Climate change and Australia - The Australian Collaboration
... committee was formed and chaired by Prime Minister Gillard. The committee consists of Government Ministers, Australian Greens, independent members of parliament and outside experts. In September 2011, the Government introduced to Parliament the first of 18 bills to establish the government’s carbon ...
... committee was formed and chaired by Prime Minister Gillard. The committee consists of Government Ministers, Australian Greens, independent members of parliament and outside experts. In September 2011, the Government introduced to Parliament the first of 18 bills to establish the government’s carbon ...
Model selection and uncertainty in climate change mitigation research
... • How much do we care about the future? • If we wish to perform a cost-benefit analysis on a future public sector project, such as climate change mitigation, we must choose a discount rate that reflects society’s preference for present benefits over future ...
... • How much do we care about the future? • If we wish to perform a cost-benefit analysis on a future public sector project, such as climate change mitigation, we must choose a discount rate that reflects society’s preference for present benefits over future ...
Could thawing permafrost accelerate global warming?
... Permafrost is soil that has been frozen for at least two consecutive years. It is found in large parts of the Arctic & in the Himalayas – encompassing about 25% of the northern hemisphere land area. There’s more than twice as much carbon stored in permafrost as there is in the whole atmosphere. Did ...
... Permafrost is soil that has been frozen for at least two consecutive years. It is found in large parts of the Arctic & in the Himalayas – encompassing about 25% of the northern hemisphere land area. There’s more than twice as much carbon stored in permafrost as there is in the whole atmosphere. Did ...
Climate is changing
... Estimates of future deposition and fluxes of substances like sulphur , nitrogen oxides, and carbondioxide depend on future emissions. Atmospheric factors are less important than emission changes. In the narrow coastal zone plant and animal communities have to adapt to changing climate and to land up ...
... Estimates of future deposition and fluxes of substances like sulphur , nitrogen oxides, and carbondioxide depend on future emissions. Atmospheric factors are less important than emission changes. In the narrow coastal zone plant and animal communities have to adapt to changing climate and to land up ...
CLIMATE CHANGE AND GLOBAL WARMING I. INTRODUCTION
... agriculture and urban growth, and harvesting timber for fuel, construction, and paper. Currently, up to a quarter of the carbon dioxide emissions to the atmosphere can be attributed to land-use change. 3. Sulfate Aerosols and Black Carbon Sulfate aerosols and black carbon are two important additiona ...
... agriculture and urban growth, and harvesting timber for fuel, construction, and paper. Currently, up to a quarter of the carbon dioxide emissions to the atmosphere can be attributed to land-use change. 3. Sulfate Aerosols and Black Carbon Sulfate aerosols and black carbon are two important additiona ...
When researching back and looking at some of the things we need
... city as foul-smelling fog, or smog, that I couldn't run away from. A > B > L >B (VL) Smoke from forest fires can choke oxygen-breathing animals even if fire does not get to scorch them. The fire benefits the lithosphere some. The soil gets breathing space as dense undergrowth is cleared and ashes al ...
... city as foul-smelling fog, or smog, that I couldn't run away from. A > B > L >B (VL) Smoke from forest fires can choke oxygen-breathing animals even if fire does not get to scorch them. The fire benefits the lithosphere some. The soil gets breathing space as dense undergrowth is cleared and ashes al ...
Climate Forcing
... effects dominate over heating effects. For example, that somehow there are more low stratus clouds and fewer high cirrus clouds (this would indeed have a net planetary cooling effect). • If greenhouse warming itself is what creates the cloud response which causes cooling, then lowering the warming e ...
... effects dominate over heating effects. For example, that somehow there are more low stratus clouds and fewer high cirrus clouds (this would indeed have a net planetary cooling effect). • If greenhouse warming itself is what creates the cloud response which causes cooling, then lowering the warming e ...
The Geological Triggers of Climate Change
... if glacier-clad volcanoes are subject to increased ice melt caused by climate warming, they, too, would be less stable. The next chapter tries to link volcanic eruptions to shrinking glaciers, the notion being that, as the weight of the ice decreases, the magma vents more easily, and eruptions incre ...
... if glacier-clad volcanoes are subject to increased ice melt caused by climate warming, they, too, would be less stable. The next chapter tries to link volcanic eruptions to shrinking glaciers, the notion being that, as the weight of the ice decreases, the magma vents more easily, and eruptions incre ...
Introduction - San Jose State University
... Activity (groups of two) – clicker Imagine that the global temperature were to increase significantly for some reason. 1. How would the silicate-to-carbonate conversion process change during this warming period. Explain. 2. How would this affect atmospheric CO2 levels and as a result, global temper ...
... Activity (groups of two) – clicker Imagine that the global temperature were to increase significantly for some reason. 1. How would the silicate-to-carbonate conversion process change during this warming period. Explain. 2. How would this affect atmospheric CO2 levels and as a result, global temper ...
Atmospheric science: Increasing wind sinks heat
... steady since around the turn of this century. A variety of causes have been proposed for this global warming hiatus1, which fall into two categories. First is a reduction in the top-of-atmosphere radiative imbalance, which could be a result of solar variability, stratospheric water vapour increase, ...
... steady since around the turn of this century. A variety of causes have been proposed for this global warming hiatus1, which fall into two categories. First is a reduction in the top-of-atmosphere radiative imbalance, which could be a result of solar variability, stratospheric water vapour increase, ...
Greenland is melting!
... • “Bottom-up” mitigation pledges – Bound nationally, accountable internationally – Differentiation, comparability/fairness, ambition/revision ...
... • “Bottom-up” mitigation pledges – Bound nationally, accountable internationally – Differentiation, comparability/fairness, ambition/revision ...
How We Know Global Warming is Real
... Some global warming is necessary in order to make the Earth habitable for creatures like us. These two graphics show how it works. The IPCC caption reads: “Estimate of the Earth’s annual and global mean energy balance. Over the long term, the amount of incoming solar radiation absorbed by the Earth ...
... Some global warming is necessary in order to make the Earth habitable for creatures like us. These two graphics show how it works. The IPCC caption reads: “Estimate of the Earth’s annual and global mean energy balance. Over the long term, the amount of incoming solar radiation absorbed by the Earth ...
LESSON 9: CONCEPTUALIZING MODULE II Factors Influencing
... Scientists often want a single measure of surface temperature for the entire globe. To calculate this value, they average together temperature measured at stations located all over the globe. They must be careful to use stations that accurately reflect large-scale trends rather than local influences ...
... Scientists often want a single measure of surface temperature for the entire globe. To calculate this value, they average together temperature measured at stations located all over the globe. They must be careful to use stations that accurately reflect large-scale trends rather than local influences ...
Breaking the partisan impasse in Congress on climate change
... “Any efforts to mitigate the risks of, prepare for, or otherwise address our changing climate and its effects should not constrain the United States economy, especially in regards to global competitiveness.” Rather than constrain the economy, the approach known as Carbon Fee and Dividend would actua ...
... “Any efforts to mitigate the risks of, prepare for, or otherwise address our changing climate and its effects should not constrain the United States economy, especially in regards to global competitiveness.” Rather than constrain the economy, the approach known as Carbon Fee and Dividend would actua ...
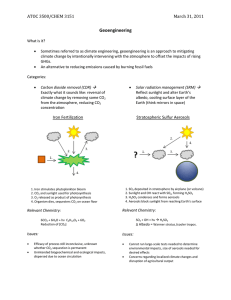
Geoengineering - Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences
... climate change by intentionally intervening with the atmosphere to offset the impacts of rising GHGs. An alternative to reducing emissions caused by burning fossil fuels ...
... climate change by intentionally intervening with the atmosphere to offset the impacts of rising GHGs. An alternative to reducing emissions caused by burning fossil fuels ...
How are people changing the climate?
... 8,200 years ago. This event is also seen in temperature reconstructions from other locations in Europe and in ice cores from Greenland. It was probably caused by shifts in the ocean currents, caused by huge amounts of freshwater which were released to the oceans when the melting ice caps still left ...
... 8,200 years ago. This event is also seen in temperature reconstructions from other locations in Europe and in ice cores from Greenland. It was probably caused by shifts in the ocean currents, caused by huge amounts of freshwater which were released to the oceans when the melting ice caps still left ...
Lecture 13:Climate Change
... • The Artic cap has decreased in size since the first satellite were taken in the 1970”s. • Melting of sea ice has been the most dramatic, but it does not rise sea levels as glaciers do. • Artic glaciers are shrinking at an increasing rate and contribute to a rise in sea level of only 0.2 cm per dec ...
... • The Artic cap has decreased in size since the first satellite were taken in the 1970”s. • Melting of sea ice has been the most dramatic, but it does not rise sea levels as glaciers do. • Artic glaciers are shrinking at an increasing rate and contribute to a rise in sea level of only 0.2 cm per dec ...
Climate Change - Norfolk Coast Partnership
... “The warming of the global climate system is unequivocal, as is now evident from observations of increases in global air and ocean temperatures, widespread melting of ice and snow and rising global sea level” (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) Climate change refers to changes in climate on ...
... “The warming of the global climate system is unequivocal, as is now evident from observations of increases in global air and ocean temperatures, widespread melting of ice and snow and rising global sea level” (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) Climate change refers to changes in climate on ...
Downlaod File
... have done over the past 20 years has been indicating in recent years that humidity, glaciers and ocean heat has all been in constant change from abnormal reasons other than nature. Suggestion that this may perhaps not be a natural cycle happening from nature and indeed from Human beings omitting an ...
... have done over the past 20 years has been indicating in recent years that humidity, glaciers and ocean heat has all been in constant change from abnormal reasons other than nature. Suggestion that this may perhaps not be a natural cycle happening from nature and indeed from Human beings omitting an ...
Setting the Record Straight - Center for Science in the Earth System
... ice ages occurred when CO2 was very low. This data gives climate scientists great confidence that temperature and the abundance of CO2 are closely correlated. Further, there is no theory of climate where rising atmospheric CO2 levels does not increase global mean temperatures. There is no dispute ab ...
... ice ages occurred when CO2 was very low. This data gives climate scientists great confidence that temperature and the abundance of CO2 are closely correlated. Further, there is no theory of climate where rising atmospheric CO2 levels does not increase global mean temperatures. There is no dispute ab ...
Fall07_Exam3
... 17. The most recent ice age cycles on Earth (over the last two million years) were most likely triggered by ___________ . (a) changes in the positions of the continents (b) decreases in the energy output of the Sun (c) variations in Earth's orbit around the Sun (d) volcanic eruptions which eject mas ...
... 17. The most recent ice age cycles on Earth (over the last two million years) were most likely triggered by ___________ . (a) changes in the positions of the continents (b) decreases in the energy output of the Sun (c) variations in Earth's orbit around the Sun (d) volcanic eruptions which eject mas ...
5. Table 5.1 Selected chapters in hydrology
... materials (Physical water quality. Chemical water quality. Biogeochemical cycles.). Patterns of hydrological behaviour (Indicators. Variation over space. Variation over time.). Detecting and estimating change in the catchment (Land cover change effects. Catchment water use effects. Physical changes ...
... materials (Physical water quality. Chemical water quality. Biogeochemical cycles.). Patterns of hydrological behaviour (Indicators. Variation over space. Variation over time.). Detecting and estimating change in the catchment (Land cover change effects. Catchment water use effects. Physical changes ...
Global warming
Global warming and climate change are terms for the observed century-scale rise in the average temperature of the Earth's climate system and its related effects.Multiple lines of scientific evidence show that the climate system is warming. Although the increase of near-surface atmospheric temperature is the measure of global warming often reported in the popular press, most of the additional energy stored in the climate system since 1970 has gone into ocean warming. The remainder has melted ice, and warmed the continents and atmosphere. Many of the observed changes since the 1950s are unprecedented over decades to millennia.Scientific understanding of global warming is increasing. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reported in 2014 that scientists were more than 95% certain that most of global warming is caused by increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases and other human (anthropogenic) activities. Climate model projections summarized in the report indicated that during the 21st century the global surface temperature is likely to rise a further 0.3 to 1.7 °C (0.5 to 3.1 °F) for their lowest emissions scenario using stringent mitigation and 2.6 to 4.8 °C (4.7 to 8.6 °F) for their highest. These findings have been recognized by the national science academies of the major industrialized nations.Future climate change and associated impacts will differ from region to region around the globe. Anticipated effects include warming global temperature, rising sea levels, changing precipitation, and expansion of deserts in the subtropics. Warming is expected to be greatest in the Arctic, with the continuing retreat of glaciers, permafrost and sea ice. Other likely changes include more frequent extreme weather events including heat waves, droughts, heavy rainfall, and heavy snowfall; ocean acidification; and species extinctions due to shifting temperature regimes. Effects significant to humans include the threat to food security from decreasing crop yields and the abandonment of populated areas due to flooding.Possible societal responses to global warming include mitigation by emissions reduction, adaptation to its effects, building systems resilient to its effects, and possible future climate engineering. Most countries are parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC),whose ultimate objective is to prevent dangerous anthropogenic climate change. The UNFCCC have adopted a range of policies designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and to assist in adaptation to global warming. Parties to the UNFCCC have agreed that deep cuts in emissions are required, and that future global warming should be limited to below 2.0 °C (3.6 °F) relative to the pre-industrial level.