TCP for Mobile and Wireless Hosts
... RREP may need a route discovery for S from node D Unless node D already knows a route to node S If a route discovery is initiated by D for a route to S, then the Route Reply is piggybacked on the Route Request from D. ...
... RREP may need a route discovery for S from node D Unless node D already knows a route to node S If a route discovery is initiated by D for a route to S, then the Route Reply is piggybacked on the Route Request from D. ...
3rd Edition: Chapter 4 - Web Services Overview
... (computers) service can adapt, perform “dumb” end systems control, error recovery telephones simple inside network, complexity inside complexity at “edge” network many link types different characteristics uniform service difficult Network Layer 4-13 ...
... (computers) service can adapt, perform “dumb” end systems control, error recovery telephones simple inside network, complexity inside complexity at “edge” network many link types different characteristics uniform service difficult Network Layer 4-13 ...
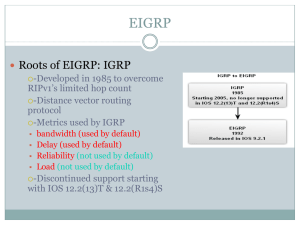
EIGRP
... • The IP-EIGRP module is responsible for sending and receiving EIGRP packets that are encapsulated in IP and for using DUAL to build and maintain the IP routing table. • The IPX EIGRP module is responsible for exchanging routing information about IPX networks with other IPX EIGRP routers. • Apple-Ta ...
... • The IP-EIGRP module is responsible for sending and receiving EIGRP packets that are encapsulated in IP and for using DUAL to build and maintain the IP routing table. • The IPX EIGRP module is responsible for exchanging routing information about IPX networks with other IPX EIGRP routers. • Apple-Ta ...
Collection Tree Protocol
... hysteresis has the danger of allowing CTP Noe to use suboptimal routes, it can be shown that noise in link estimates causes better routes to dominate a node’s next hop selection. ...
... hysteresis has the danger of allowing CTP Noe to use suboptimal routes, it can be shown that noise in link estimates causes better routes to dominate a node’s next hop selection. ...
Chapter 1
... • Remote networks are added to the routing table using two methods: • Dynamic Routing Protocols: • Routes to remote networks that were learned automatically by the router. • Static Routes: • Routes manually configured. • Either or both methods can be used in the same router. CCNA2-61 ...
... • Remote networks are added to the routing table using two methods: • Dynamic Routing Protocols: • Routes to remote networks that were learned automatically by the router. • Static Routes: • Routes manually configured. • Either or both methods can be used in the same router. CCNA2-61 ...
Computer Networks
... their BGP routers, only when routes change BGP routing information – a sequence of AS’s indicating the path traversed by a route; next hop General operations of a BGP router: Learns multiple paths Picks best path according to its AS policies Install best pick in IP forwarding tables Univ. of Teh ...
... their BGP routers, only when routes change BGP routing information – a sequence of AS’s indicating the path traversed by a route; next hop General operations of a BGP router: Learns multiple paths Picks best path according to its AS policies Install best pick in IP forwarding tables Univ. of Teh ...
eigrp
... the following major categories: –Compatibility mode – IGRP and EIGRP are compatible with each other. –Metric calculation – EIGRP scales the metric of IGRP by a factor of 256. That is because EIGRP uses a metric that is 32 bits long, and IGRP uses a 24-bit metric. –Hop count – IGRP has a maximum hop ...
... the following major categories: –Compatibility mode – IGRP and EIGRP are compatible with each other. –Metric calculation – EIGRP scales the metric of IGRP by a factor of 256. That is because EIGRP uses a metric that is 32 bits long, and IGRP uses a 24-bit metric. –Hop count – IGRP has a maximum hop ...
Accurate Real-time Identification of IP Prefix
... validate received routing information by querying the IRV server in the relevant AS. However, it does not prevent an AS from originating a prefix it does not own. The Listen and Whisper scheme [46] also helps identify inconsistent routing advertisement, but does not deterministically detect IP hija ...
... validate received routing information by querying the IRV server in the relevant AS. However, it does not prevent an AS from originating a prefix it does not own. The Listen and Whisper scheme [46] also helps identify inconsistent routing advertisement, but does not deterministically detect IP hija ...
MPLS QoS - Lyle School of Engineering
... Forwarding Equivalence Class (FEC) • Introduced to denote packet forwarding classes • Comprises traffic – To a particular destination – To destination with distinct service ...
... Forwarding Equivalence Class (FEC) • Introduced to denote packet forwarding classes • Comprises traffic – To a particular destination – To destination with distinct service ...
to the paper
... to be entry guards, which are used as an entrance router. We use the terms entrance guard and entrance router synonymously throughout this paper. Router information is distributed by a set of well-known and trusted directory servers. Finally, the unit of transmission through the Tor network is calle ...
... to be entry guards, which are used as an entrance router. We use the terms entrance guard and entrance router synonymously throughout this paper. Router information is distributed by a set of well-known and trusted directory servers. Finally, the unit of transmission through the Tor network is calle ...
Resilient Overlay Networks Abstract MIT Laboratory for Computer Science
... in the conference, and using loss rates, delay jitter, or applicationobserved throughput as metrics on which to choose paths. An administrator may wish to use a RON-based router application to form an overlay network between multiple LANs as an “Overlay VPN.” This idea can be extended further to dev ...
... in the conference, and using loss rates, delay jitter, or applicationobserved throughput as metrics on which to choose paths. An administrator may wish to use a RON-based router application to form an overlay network between multiple LANs as an “Overlay VPN.” This idea can be extended further to dev ...
OSPFN - Named Data Networking (NDN)
... OSPF [4] is a link state routing protocol that works within an autonomous system (AS). Each router in the system gathers link state information about the network to build a Link State Database (LSDB). This LSDB is updated through the flooding of Link State Advertisements (LSA). All the routers in th ...
... OSPF [4] is a link state routing protocol that works within an autonomous system (AS). Each router in the system gathers link state information about the network to build a Link State Database (LSDB). This LSDB is updated through the flooding of Link State Advertisements (LSA). All the routers in th ...
NetVanta 6330 Series - Walker and Associates
... to the feature server is lost, calls may continue between IP and analog phones onsite, or outbound from an FXO POTS line to the PSTN. Standards-based Routing Protocols Complementing the versatile hardware, the AOS allows for the support of standards-based switching, Virtual LAN (VLAN) tagging, stati ...
... to the feature server is lost, calls may continue between IP and analog phones onsite, or outbound from an FXO POTS line to the PSTN. Standards-based Routing Protocols Complementing the versatile hardware, the AOS allows for the support of standards-based switching, Virtual LAN (VLAN) tagging, stati ...
5 – Network Layer
... Flooding A simple method to send a packet to all network nodes Each node floods a new packet received on an incoming link by sending it out all of the other links Nodes need to keep track of flooded packets to stop the flood; even using a hop limit can blow up exponentially ...
... Flooding A simple method to send a packet to all network nodes Each node floods a new packet received on an incoming link by sending it out all of the other links Nodes need to keep track of flooded packets to stop the flood; even using a hop limit can blow up exponentially ...
Chapter 17
... – a multicast router has a conventional routing table with shortest paths to all destinations • the router extracts the source address and finds the interface that leads to the source • the router forwards a copy of the datagram over all other interfaces, but not the one back to the source • this me ...
... – a multicast router has a conventional routing table with shortest paths to all destinations • the router extracts the source address and finds the interface that leads to the source • the router forwards a copy of the datagram over all other interfaces, but not the one back to the source • this me ...
Performance Analysis of RIP and OSPF in Network Using
... 6.2 OSPF Faisalabad Location internal structure. Fig 4 OSPF multi areas at Faisalabad location shows that there are two types of routers is placed Access routers and Edge routers. The figure clearly shows that network topology used at Faisalabad location is Tree topology. Access routers directly att ...
... 6.2 OSPF Faisalabad Location internal structure. Fig 4 OSPF multi areas at Faisalabad location shows that there are two types of routers is placed Access routers and Edge routers. The figure clearly shows that network topology used at Faisalabad location is Tree topology. Access routers directly att ...
in router
... Static vs. dynamic routes • Static routes: – For hiding parts of an internetwork. – To test a particular link in a network. – For maintaining routing tables whenever there is only one path to a destination network. ...
... Static vs. dynamic routes • Static routes: – For hiding parts of an internetwork. – To test a particular link in a network. – For maintaining routing tables whenever there is only one path to a destination network. ...