AP Chap 2
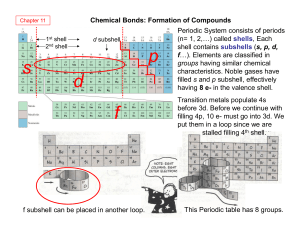
... In biological elements, remember electrons are filled in shells in the following order: ...
... In biological elements, remember electrons are filled in shells in the following order: ...
Pore-Scale Controls on Reaction-Driven Fracturing - DUO
... We will now take a closer look at the pore-scale mechanisms that lead to the stresses and fracture patterns discussed in the preceding section. The key requirement for reactions to take place is that water has access to the reactive surface. In the examples given below, we will show how fracturing c ...
... We will now take a closer look at the pore-scale mechanisms that lead to the stresses and fracture patterns discussed in the preceding section. The key requirement for reactions to take place is that water has access to the reactive surface. In the examples given below, we will show how fracturing c ...
Nonlinear multiresolution: a shape-from-shading example - CS
... Based on the value T as computed in (6), the suggested algorithm for building the gray level pyramid for shape from shading purposes is as follows: 1) TO is calculated from the given input image 10 using (6). 2) A Gaussian pyramid T O . .T,-1 is being built, whose basis is TO,as described in Section ...
... Based on the value T as computed in (6), the suggested algorithm for building the gray level pyramid for shape from shading purposes is as follows: 1) TO is calculated from the given input image 10 using (6). 2) A Gaussian pyramid T O . .T,-1 is being built, whose basis is TO,as described in Section ...
Electrons - biospaces
... Concept 2.3: The formation and function of molecules depend on chemical bonding between atoms Atoms with incomplete valence shells can share or transfer valence electrons with certain other atoms These interactions usually result in atoms staying close together, held by attractions ...
... Concept 2.3: The formation and function of molecules depend on chemical bonding between atoms Atoms with incomplete valence shells can share or transfer valence electrons with certain other atoms These interactions usually result in atoms staying close together, held by attractions ...
Chemistry for BIOS 302
... • Atoms can combine with each other to form molecules. Very few elements exist naturally in an uncombined state: mostly they are joined into molecules. • A molecule is a defined number of atoms grouped into a defined spatial relationship. For example, water, H2O, is 2 hydrogen atoms connected to an ...
... • Atoms can combine with each other to form molecules. Very few elements exist naturally in an uncombined state: mostly they are joined into molecules. • A molecule is a defined number of atoms grouped into a defined spatial relationship. For example, water, H2O, is 2 hydrogen atoms connected to an ...
Adhesion

Adhesion is the tendency of dissimilar particles or surfaces to cling to one another (cohesion refers to the tendency of similar or identical particles/surfaces to cling to one another). The forces that cause adhesion and cohesion can be divided into several types. The intermolecular forces responsible for the function of various kinds of stickers and sticky tape fall into the categories of chemical adhesion, dispersive adhesion, and diffusive adhesion. In addition to the cumulative magnitudes of these intermolecular forces, there are certain emergent mechanical effects that will also be discussed at the end of the article.