information
... Availability: ensure survivability of the network despite denial of service attacks. The DoS can be targeted at any layer Confidentiality: ensures that certain information is not disclosed to unauthorized entities. Eg Routing information information should not be leaked out because it can help to id ...
... Availability: ensure survivability of the network despite denial of service attacks. The DoS can be targeted at any layer Confidentiality: ensures that certain information is not disclosed to unauthorized entities. Eg Routing information information should not be leaked out because it can help to id ...
Advanced Routing - Fortinet Document Library
... Dynamic Routing Overview provides an overview of dynamic routing, compares static and dynamic routing, and helps you decide which dynamic routing protocol is best for you. Routing Information Protocol (RIP) describes a distance-vector routing protocol intended for small, relatively homogeneous netwo ...
... Dynamic Routing Overview provides an overview of dynamic routing, compares static and dynamic routing, and helps you decide which dynamic routing protocol is best for you. Routing Information Protocol (RIP) describes a distance-vector routing protocol intended for small, relatively homogeneous netwo ...
4) Distributed Cache Management
... Only flooding or OSPF-like shortest path mechanisms have been proposed. Recently hash-routing (similar to datacenters) has been proposed to maximize cache hit within a domain regardless of the traffic. ...
... Only flooding or OSPF-like shortest path mechanisms have been proposed. Recently hash-routing (similar to datacenters) has been proposed to maximize cache hit within a domain regardless of the traffic. ...
Tricha Anjali of - BWN-Lab
... Available Bandwidth Measurement - “ABEst: An Available Bandwidth Estimator within an Autonomous System,” Proceedings of ...
... Available Bandwidth Measurement - “ABEst: An Available Bandwidth Estimator within an Autonomous System,” Proceedings of ...
module10b
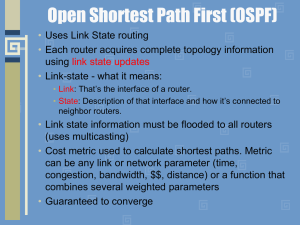
... Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) • Uses Link State routing • Each router acquires complete topology information using link state updates • Link-state - what it means: • Link: That’s the interface of a router. • State: Description of that interface and how it’s connected to neighbor routers. ...
... Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) • Uses Link State routing • Each router acquires complete topology information using link state updates • Link-state - what it means: • Link: That’s the interface of a router. • State: Description of that interface and how it’s connected to neighbor routers. ...
PDF
... address space presumed to be under uniform administrative control. A BGP speaker is any router that implements BGP. BGP speakers are usually routers at the edges of autonomous systems. A large autonomous system may have many BGP speakers that coordinate to present a consistent view. BGP speakers mai ...
... address space presumed to be under uniform administrative control. A BGP speaker is any router that implements BGP. BGP speakers are usually routers at the edges of autonomous systems. A large autonomous system may have many BGP speakers that coordinate to present a consistent view. BGP speakers mai ...
Design and Implementation of a Routing Control Platform Matthew Caesar Donald Caldwell
... Observation 1 The IGP Viewer has the complete IGP topology for all partitions that it connects to. The IGP Viewer computes pairwise shortest paths for all routers in the AS and provides this information to the RCS. The IGP Viewer must discover only the path costs between any two routers in the AS, b ...
... Observation 1 The IGP Viewer has the complete IGP topology for all partitions that it connects to. The IGP Viewer computes pairwise shortest paths for all routers in the AS and provides this information to the RCS. The IGP Viewer must discover only the path costs between any two routers in the AS, b ...
2. HBR Overview - Computer Science, Columbia University
... MIP is designed to work with IPv4. MIPv6 is the corresponding framework for IPv6. Since address autoconfiguration is a standard part of IPv6, the MH will always be able to obtain a COA routable to the foreign network. Furthermore, there are more than enough address in the IPv6 space that the network ...
... MIP is designed to work with IPv4. MIPv6 is the corresponding framework for IPv6. Since address autoconfiguration is a standard part of IPv6, the MH will always be able to obtain a COA routable to the foreign network. Furthermore, there are more than enough address in the IPv6 space that the network ...
Design and Implementation of a Routing Control Platform Matthew Caesar Donald Caldwell
... Observation 1 The IGP Viewer has the complete IGP topology for all partitions that it connects to. The IGP Viewer computes pairwise shortest paths for all routers in the AS and provides this information to the RCS. The IGP Viewer must discover only the path costs between any two routers in the AS, b ...
... Observation 1 The IGP Viewer has the complete IGP topology for all partitions that it connects to. The IGP Viewer computes pairwise shortest paths for all routers in the AS and provides this information to the RCS. The IGP Viewer must discover only the path costs between any two routers in the AS, b ...
Chapter 7 Lecture Presentation
... Routing: mechanisms for determining the set of best paths for routing packets requires the collaboration of network elements Forwarding: transfer of packets from NE inputs to outputs Priority & Scheduling: determining order of packet transmission in each NE ...
... Routing: mechanisms for determining the set of best paths for routing packets requires the collaboration of network elements Forwarding: transfer of packets from NE inputs to outputs Priority & Scheduling: determining order of packet transmission in each NE ...
FLIP: an Internetwork Protocol for Supporting Distributed Systems,
... Distributed systems place different requirements on the operating system than do traditional network systems. Network systems run all of a user’s applications on a single workstation. Workstations run a copy of the complete operating system; the only thing that is shared is the file system. Applicat ...
... Distributed systems place different requirements on the operating system than do traditional network systems. Network systems run all of a user’s applications on a single workstation. Workstations run a copy of the complete operating system; the only thing that is shared is the file system. Applicat ...
Routing Information Protocol
... - Routing Information Protocol RIP (Routing Information Protocol) RIP is a standardized Distance Vector protocol, designed for use on smaller networks. RIP was one of the first true Distance Vector routing protocols, and is supported on a wide variety of systems. RIP adheres to the following Distanc ...
... - Routing Information Protocol RIP (Routing Information Protocol) RIP is a standardized Distance Vector protocol, designed for use on smaller networks. RIP was one of the first true Distance Vector routing protocols, and is supported on a wide variety of systems. RIP adheres to the following Distanc ...
layered approach for runtime fault recovery in noc-based
... approach to a fault-tolerant MPSoC, where each layer is responsible for solving one part of the problem. The approach is built on top of a novel small specialized network used to search fault-free paths. The first layer, named physical layer, is responsible for the fault detection and fault isolatio ...
... approach to a fault-tolerant MPSoC, where each layer is responsible for solving one part of the problem. The approach is built on top of a novel small specialized network used to search fault-free paths. The first layer, named physical layer, is responsible for the fault detection and fault isolatio ...
S D x oftware
... Supports Remote Control • ASes can control exchange traffic remotely • Opportunity to process packets and control routing decisions remotely • Example – Prevent selection of paths via problematic ASes – DDoS Squelching ...
... Supports Remote Control • ASes can control exchange traffic remotely • Opportunity to process packets and control routing decisions remotely • Example – Prevent selection of paths via problematic ASes – DDoS Squelching ...
User-level Internet Path Diagnosis
... compared it with a promising alternative approach: network tomography that infers the location of faults by comparing observations on overlapping paths taken from multiple vantage points. While to our knowledge there are no widely available tomography tools that can diagnose arbitrary paths, the app ...
... compared it with a promising alternative approach: network tomography that infers the location of faults by comparing observations on overlapping paths taken from multiple vantage points. While to our knowledge there are no widely available tomography tools that can diagnose arbitrary paths, the app ...
show ip route
... • The routing table process compares the left-most bits in the packet’s destination IP address with the left-most bits in the route in the routing table, looking for a longest-bit-match. • The subnet mask of the route in the routing table specifies the minimum number of left-most bits that must matc ...
... • The routing table process compares the left-most bits in the packet’s destination IP address with the left-most bits in the route in the routing table, looking for a longest-bit-match. • The subnet mask of the route in the routing table specifies the minimum number of left-most bits that must matc ...
ppt
... MIRO is backward compatible with BGP MIRO can provide the flexibility to negotiate alternate routes as needed MIRO can provide transit AS more control over traffic across their network MIRO is comparable to Source Routing at avoiding an intermediate AS Most alternate route possibilities are provided ...
... MIRO is backward compatible with BGP MIRO can provide the flexibility to negotiate alternate routes as needed MIRO can provide transit AS more control over traffic across their network MIRO is comparable to Source Routing at avoiding an intermediate AS Most alternate route possibilities are provided ...
Reputation based Trust in Service-Oriented Network Environments by
... (user application) layer, that is, the application layer. On the lower levels (and more specifically on the network routing level) there is a shortage of protection mechanisms. Most protection mechanisms on the network routing level are based on encryption [20, 51, 86]. Thus, routing devices are vul ...
... (user application) layer, that is, the application layer. On the lower levels (and more specifically on the network routing level) there is a shortage of protection mechanisms. Most protection mechanisms on the network routing level are based on encryption [20, 51, 86]. Thus, routing devices are vul ...
cis185-ROUTE-lecture6-BGP-Part1
... Suppose, for example, that through some misconfiguration you advertise 207.46.0.0/16 to your ISP. On the receiving side, the ISP does not filter out this incorrect route, allowing it to be advertised to the rest of the Internet. This particular CIDR block belongs to Microsoft, and you have jus ...
... Suppose, for example, that through some misconfiguration you advertise 207.46.0.0/16 to your ISP. On the receiving side, the ISP does not filter out this incorrect route, allowing it to be advertised to the rest of the Internet. This particular CIDR block belongs to Microsoft, and you have jus ...
Chapter 4
... – Instead, match the address’ prefix with forwarding table entries – Use the longest prefix matching rule • Match the longest prefix possible in the forwarding table • For this to be practical, large ranges of addresses should go to each link, or the table will be huge! INFO 330 Chapter 4 ...
... – Instead, match the address’ prefix with forwarding table entries – Use the longest prefix matching rule • Match the longest prefix possible in the forwarding table • For this to be practical, large ranges of addresses should go to each link, or the table will be huge! INFO 330 Chapter 4 ...