Signal Encoding Techniques - Ohio State Computer Science and
... than twice the highest signal frequency, the samples contain all the information of the original signal • Those are analog samples (Pulse Amplitude Modulation, PAM) • Each sample is then assigned digital value by rounding or truncation – Quantizing error or noise introduced • Approximations mean it ...
... than twice the highest signal frequency, the samples contain all the information of the original signal • Those are analog samples (Pulse Amplitude Modulation, PAM) • Each sample is then assigned digital value by rounding or truncation – Quantizing error or noise introduced • Approximations mean it ...
SHAPES: a tiled scalable software hardware architecture platform
... •one interface for the DXM (Distributed External Memory) owned by each tile. ...
... •one interface for the DXM (Distributed External Memory) owned by each tile. ...
Circuit Switching
... single link shared by many packets over time packets queued and transmitted as fast as possible stations connects to local node at own speed nodes buffer data if required to equalize rates ...
... single link shared by many packets over time packets queued and transmitted as fast as possible stations connects to local node at own speed nodes buffer data if required to equalize rates ...
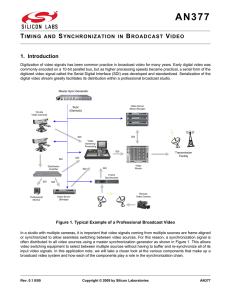
Timing and Synchronization in Broadcast Video
... The sample rate needed to capture video depends on its resolution. Table 1 lists the various sampling rates for common video formats. Note that the color difference (PbPr) signals are sampled at half the rate of the luma (Y) signal since human vision is more sensitive to changes in light intensity t ...
... The sample rate needed to capture video depends on its resolution. Table 1 lists the various sampling rates for common video formats. Note that the color difference (PbPr) signals are sampled at half the rate of the luma (Y) signal since human vision is more sensitive to changes in light intensity t ...
R&D at LPHE/EPFL: SiPM and electronics
... with the necessary data bandwidth, for example 300 Gbit/s input and 40 Gbit/s output bandwidth is required (TELL1 x 10 in bandwidth). Make use of the future Gigabit Bidirectional Trigger and Data link (GBT) developed by Cern as interconnect between the FE and the DAQ. Minimize power consumption as i ...
... with the necessary data bandwidth, for example 300 Gbit/s input and 40 Gbit/s output bandwidth is required (TELL1 x 10 in bandwidth). Make use of the future Gigabit Bidirectional Trigger and Data link (GBT) developed by Cern as interconnect between the FE and the DAQ. Minimize power consumption as i ...
Physical Layer
... • Nonreturn to zero inverted on ones • Constant voltage pulse for duration of bit • Data encoded as presence or absence of signal transition at beginning of bit time • 1: Transition (low to high or high to low) ...
... • Nonreturn to zero inverted on ones • Constant voltage pulse for duration of bit • Data encoded as presence or absence of signal transition at beginning of bit time • 1: Transition (low to high or high to low) ...
Chapter6 - UTK-EECS
... • Nonreturn to zero inverted on ones • Constant voltage pulse for duration of bit • Data encoded as presence or absence of signal transition at beginning of bit time • 1: Transition (low to high or high to low) ...
... • Nonreturn to zero inverted on ones • Constant voltage pulse for duration of bit • Data encoded as presence or absence of signal transition at beginning of bit time • 1: Transition (low to high or high to low) ...
EEL 5718 Computer Communications
... • Nonreturn to zero inverted on ones • Constant voltage pulse for duration of bit • Data encoded as presence or absence of signal transition at beginning of bit time • 1: Transition (low to high or high to low) ...
... • Nonreturn to zero inverted on ones • Constant voltage pulse for duration of bit • Data encoded as presence or absence of signal transition at beginning of bit time • 1: Transition (low to high or high to low) ...
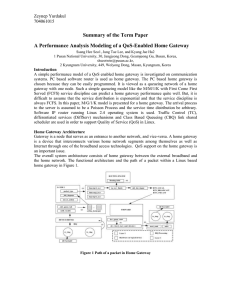
A performance analysis modeling of a QoS
... home gateway is composed of two main parts. The first part consists of processors on network interface cards that have functions to receive and transmit packets. The second part is the CPU of the PC machine that forwards packets not destined for itself, and process packets destined for itself. The b ...
... home gateway is composed of two main parts. The first part consists of processors on network interface cards that have functions to receive and transmit packets. The second part is the CPU of the PC machine that forwards packets not destined for itself, and process packets destined for itself. The b ...
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE)
... data transferred. This is because the technology is packet- based. For example, there are service plans where there is a flat rate for the first Gigabyte of data transferred, and a per minute cost for each additional Megabyte. The first thing you require is a device (e.g. a mobile phone) that is 3G ...
... data transferred. This is because the technology is packet- based. For example, there are service plans where there is a flat rate for the first Gigabyte of data transferred, and a per minute cost for each additional Megabyte. The first thing you require is a device (e.g. a mobile phone) that is 3G ...
lecture3 - Andrew.cmu.edu
... Simplex, half duplex, full duplex Characteristics - Bit Error Rate - Data Rate (what is the difference between data rate & bandwidth?) - Degradation with distance ...
... Simplex, half duplex, full duplex Characteristics - Bit Error Rate - Data Rate (what is the difference between data rate & bandwidth?) - Degradation with distance ...
Document
... spectrum into multiple channels, each channel dedicated to a particular use – TDM: Time Division Multiplexing: using the entire frequency bandwidth allotted but uses “logical slots” to transmit different channels at specific points of relative time within a logical frame that is transmitted. ...
... spectrum into multiple channels, each channel dedicated to a particular use – TDM: Time Division Multiplexing: using the entire frequency bandwidth allotted but uses “logical slots” to transmit different channels at specific points of relative time within a logical frame that is transmitted. ...
Broadcast-and-select networks
... • Nodes can be equipped with one or more tx and rx devices, which may be tunable or fixed • Tunable txs and rxs are more expensive (and tunable usually cost more than tunable txs) • For example: 2 fixed tx/rx per node allow to build a shuffle topology ...
... • Nodes can be equipped with one or more tx and rx devices, which may be tunable or fixed • Tunable txs and rxs are more expensive (and tunable usually cost more than tunable txs) • For example: 2 fixed tx/rx per node allow to build a shuffle topology ...
COBAS AmpliPrep / COBAS Taqman System
... 65" x 29" x 37" (W x D x H) 683 lbs. Line voltage: 100 – 125 & 200 – 240 VAC (+10, -15%) Frequency: 50 – 60 Hz 1,000 VA (instrument) 200 VA (data station) Solution-phase magnetic bead separation Requires test-specific, bar-coded, ready-to-use COBAS AmpliPrep Kits Up to 144 specimens per day, based o ...
... 65" x 29" x 37" (W x D x H) 683 lbs. Line voltage: 100 – 125 & 200 – 240 VAC (+10, -15%) Frequency: 50 – 60 Hz 1,000 VA (instrument) 200 VA (data station) Solution-phase magnetic bead separation Requires test-specific, bar-coded, ready-to-use COBAS AmpliPrep Kits Up to 144 specimens per day, based o ...
Serial digital interface
.jpg?width=300)
Serial digital interface (SDI) is a family of digital video interfaces first standardized by SMPTE (The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers) in 1989. For example, ITU-R BT.656 and SMPTE 259M define digital video interfaces used for broadcast-grade video. A related standard, known as high-definition serial digital interface (HD-SDI), is standardized in SMPTE 292M; this provides a nominal data rate of 1.485 Gbit/s.Additional SDI standards have been introduced to support increasing video resolutions (HD, UHD and beyond), frame rates, stereoscopic (3D) video, and color depth. Dual link HD-SDI consists of a pair of SMPTE 292M links, standardized by SMPTE 372M in 1998; this provides a nominal 2.970 Gbit/s interface used in applications (such as digital cinema or HDTV 1080P) that require greater fidelity and resolution than standard HDTV can provide. 3G-SDI (standardized in SMPTE 424M) consists of a single 2.970 Gbit/s serial link that allows replacing dual link HD-SDI. As of August 2014, 6G-SDI and 12G-SDI products are already in the market, although their corresponding standards are still in proposal phase.These standards are used for transmission of uncompressed, unencrypted digital video signals (optionally including embedded audio and time code) within television facilities; they can also be used for packetized data. Coaxial variants of the specification range in length but are typically less than 300 meters. Fiber optic variants of the specification such as 297M allow for long-distance transmission limited only by maximum fiber length or repeaters. SDI and HD-SDI are usually available only in professional video equipment because various licensing agreements restrict the use of unencrypted digital interfaces, such as SDI, prohibiting their use in consumer equipment. Several professional video and HD-video capable DSLR cameras and all uncompressed video capable consumer cameras use the HDMI interface, often called Clean HDMI. There are various mod kits for existing DVD players and other devices, which allow a user to add a serial digital interface to these devices.