CHAPTER 1 Differentiate b/w Mendeleev`s periodic law and modern
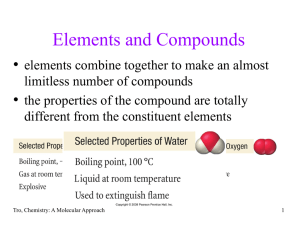
... The electronegativities of group IV-A decrease down the group along with their increasing sizes. These two parameters are responsible for creating van der Waal's forces of attraction among the hydrides. In this way, their melting and boiling points increase. Water is liquid at room temperature while ...
... The electronegativities of group IV-A decrease down the group along with their increasing sizes. These two parameters are responsible for creating van der Waal's forces of attraction among the hydrides. In this way, their melting and boiling points increase. Water is liquid at room temperature while ...
Chapter
... • Identify the symbols of the elements nitrogen = N oxide = oxygen = O • Write the formula using prefix number for subscript di = 2, penta = 5 N2O5 Tro, Chemistry: A Molecular Approach ...
... • Identify the symbols of the elements nitrogen = N oxide = oxygen = O • Write the formula using prefix number for subscript di = 2, penta = 5 N2O5 Tro, Chemistry: A Molecular Approach ...
PHOSPHORUS AND SULFUR COSMOCHEMISTRY
... Phosphorus is a key element for life. This work reviews the role of phosphorus in life. Theories on the origin of life are confounded by a lack of reactive phosphorus, and attempts to overcome the dearth of reactive phosphorus must employ unrealistic phosphorus compounds, energetic organic compounds ...
... Phosphorus is a key element for life. This work reviews the role of phosphorus in life. Theories on the origin of life are confounded by a lack of reactive phosphorus, and attempts to overcome the dearth of reactive phosphorus must employ unrealistic phosphorus compounds, energetic organic compounds ...
1 Assignment 4 Hydrogen – The Unique Element
... Both molecular and saline hydrides are quite reactive. Group 1 and 2 hydrides react vigorously with water to produce hydrogen gas and a metal hydroxide. This means that they can be used as drying agents for solvents – the most commonly used in this regard is CaH2. p-Block molecular hydrides have dif ...
... Both molecular and saline hydrides are quite reactive. Group 1 and 2 hydrides react vigorously with water to produce hydrogen gas and a metal hydroxide. This means that they can be used as drying agents for solvents – the most commonly used in this regard is CaH2. p-Block molecular hydrides have dif ...
CHEM 250Q
... Sodium (Na) reacts with sulfur (S) to form a compound in the ratio of two sodium atoms to one sulfur atom. Element X also reacts with sodium in the ratio of two sodium atoms to one element X atom. Which is most likely the identity of element X? A. ...
... Sodium (Na) reacts with sulfur (S) to form a compound in the ratio of two sodium atoms to one sulfur atom. Element X also reacts with sodium in the ratio of two sodium atoms to one element X atom. Which is most likely the identity of element X? A. ...
1 Assignment 5 Hydrogen – The Unique Element
... Both molecular and saline hydrides are quite reactive. Group 1 and 2 hydrides react vigorously with water to produce hydrogen gas and a metal hydroxide. This means that they can be used as drying agents for solvents – the most commonly used in this regard is CaH2. p-Block molecular hydrides have dif ...
... Both molecular and saline hydrides are quite reactive. Group 1 and 2 hydrides react vigorously with water to produce hydrogen gas and a metal hydroxide. This means that they can be used as drying agents for solvents – the most commonly used in this regard is CaH2. p-Block molecular hydrides have dif ...
PDF of this page
... A chemistry course with a focus on real-world societal issues. Students will develop critical thinking skills and an appreciation for the theoretical and practical aspects of chemistry while learning the fundamentals of chemistry. Chemical knowledge will be developed on a need-to-know basis in decis ...
... A chemistry course with a focus on real-world societal issues. Students will develop critical thinking skills and an appreciation for the theoretical and practical aspects of chemistry while learning the fundamentals of chemistry. Chemical knowledge will be developed on a need-to-know basis in decis ...
Chemistry
... of matter that gives rise to these interactions. At O-Level, students have been introduced to the fundamental idea that matter is made up of particles and the simple atomic model (electrons in discrete shells around a positively charged nucleus). This allows students to apply the key ideas of conser ...
... of matter that gives rise to these interactions. At O-Level, students have been introduced to the fundamental idea that matter is made up of particles and the simple atomic model (electrons in discrete shells around a positively charged nucleus). This allows students to apply the key ideas of conser ...
225 Unit 7, Lab 1 - Pope John Paul II High School
... In the example seen above, 3O2 had to be added to the right side of the equation to balance it and show that the excess oxygen is not consumed during the reaction. In this example, methane is called the limiting reactant. Although we have discussed balancing equations in terms of numbers of atoms an ...
... In the example seen above, 3O2 had to be added to the right side of the equation to balance it and show that the excess oxygen is not consumed during the reaction. In this example, methane is called the limiting reactant. Although we have discussed balancing equations in terms of numbers of atoms an ...
Section 1 Describing Chemical Reactions Chapter 8
... CH4(g) + Al(OH)3(s) (not balanced) • Balance Al atoms Al4C3(s) + H2O(l) CH4(g) + 4Al(OH)3(s) (partially balanced) ...
... CH4(g) + Al(OH)3(s) (not balanced) • Balance Al atoms Al4C3(s) + H2O(l) CH4(g) + 4Al(OH)3(s) (partially balanced) ...
Physical chemistry and transition elements 5.1 Rates, equilibrium
... An increase in concentration of NO(g) increases the term on the bottom of the expression for both Kc and Kp. The equilibrium moves to restore Kc or Kp by increasing the top and decreasing the bottom – so the equilibrium moves from left to right. There are more concentration or partial pressure terms ...
... An increase in concentration of NO(g) increases the term on the bottom of the expression for both Kc and Kp. The equilibrium moves to restore Kc or Kp by increasing the top and decreasing the bottom – so the equilibrium moves from left to right. There are more concentration or partial pressure terms ...
친환경 촉매 Iron (III) phosphate: 실온/무용매 반응조건에서 알코올과
... Also, isoamyl acetate is a kind of flavor reagent with fruit taste. It is traditionally prepared with H2SO4 as catalyst.7 The use of H2SO4 often causes the problems such as corrosion for equipments and pollution for environment. Until now, the tried replaces include FeCl3, CuSO4, ferric tri-dodecane ...
... Also, isoamyl acetate is a kind of flavor reagent with fruit taste. It is traditionally prepared with H2SO4 as catalyst.7 The use of H2SO4 often causes the problems such as corrosion for equipments and pollution for environment. Until now, the tried replaces include FeCl3, CuSO4, ferric tri-dodecane ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... in a reaction is called stoichiometry the coefficients in a balanced chemical equation specify the relative amounts in moles of each of the substances involved in the reaction ...
... in a reaction is called stoichiometry the coefficients in a balanced chemical equation specify the relative amounts in moles of each of the substances involved in the reaction ...
Isomers and Isomerism Isomers
... Propionic acid and methyl acetate represent another example of functional group isomerism . In both examples of functional group isomerism, the atoms are arranged in different ways. This leads to different structural formulas and therefore different physical and chemical properties. The differences ...
... Propionic acid and methyl acetate represent another example of functional group isomerism . In both examples of functional group isomerism, the atoms are arranged in different ways. This leads to different structural formulas and therefore different physical and chemical properties. The differences ...
theodore l. brown h. eugene lemay, jr. bruce e. bursten catherine j
... system, or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or likewise. To obtain permission(s) to use material from this work, please submit a written request to Pearson Education, Inc., Permissions Department, 1900 E. Lake Ave., Glenview, IL 60025. Many o ...
... system, or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or likewise. To obtain permission(s) to use material from this work, please submit a written request to Pearson Education, Inc., Permissions Department, 1900 E. Lake Ave., Glenview, IL 60025. Many o ...
Class 11 Class 12 The p- Block Element • Group13 (B to Tl
... • Borazine has a cyclic structure similar to benzene and thus is called inorganic benzene • The other elements of this group form only a few stable hydrides. The thermal stability decreases as we move down the group. • AlH3 is a colourless solid polymerized via Al - H - Al bridging units. The ...
... • Borazine has a cyclic structure similar to benzene and thus is called inorganic benzene • The other elements of this group form only a few stable hydrides. The thermal stability decreases as we move down the group. • AlH3 is a colourless solid polymerized via Al - H - Al bridging units. The ...
Topic 4
... We’ve stated the terms strong acid, strong base, soluble salt, insoluble salt, but we haven’t describe how to determine which species fall under these terms. To be able to write chemical reactions correctly, we will need to understand solubility and how strong and weak species dissociate in water. ...
... We’ve stated the terms strong acid, strong base, soluble salt, insoluble salt, but we haven’t describe how to determine which species fall under these terms. To be able to write chemical reactions correctly, we will need to understand solubility and how strong and weak species dissociate in water. ...
11.2 Types of Chemical Reactions
... potassium carbonate and barium chloride results in a chemical reaction. A white precipitate of solid barium carbonate is formed. Potassium chloride, the other product of the reaction, remains in solution. This is an example of a double-replacement reaction, which is a chemical change involving an ex ...
... potassium carbonate and barium chloride results in a chemical reaction. A white precipitate of solid barium carbonate is formed. Potassium chloride, the other product of the reaction, remains in solution. This is an example of a double-replacement reaction, which is a chemical change involving an ex ...
Chapter 1: Matter and Change
... of the substance is called a physical change. Examples of physical changes include grinding, cutting, melting, and boiling a material. These types of changes do not change the identity of the substance present. Melting and boiling are part of an important class of physical changes called changes of ...
... of the substance is called a physical change. Examples of physical changes include grinding, cutting, melting, and boiling a material. These types of changes do not change the identity of the substance present. Melting and boiling are part of an important class of physical changes called changes of ...
Chemistry Olympiad Support Booklet
... Every year the Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) organises the selection of the UK team for the International Chemistry Olympiad (IChO). The IChO has been running for 40 years, and the UK has been involved since 1983. Next year, in July 2009, the UK will be hosting the competition, and almost 300 stu ...
... Every year the Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) organises the selection of the UK team for the International Chemistry Olympiad (IChO). The IChO has been running for 40 years, and the UK has been involved since 1983. Next year, in July 2009, the UK will be hosting the competition, and almost 300 stu ...
SUGGESTED TIMELINE: 4 Weeks - Hazlet Township Public Schools
... metric system and what do the values represent? What is dimensional analysis and how is it used to convert between units? How do we make and interpret measurement in chemistry? How is quantitative data expressed with correct precision? Why are numbers put in scientific notation? ...
... metric system and what do the values represent? What is dimensional analysis and how is it used to convert between units? How do we make and interpret measurement in chemistry? How is quantitative data expressed with correct precision? Why are numbers put in scientific notation? ...
Chemistry
... additions their mechanisms (Markownikoff/ Anti Markownikoff addition), mechanism of oxymercuration-demercuration, hydroboration- oxidation, ozonolysis, reduction (catalytic and chemical), syn and anti-hydroxylation(oxidation). 1,2-and 1,4-addition reactions in conjugated dienes and Diels-Alder react ...
... additions their mechanisms (Markownikoff/ Anti Markownikoff addition), mechanism of oxymercuration-demercuration, hydroboration- oxidation, ozonolysis, reduction (catalytic and chemical), syn and anti-hydroxylation(oxidation). 1,2-and 1,4-addition reactions in conjugated dienes and Diels-Alder react ...
articles - Geoscience Research Institute
... to demonstrate experimentally that biological compounds could have been formed under prebiotic conditions. Such efforts are based on the assumption that life emerged spontaneously on the surface of the primitive earth after normal chemical processes had brought carbon-containing molecules to a stage ...
... to demonstrate experimentally that biological compounds could have been formed under prebiotic conditions. Such efforts are based on the assumption that life emerged spontaneously on the surface of the primitive earth after normal chemical processes had brought carbon-containing molecules to a stage ...
Redox Balancing Worksheet
... Fortunately, the film of Ag2S that collects on the metal surface forms a protective coating that slows down further oxidation of the silver metal. For many years, chemists thought of oxidation and reduction as involving the element oxygen in some way or another. That's where the name oxidation came ...
... Fortunately, the film of Ag2S that collects on the metal surface forms a protective coating that slows down further oxidation of the silver metal. For many years, chemists thought of oxidation and reduction as involving the element oxygen in some way or another. That's where the name oxidation came ...
UNIVERSITY OF DELHI FACULTY OF SCIENCE SYLLABUS OF COURSES TO BE OFFERED
... grading system will also enable potential employers in assessing the performance of the candidates. In order to bring uniformity in evaluation system and computation of the Cumulative Grade Point Average (CGPA) based on student’s performance in examinations, the UGC has formulated the guidelines to ...
... grading system will also enable potential employers in assessing the performance of the candidates. In order to bring uniformity in evaluation system and computation of the Cumulative Grade Point Average (CGPA) based on student’s performance in examinations, the UGC has formulated the guidelines to ...
Organic chemistry

Organic chemistry is a chemistry subdiscipline involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms. Study of structure includes many physical and chemical methods to determine the chemical composition and the chemical constitution of organic compounds and materials. Study of properties includes both physical properties and chemical properties, and uses similar methods as well as methods to evaluate chemical reactivity, with the aim to understand the behavior of the organic matter in its pure form (when possible), but also in solutions, mixtures, and fabricated forms. The study of organic reactions includes probing their scope through use in preparation of target compounds (e.g., natural products, drugs, polymers, etc.) by chemical synthesis, as well as the focused study of the reactivities of individual organic molecules, both in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study.The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry include hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen), as well as myriad compositions based always on carbon, but also containing other elements, especially oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus (these, included in many organic chemicals in biology) and the radiostable elements of the halogens.In the modern era, the range extends further into the periodic table, with main group elements, including:Group 1 and 2 organometallic compounds, i.e., involving alkali (e.g., lithium, sodium, and potassium) or alkaline earth metals (e.g., magnesium)Metalloids (e.g., boron and silicon) or other metals (e.g., aluminium and tin)In addition, much modern research focuses on organic chemistry involving further organometallics, including the lanthanides, but especially the transition metals; (e.g., zinc, copper, palladium, nickel, cobalt, titanium and chromium)Finally, organic compounds form the basis of all earthly life and constitute a significant part of human endeavors in chemistry. The bonding patterns open to carbon, with its valence of four—formal single, double, and triple bonds, as well as various structures with delocalized electrons—make the array of organic compounds structurally diverse, and their range of applications enormous. They either form the basis of, or are important constituents of, many commercial products including pharmaceuticals; petrochemicals and products made from them (including lubricants, solvents, etc.); plastics; fuels and explosives; etc. As indicated, the study of organic chemistry overlaps with organometallic chemistry and biochemistry, but also with medicinal chemistry, polymer chemistry, as well as many aspects of materials science.