Ethernet - Inst.eecs.berkeley.edu
... • Multiple Access: multiple computers use the same shared media. Each uses same access algorithm. • Collision Detection: Listen to medium – detect if another station’s signal interferes – back off and try again later. ...
... • Multiple Access: multiple computers use the same shared media. Each uses same access algorithm. • Collision Detection: Listen to medium – detect if another station’s signal interferes – back off and try again later. ...
01_02_03_05b-TransmissionOfInformation
... and other electronic audio devices. The audio data in a standard AIFF file is uncompressed pulse-code modulation (PCM). There is also a compressed variant of AIFF known as AIFF-C or AIFC, with various defined compression codecs. Like any non-compressed, lossless format, it uses much more disk space ...
... and other electronic audio devices. The audio data in a standard AIFF file is uncompressed pulse-code modulation (PCM). There is also a compressed variant of AIFF known as AIFF-C or AIFC, with various defined compression codecs. Like any non-compressed, lossless format, it uses much more disk space ...
Working Paper on Digitizing Audio for the Nation
... It is not obvious that an exact reconstruction of an analog signal should be possible, since a complete continuous signal is replaced by a finite number of samples taken at equal time intervals. The problem is to have complete information between the samples. The answer lies in the mathematical resu ...
... It is not obvious that an exact reconstruction of an analog signal should be possible, since a complete continuous signal is replaced by a finite number of samples taken at equal time intervals. The problem is to have complete information between the samples. The answer lies in the mathematical resu ...
PJ2325572560
... normally be done by dedicated hardware, on or off chip, (e.g. SJA1000) but an overview of these functions will be useful in order to design, setup and control a CAN system. B. Signal Characteristics CAN may be implemented over a number of physical media so long as the drivers are open-collector and ...
... normally be done by dedicated hardware, on or off chip, (e.g. SJA1000) but an overview of these functions will be useful in order to design, setup and control a CAN system. B. Signal Characteristics CAN may be implemented over a number of physical media so long as the drivers are open-collector and ...
A Study of Live Video Streaming over Highway Vehicular Ad hoc
... connected to the Internet and provide necessary services to vehicles. • Two network metrics, packet delay and packet loss, greatly affect the quality of the video in the receiver end. ...
... connected to the Internet and provide necessary services to vehicles. • Two network metrics, packet delay and packet loss, greatly affect the quality of the video in the receiver end. ...
Network Data - Andrew.cmu.edu
... Simplex defines one way communication from sender to receiver Half Duplex defines bi-directional communication with information traveling in only one way at a time Full Duplex permits bi-directional communication simultaneously ...
... Simplex defines one way communication from sender to receiver Half Duplex defines bi-directional communication with information traveling in only one way at a time Full Duplex permits bi-directional communication simultaneously ...
Packet Switching
... – Is not equal to the sum of speeds of input/output links – Depends also on packet size (some operations have to be executed for all packets independently of their size): packet per second metric => Throughput is a function of traffic ...
... – Is not equal to the sum of speeds of input/output links – Depends also on packet size (some operations have to be executed for all packets independently of their size): packet per second metric => Throughput is a function of traffic ...
LDA -8(16,24,32)/60
... LDA can receive data from various sources in simple ASCII format using one of three available serial interfaces. Displayed messages can be formatted or scrolled if needed. LDA ASCII protocol is very flexible and can be configured to almost all serial communication applications. ...
... LDA can receive data from various sources in simple ASCII format using one of three available serial interfaces. Displayed messages can be formatted or scrolled if needed. LDA ASCII protocol is very flexible and can be configured to almost all serial communication applications. ...
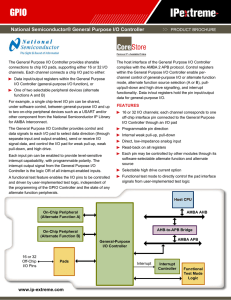
General-Purpose I/O Controller Brochure
... connections to chip I/O pads, supporting either 16 or 32 I/O channels. Each channel connects a chip I/O pad to either: Data input/output registers within the General Purpose I/O Controller (general-purpose I/O function), or One of two selectable peripheral devices (alternate functions A and B) For e ...
... connections to chip I/O pads, supporting either 16 or 32 I/O channels. Each channel connects a chip I/O pad to either: Data input/output registers within the General Purpose I/O Controller (general-purpose I/O function), or One of two selectable peripheral devices (alternate functions A and B) For e ...
Introduction
... • Each sending device modulate different CF, which in turn combined into a composite signal for transmission • CF separated by sufficient BW to accommodate modulated signal •Channels are separated by strips of unused BW called GUARDBAND that prevent signals from overlapping •To use FDM for digital s ...
... • Each sending device modulate different CF, which in turn combined into a composite signal for transmission • CF separated by sufficient BW to accommodate modulated signal •Channels are separated by strips of unused BW called GUARDBAND that prevent signals from overlapping •To use FDM for digital s ...
Serial digital interface
.jpg?width=300)
Serial digital interface (SDI) is a family of digital video interfaces first standardized by SMPTE (The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers) in 1989. For example, ITU-R BT.656 and SMPTE 259M define digital video interfaces used for broadcast-grade video. A related standard, known as high-definition serial digital interface (HD-SDI), is standardized in SMPTE 292M; this provides a nominal data rate of 1.485 Gbit/s.Additional SDI standards have been introduced to support increasing video resolutions (HD, UHD and beyond), frame rates, stereoscopic (3D) video, and color depth. Dual link HD-SDI consists of a pair of SMPTE 292M links, standardized by SMPTE 372M in 1998; this provides a nominal 2.970 Gbit/s interface used in applications (such as digital cinema or HDTV 1080P) that require greater fidelity and resolution than standard HDTV can provide. 3G-SDI (standardized in SMPTE 424M) consists of a single 2.970 Gbit/s serial link that allows replacing dual link HD-SDI. As of August 2014, 6G-SDI and 12G-SDI products are already in the market, although their corresponding standards are still in proposal phase.These standards are used for transmission of uncompressed, unencrypted digital video signals (optionally including embedded audio and time code) within television facilities; they can also be used for packetized data. Coaxial variants of the specification range in length but are typically less than 300 meters. Fiber optic variants of the specification such as 297M allow for long-distance transmission limited only by maximum fiber length or repeaters. SDI and HD-SDI are usually available only in professional video equipment because various licensing agreements restrict the use of unencrypted digital interfaces, such as SDI, prohibiting their use in consumer equipment. Several professional video and HD-video capable DSLR cameras and all uncompressed video capable consumer cameras use the HDMI interface, often called Clean HDMI. There are various mod kits for existing DVD players and other devices, which allow a user to add a serial digital interface to these devices.