Unit 1 Powerpoint
... immediate energy for cell activities. Plants, some animals, and other organisms also use carbohydrates for structural purposes. ...
... immediate energy for cell activities. Plants, some animals, and other organisms also use carbohydrates for structural purposes. ...
29.2 Chemical Bonds
... The concept of temperature and changes of phase between solid, liquid, and gas are traditionally considered part of chemistry, as are the gas laws. These kinds of changes in matter are called physical changes, because matter changes physical form but one substance does not change into a complete ...
... The concept of temperature and changes of phase between solid, liquid, and gas are traditionally considered part of chemistry, as are the gas laws. These kinds of changes in matter are called physical changes, because matter changes physical form but one substance does not change into a complete ...
chapter 2 - Scranton Prep Biology
... Atoms with the same number of valence electrons show similar chemical behavior. NOTE: The consequenceof this unifiing chemical principle is th-atthe.valence to most electronsur. ,.rponrible for the atom's bonding capacity. This rule applies of the representativeelements,but not all' B. Atoms combine ...
... Atoms with the same number of valence electrons show similar chemical behavior. NOTE: The consequenceof this unifiing chemical principle is th-atthe.valence to most electronsur. ,.rponrible for the atom's bonding capacity. This rule applies of the representativeelements,but not all' B. Atoms combine ...
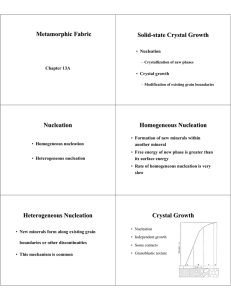
Modern Surface Science and Surface Technologies: An Introduction
... that are more open and contain sites that are surrounded by seven iron neighbor atoms (C7 sites) are the most active. These are the (111) and (211) crystal faces. The structure of the (110) crystal face does not allow the adsorbed nitrogen species to bind with second and third layer atoms, and proba ...
... that are more open and contain sites that are surrounded by seven iron neighbor atoms (C7 sites) are the most active. These are the (111) and (211) crystal faces. The structure of the (110) crystal face does not allow the adsorbed nitrogen species to bind with second and third layer atoms, and proba ...
Adhesion

Adhesion is the tendency of dissimilar particles or surfaces to cling to one another (cohesion refers to the tendency of similar or identical particles/surfaces to cling to one another). The forces that cause adhesion and cohesion can be divided into several types. The intermolecular forces responsible for the function of various kinds of stickers and sticky tape fall into the categories of chemical adhesion, dispersive adhesion, and diffusive adhesion. In addition to the cumulative magnitudes of these intermolecular forces, there are certain emergent mechanical effects that will also be discussed at the end of the article.