Important People Social Psychology
... shock to a protesting stranger. He also invented several research techniques unrelated to obedience, such as the lost-letter technique, cyranoid technique, and small-world technique. ("six degrees of separation") Participants were told that they were taking part in a study on learning, but always ac ...
... shock to a protesting stranger. He also invented several research techniques unrelated to obedience, such as the lost-letter technique, cyranoid technique, and small-world technique. ("six degrees of separation") Participants were told that they were taking part in a study on learning, but always ac ...
Social psychology Unit 8 Objectives
... UNIT OUTLINE/ASSIGNMENTS/TERMS TO KNOW FOR AP PSYCHOLOGY UNIT 8 – SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY UNIT 8 OBJECTIVES This part of the course focuses on how individuals relate to one another in social situations. Social psychologists study social attitudes, social influence, and other social phenomena. AP students ...
... UNIT OUTLINE/ASSIGNMENTS/TERMS TO KNOW FOR AP PSYCHOLOGY UNIT 8 – SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY UNIT 8 OBJECTIVES This part of the course focuses on how individuals relate to one another in social situations. Social psychologists study social attitudes, social influence, and other social phenomena. AP students ...
UNIT - 01 INTRODUCTION - SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY
... Vinayaka Missions University,Directorate of Distance Education Salem India ...
... Vinayaka Missions University,Directorate of Distance Education Salem India ...
Are You suprised
... a. Prejudice means, literally, prejudgment b. Means deciding beforehand what a person will be like instead of withholding judgment until it can be based on his or her individual qualities c. To hold stereotypes about a group of people is to be prejudiced about them d. Prejudice is not necessarily ne ...
... a. Prejudice means, literally, prejudgment b. Means deciding beforehand what a person will be like instead of withholding judgment until it can be based on his or her individual qualities c. To hold stereotypes about a group of people is to be prejudiced about them d. Prejudice is not necessarily ne ...
History and Approaches
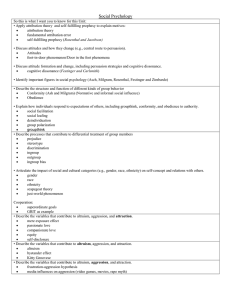
... • Describe the structure and function of different kinds of group behavior (e.g., deindividuation, group polarization). • Explain how individuals respond to expectations of others, including groupthink, conformity, and obedience to authority. • Predict the impact of the presence of others on individ ...
... • Describe the structure and function of different kinds of group behavior (e.g., deindividuation, group polarization). • Explain how individuals respond to expectations of others, including groupthink, conformity, and obedience to authority. • Predict the impact of the presence of others on individ ...
Lecture 6
... External factors: People events, and other stimuli in an individual’s environment can affect her thoughts, feelings, attitudes and behaviours Internal factors: A person’s traits, needs and intentions can affect her thoughts, feelings, attitudes and behaviours ...
... External factors: People events, and other stimuli in an individual’s environment can affect her thoughts, feelings, attitudes and behaviours Internal factors: A person’s traits, needs and intentions can affect her thoughts, feelings, attitudes and behaviours ...
Social Influence -Social Comparison
... A state that occurs when a person's attitudes, beliefs and behaviors are in conflict. People are motivated to reduce the dissonance. In order to relieve the dissonance, the person will try to change the cognitions so that they will be in agreement. ...
... A state that occurs when a person's attitudes, beliefs and behaviors are in conflict. People are motivated to reduce the dissonance. In order to relieve the dissonance, the person will try to change the cognitions so that they will be in agreement. ...
hypothetical construct
... • Quantitative index of the affective component • Measurement equals ‘science’ • Parallel developments of the cognitive component not pursued • Justification from consistency theory – the three components in a dynamic equilibrium cf Festinger’s cognitive dissonance – if behaviour is at variance with ...
... • Quantitative index of the affective component • Measurement equals ‘science’ • Parallel developments of the cognitive component not pursued • Justification from consistency theory – the three components in a dynamic equilibrium cf Festinger’s cognitive dissonance – if behaviour is at variance with ...
These are my Unit goals for Social Psychology
... Social Psychology So this is what I want you to know for this Unit: • Apply attribution theory and self-fulfilling prophesy to explain motives: ...
... Social Psychology So this is what I want you to know for this Unit: • Apply attribution theory and self-fulfilling prophesy to explain motives: ...
Introduction to Psychology
... Social Psychology Scientific study of how we think about, influence, & relate to one another Attribution Theory Tendency to give causal explanation for someone’s behavior, often by crediting either situation or person’s disposition ...
... Social Psychology Scientific study of how we think about, influence, & relate to one another Attribution Theory Tendency to give causal explanation for someone’s behavior, often by crediting either situation or person’s disposition ...
Chapter 9: Social Influence
... Informational & Normative Social Influence Informational pressure we are concerned about being right – others seen as trustworthy evidence about objective reality Normative pressure we are concerned about being liked – avoid rejection and gain approval and acceptance from others ...
... Informational & Normative Social Influence Informational pressure we are concerned about being right – others seen as trustworthy evidence about objective reality Normative pressure we are concerned about being liked – avoid rejection and gain approval and acceptance from others ...
File - Ms.Carey`s Webpage!
... example: some people assume homeless people are too lazy to get a job- not true What is Attribution?- why certain events occurred or why a person acted a certain way ...
... example: some people assume homeless people are too lazy to get a job- not true What is Attribution?- why certain events occurred or why a person acted a certain way ...
Social Psychology Key Terms 1. Social Norms 2. Asch Effect 3
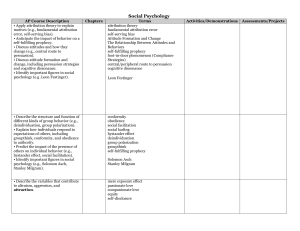
... • Identify important figures in social psychology (e.g., Solomon Asch, Leon Festinger, Stanley Milgram, Philip ...
... • Identify important figures in social psychology (e.g., Solomon Asch, Leon Festinger, Stanley Milgram, Philip ...
History of Social Psychology
... • The computer as a metaphor for human cognition – Simon • Miller discovery of 7 + or - 2 rule of short-term memory • Bruner’s work on going beyond the information given • Neisser’s work on schemas ...
... • The computer as a metaphor for human cognition – Simon • Miller discovery of 7 + or - 2 rule of short-term memory • Bruner’s work on going beyond the information given • Neisser’s work on schemas ...
Social Psychology
... Social Psychology Social psychology is the study of how people and groups interact. Scholars in this interdisciplinary area are typically either psychologists or sociologists, though all social psychologists use both the individual and the group as their subject to study. Their approach to the field ...
... Social Psychology Social psychology is the study of how people and groups interact. Scholars in this interdisciplinary area are typically either psychologists or sociologists, though all social psychologists use both the individual and the group as their subject to study. Their approach to the field ...
Unit X: Social Psychology
... February 25 and 26 (Mon. and Tue.) Unit X: Social Psychology This part of the course focuses on how individuals relate to one another in social situations. Social psychologists study social attitudes, social influence, and othe ...
... February 25 and 26 (Mon. and Tue.) Unit X: Social Psychology This part of the course focuses on how individuals relate to one another in social situations. Social psychologists study social attitudes, social influence, and othe ...
Social Judgment Theory Paper
... Queens. In similar meaning, our latitude of acceptance is made up of positions we accept. The second latitude is the latitude of rejection. This latitude suggests that there is a range of ideas that a person sees as unreasonable or objectionable. For example, the person still believes that Queens i ...
... Queens. In similar meaning, our latitude of acceptance is made up of positions we accept. The second latitude is the latitude of rejection. This latitude suggests that there is a range of ideas that a person sees as unreasonable or objectionable. For example, the person still believes that Queens i ...
Social Psych_Slide Review
... few boxes. She drops the boxes and the contents fly out in all directions. A group of teenagers passes her on their way across the street and don’t attempt to help. This is an example of what? The Bystander Effect ...
... few boxes. She drops the boxes and the contents fly out in all directions. A group of teenagers passes her on their way across the street and don’t attempt to help. This is an example of what? The Bystander Effect ...
Social Psychology Objectives
... attribuationerror, self-‐serving bias) 10.2 Describe the structure and function of different kinds of group behavior ...
... attribuationerror, self-‐serving bias) 10.2 Describe the structure and function of different kinds of group behavior ...
What is Social Psychology?
... Class Expectations (for one another) What is Social Psychology? Newspaper through the Lens of a Social Psychologist Service Learning Option (guest – Patti Gorman) Review Syllabus ...
... Class Expectations (for one another) What is Social Psychology? Newspaper through the Lens of a Social Psychologist Service Learning Option (guest – Patti Gorman) Review Syllabus ...