Y11GeUC7 Fragile PPwk26 - the InterHigh IGCSE Geography
... delta is then not able to grow rice once salt water has infiltrated it. The precipitation brought by the Monsoons and the spring melt from the Himalayas is less reliable than before, which means sometimes there are floods when more turns up that expected, while at other times there are equally unexp ...
... delta is then not able to grow rice once salt water has infiltrated it. The precipitation brought by the Monsoons and the spring melt from the Himalayas is less reliable than before, which means sometimes there are floods when more turns up that expected, while at other times there are equally unexp ...
Global Warming FAQ - Competitive Enterprise Institute
... That’s not the verdict of scientists who study Mount Kilimanjaro most closely. In “Modern Glacier Retreat on Kilimanjaro as Evidence of Climate Change: Observations and Facts14,” Kaser et al. “develop a new concept for investigating the retreat of Kilimanjaro’s glaciers, based on the physical unders ...
... That’s not the verdict of scientists who study Mount Kilimanjaro most closely. In “Modern Glacier Retreat on Kilimanjaro as Evidence of Climate Change: Observations and Facts14,” Kaser et al. “develop a new concept for investigating the retreat of Kilimanjaro’s glaciers, based on the physical unders ...
Global Temperature Change in the 21st Century
... greenhouse gas emissions and climate change? Would warming be truly global, or vary from location to location? Would warming occur mostly in summer (affecting the prevalence of heat wave, heat damage to crops, etc.), mostly in winter (potentially decreasing the severity of winters, affecting sea ice ...
... greenhouse gas emissions and climate change? Would warming be truly global, or vary from location to location? Would warming occur mostly in summer (affecting the prevalence of heat wave, heat damage to crops, etc.), mostly in winter (potentially decreasing the severity of winters, affecting sea ice ...
What causes global climate change?
... and other greenhouse gases, as well as land-use change, are the processes primarily responsible for the increase. Emissions of black carbon (soot) may also be contributing to the warming. Emissions of reflective sulfate aerosols have been associated with a net cooling effect. ...
... and other greenhouse gases, as well as land-use change, are the processes primarily responsible for the increase. Emissions of black carbon (soot) may also be contributing to the warming. Emissions of reflective sulfate aerosols have been associated with a net cooling effect. ...
Natalie Schneider, AICP - Palm Beach County Medical Society
... change – the planet is warming, and over the last half century, this warming has been driven primarily by human activity— predominantly the burning of fossil fuels ...
... change – the planet is warming, and over the last half century, this warming has been driven primarily by human activity— predominantly the burning of fossil fuels ...
What´s happening to the climate?- Ten questions and answers on
... degrees, present-day emissions will have to decrease by at least 60 percent between now and 2050. Emissions will have to start to decrease within the next few years. This represents a great challenge for the global community. The United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) notes ...
... degrees, present-day emissions will have to decrease by at least 60 percent between now and 2050. Emissions will have to start to decrease within the next few years. This represents a great challenge for the global community. The United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) notes ...
Climate Change: Science Issues
... evidence regarding changes in floods because the records are sparse and the effects are confounded with changes in land use and engineering. “Furthermore there is low agreement in this evidence, and thus overall low confidence at the global scale regarding even the sign of these changes.” “There is ...
... evidence regarding changes in floods because the records are sparse and the effects are confounded with changes in land use and engineering. “Furthermore there is low agreement in this evidence, and thus overall low confidence at the global scale regarding even the sign of these changes.” “There is ...
Climate Change Copenhagen
... US Climate Change – 2009 emissions • Total emissions up about 5% since 1990, ...
... US Climate Change – 2009 emissions • Total emissions up about 5% since 1990, ...
15-Climate_Change
... The climate system does not reach equilibrium instantaneously Other processes can change the equilibrium temperature. ...
... The climate system does not reach equilibrium instantaneously Other processes can change the equilibrium temperature. ...
Evidence
... Earth and Environmental Systems Institute Director, Earth System Science Center, Penn State University Straub Environmental Lecture Salem, Oregon May 31, 2007 ...
... Earth and Environmental Systems Institute Director, Earth System Science Center, Penn State University Straub Environmental Lecture Salem, Oregon May 31, 2007 ...
http://dieoff
... Ocean Conveyor is the Cause for Radical Climate Change The climate is constantly changing, including temperature, precipitation, droughts, storms and various other weather patterns. Cloud formations, precipitation, oceans and the sun all play major roles in determining our climate. Oceans play one o ...
... Ocean Conveyor is the Cause for Radical Climate Change The climate is constantly changing, including temperature, precipitation, droughts, storms and various other weather patterns. Cloud formations, precipitation, oceans and the sun all play major roles in determining our climate. Oceans play one o ...
Lesson 1
... warming and human activities. Since the start of the Industrial Revolution, the average temperature of the planet has increased by slightly less than one degree Celsius to its present level of about 16°C (60°F). This seemingly insignificant change represents a fairly rapid warming trend. According t ...
... warming and human activities. Since the start of the Industrial Revolution, the average temperature of the planet has increased by slightly less than one degree Celsius to its present level of about 16°C (60°F). This seemingly insignificant change represents a fairly rapid warming trend. According t ...
Climate Change - cloudfront.net
... the world. While some changes are normal, the vast majority of scientists agree that our activities are causing dramatic changes to the Earth’s climate. ...
... the world. While some changes are normal, the vast majority of scientists agree that our activities are causing dramatic changes to the Earth’s climate. ...
Climate-change-worksheet
... atmosphere in a week or two, but when material from a violent volcanic eruption is projected far above the highest cloud, these aerosols typically influence the climate for about a year or two before falling into the troposphere and being carried to the surface by precipitation. The energy that is n ...
... atmosphere in a week or two, but when material from a violent volcanic eruption is projected far above the highest cloud, these aerosols typically influence the climate for about a year or two before falling into the troposphere and being carried to the surface by precipitation. The energy that is n ...
Sebastian Catovsky, Association of British Insurers
... extreme weather • Costs doubling each decade • Since 1990, $16 bn each year on average • 2004 was costliest year on record: $40 bn • UK Floods: Boscastle, Carlisle, North Yorkshire • 2005 Scandinavia Storm ...
... extreme weather • Costs doubling each decade • Since 1990, $16 bn each year on average • 2004 was costliest year on record: $40 bn • UK Floods: Boscastle, Carlisle, North Yorkshire • 2005 Scandinavia Storm ...
MS Word
... Energy from the sun drives the earth’s weather and climate, and heats the earth’s surface; in turn, the earth radiates energy back into space. Atmospheric greenhouse gases (water vapor, carbon dioxide, and other gases) trap some of the outgoing energy, retaining heat somewhat like the glass panels o ...
... Energy from the sun drives the earth’s weather and climate, and heats the earth’s surface; in turn, the earth radiates energy back into space. Atmospheric greenhouse gases (water vapor, carbon dioxide, and other gases) trap some of the outgoing energy, retaining heat somewhat like the glass panels o ...
Conservation Easements and Climate Change
... Double coal power efficiency Increase wind power by 50 times Increase global ethanol production by 50 times • Increase solar power by 700 times • Cut vehicle use in half ...
... Double coal power efficiency Increase wind power by 50 times Increase global ethanol production by 50 times • Increase solar power by 700 times • Cut vehicle use in half ...
The Kyoto Protocol and Global Warming - Imprimis
... • As a result of the human use of coal, oil and natural gas, the air’s carbon dioxide content (along with the content of other human-produced greenhouse gases like methane) is increasing. • The greenhouse gases absorb infrared radiation and, as a result, should retain some energy near the surface of ...
... • As a result of the human use of coal, oil and natural gas, the air’s carbon dioxide content (along with the content of other human-produced greenhouse gases like methane) is increasing. • The greenhouse gases absorb infrared radiation and, as a result, should retain some energy near the surface of ...
Other Emerging Issues
... recycle energy (heat) emitted by the Earth’s surface • Greenhouse Gases - primarily water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane gas and ozone • Increasing amounts of greenhouse gases trap solar heat that would have escaped the Earth’s atmosphere ...
... recycle energy (heat) emitted by the Earth’s surface • Greenhouse Gases - primarily water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane gas and ozone • Increasing amounts of greenhouse gases trap solar heat that would have escaped the Earth’s atmosphere ...
VIDEO - American Museum of Natural History
... Every step isn’t perfectly choreographed – but a variety of records tell us that overall, Earth’s recent global warming has been driven by increasing amounts of CO2. In just the last 100 years, due to human activities, the Earth’s average surface temperature has sharply increased by three quarters o ...
... Every step isn’t perfectly choreographed – but a variety of records tell us that overall, Earth’s recent global warming has been driven by increasing amounts of CO2. In just the last 100 years, due to human activities, the Earth’s average surface temperature has sharply increased by three quarters o ...
File
... 10.4oF between 1990-2100. Temperatures will not rise equally everywhere, however. The centers of continents will warm more rapidly than land near the oceans. Landmasses in higher latitudes (polar regions) are also predicted to warm more than in lower latitudes (tropics). For example, the Arctic is p ...
... 10.4oF between 1990-2100. Temperatures will not rise equally everywhere, however. The centers of continents will warm more rapidly than land near the oceans. Landmasses in higher latitudes (polar regions) are also predicted to warm more than in lower latitudes (tropics). For example, the Arctic is p ...
United Nations Fact Sheet on Climate Change
... to ensure complete global coverage of weather and climate and to provide local data to plan for climate risks. Other regional indicators of climate change that need to be monitored include the shrinking of glaciers on Mount Kilimanjaro, Africa’s highest peak, from an estimated 12 sq. km. in 1900 to ...
... to ensure complete global coverage of weather and climate and to provide local data to plan for climate risks. Other regional indicators of climate change that need to be monitored include the shrinking of glaciers on Mount Kilimanjaro, Africa’s highest peak, from an estimated 12 sq. km. in 1900 to ...
Heat Trapping Blanket Metaphor
... the metaphor, continue to explain an impact of climate change, so that you don’t leave the impression that the increasing warmth of the atmosphere/ocean is a trivial matter or even beneficial. ...
... the metaphor, continue to explain an impact of climate change, so that you don’t leave the impression that the increasing warmth of the atmosphere/ocean is a trivial matter or even beneficial. ...
Videoconference Protocol
... seek solutions at the individual, institutional, and governmental levels and implement them at the local, regional and global scale. One of the most serious issues facing the world is global climate change. The general scientific consensus is that humans are increasing atmospheric levels of greenhou ...
... seek solutions at the individual, institutional, and governmental levels and implement them at the local, regional and global scale. One of the most serious issues facing the world is global climate change. The general scientific consensus is that humans are increasing atmospheric levels of greenhou ...
Global warming
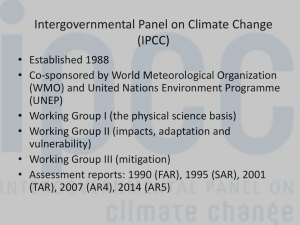
Global warming and climate change are terms for the observed century-scale rise in the average temperature of the Earth's climate system and its related effects.Multiple lines of scientific evidence show that the climate system is warming. Although the increase of near-surface atmospheric temperature is the measure of global warming often reported in the popular press, most of the additional energy stored in the climate system since 1970 has gone into ocean warming. The remainder has melted ice, and warmed the continents and atmosphere. Many of the observed changes since the 1950s are unprecedented over decades to millennia.Scientific understanding of global warming is increasing. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reported in 2014 that scientists were more than 95% certain that most of global warming is caused by increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases and other human (anthropogenic) activities. Climate model projections summarized in the report indicated that during the 21st century the global surface temperature is likely to rise a further 0.3 to 1.7 °C (0.5 to 3.1 °F) for their lowest emissions scenario using stringent mitigation and 2.6 to 4.8 °C (4.7 to 8.6 °F) for their highest. These findings have been recognized by the national science academies of the major industrialized nations.Future climate change and associated impacts will differ from region to region around the globe. Anticipated effects include warming global temperature, rising sea levels, changing precipitation, and expansion of deserts in the subtropics. Warming is expected to be greatest in the Arctic, with the continuing retreat of glaciers, permafrost and sea ice. Other likely changes include more frequent extreme weather events including heat waves, droughts, heavy rainfall, and heavy snowfall; ocean acidification; and species extinctions due to shifting temperature regimes. Effects significant to humans include the threat to food security from decreasing crop yields and the abandonment of populated areas due to flooding.Possible societal responses to global warming include mitigation by emissions reduction, adaptation to its effects, building systems resilient to its effects, and possible future climate engineering. Most countries are parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC),whose ultimate objective is to prevent dangerous anthropogenic climate change. The UNFCCC have adopted a range of policies designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and to assist in adaptation to global warming. Parties to the UNFCCC have agreed that deep cuts in emissions are required, and that future global warming should be limited to below 2.0 °C (3.6 °F) relative to the pre-industrial level.