presentación - Vicens Vives
... – Recognise in drawings, posters and models the different organs which make up the respiratory, circulatory, excretory and reproductive systems. – Understand the specific functions of the respiratory, circulatory, excretory and reproductive systems. – Differentiate the male and female reproductive s ...
... – Recognise in drawings, posters and models the different organs which make up the respiratory, circulatory, excretory and reproductive systems. – Understand the specific functions of the respiratory, circulatory, excretory and reproductive systems. – Differentiate the male and female reproductive s ...
Kingdom Animalia Part 2
... body specialized for different purposes? – Skeleton- internal, external, or hydrostatic? – Examples- what do animals in this phylum look like? ...
... body specialized for different purposes? – Skeleton- internal, external, or hydrostatic? – Examples- what do animals in this phylum look like? ...
the classification of living organisms
... Natural Science: Grade 7 Life and Living: The Classification of Living Organisms ...
... Natural Science: Grade 7 Life and Living: The Classification of Living Organisms ...
File - Mrs. Oram Science
... 4. What is the difference between external and internal fertilization? In external fertilization, eggs are fertilized outside the body of the egg-producing individual. In internal fertilization, eggs are fertilized inside the body of the eggproducing individual. ...
... 4. What is the difference between external and internal fertilization? In external fertilization, eggs are fertilized outside the body of the egg-producing individual. In internal fertilization, eggs are fertilized inside the body of the eggproducing individual. ...
Ch. 46 Lecture 46_Lecture_2014
... Variation in Patterns of Sexual Reproduction • For many animals, finding a partner for sexual reproduction may be challenging • One solution is hermaphroditism, in which each individual has male and female reproductive systems • Two hermaphrodites can mate, and some hermaphrodites can self-fertiliz ...
... Variation in Patterns of Sexual Reproduction • For many animals, finding a partner for sexual reproduction may be challenging • One solution is hermaphroditism, in which each individual has male and female reproductive systems • Two hermaphrodites can mate, and some hermaphrodites can self-fertiliz ...
unit 3 – how do living
... Through nutrition, organisms obtain matter and energy. They are necessary to build new cells, to increase in size, to renew cells, to reconstruct lost parts etc. Energy is required to carry out some processes. There are processes that do not require energy, for example when we sleep we don’t use ene ...
... Through nutrition, organisms obtain matter and energy. They are necessary to build new cells, to increase in size, to renew cells, to reconstruct lost parts etc. Energy is required to carry out some processes. There are processes that do not require energy, for example when we sleep we don’t use ene ...
CSEC Biology Revision Guide Answers.indd
... out of cells and out of organisms through gaseous exchange surfaces by diffusion. - Carbon dioxide, for use in photosynthesis, moves into leaves and plant cells by diffusion. - Oxygen, produced in photosynthesis, moves out of plant cells and leaves by diffusion. - Some of the glucose and amino acids ...
... out of cells and out of organisms through gaseous exchange surfaces by diffusion. - Carbon dioxide, for use in photosynthesis, moves into leaves and plant cells by diffusion. - Oxygen, produced in photosynthesis, moves out of plant cells and leaves by diffusion. - Some of the glucose and amino acids ...
Syllabus
... To gain a general overview, you will want to look at the texts used for MCB 104, or any other Genetics or Cell Biology course. These include Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al, 5th edition, Chapters 4, 5 or Genetics: From Genes to Genomes, Hartwell et al, 3rd edition, Chapters 4, 13, 14, 1 ...
... To gain a general overview, you will want to look at the texts used for MCB 104, or any other Genetics or Cell Biology course. These include Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al, 5th edition, Chapters 4, 5 or Genetics: From Genes to Genomes, Hartwell et al, 3rd edition, Chapters 4, 13, 14, 1 ...
Frog Dissection
... 9. Suppose in a living frog the spinal nerve extending to the leg muscle were cut. What ability would the frog lose? Why? 10. The abdominal cavity of a frog at the end of hibernation season would contain very small fat bodies or none at all. What is the function of the fat bodies? 11. Structures of ...
... 9. Suppose in a living frog the spinal nerve extending to the leg muscle were cut. What ability would the frog lose? Why? 10. The abdominal cavity of a frog at the end of hibernation season would contain very small fat bodies or none at all. What is the function of the fat bodies? 11. Structures of ...
Biology IGCSE FALL 2011_2012 - Biology
... ● Annelids ● Nematodes ● Mollusks Flowering plants (basics) Monocotyledons Eudicotyledons (Dicotyledons) Use simple dichotomous keys on easily identifiable features 9 instructional days Cells and Organization September 3-13, ...
... ● Annelids ● Nematodes ● Mollusks Flowering plants (basics) Monocotyledons Eudicotyledons (Dicotyledons) Use simple dichotomous keys on easily identifiable features 9 instructional days Cells and Organization September 3-13, ...
Chapter 22 Study Guide Answers
... vital body organs form at this time. 2. (a) – The extraembryonic membranes support and provide nutrients to the embryo or fetus. 3. (c) – By the sixth week, the liver is sufficiently developed to produce blood cells. 4. (d) – The villi from the chorion frondosum penetrate into the decidua basalis of ...
... vital body organs form at this time. 2. (a) – The extraembryonic membranes support and provide nutrients to the embryo or fetus. 3. (c) – By the sixth week, the liver is sufficiently developed to produce blood cells. 4. (d) – The villi from the chorion frondosum penetrate into the decidua basalis of ...
Section 3 - Studying Life
... stop growing and developing? (The process goes on at different rates but does not completely stop until death.) ...
... stop growing and developing? (The process goes on at different rates but does not completely stop until death.) ...
Sponges are sessile, feed by phagocytosis, and reproduce sexually
... and remain dormant for long periods, they are an excellent means of colonization for a sessile organism. Sexual reproduction in sponges occurs when gametes are generated. Sponges are monoecious (hermaphroditic), which means that one individual can produce both gametes (eggs and sperm) simultaneously ...
... and remain dormant for long periods, they are an excellent means of colonization for a sessile organism. Sexual reproduction in sponges occurs when gametes are generated. Sponges are monoecious (hermaphroditic), which means that one individual can produce both gametes (eggs and sperm) simultaneously ...
Arthropods Notes
... – air filled chambers with leaf-like plates – stacked plates are arranged like pages of a book ...
... – air filled chambers with leaf-like plates – stacked plates are arranged like pages of a book ...
lecture notes ch31 fungi
... growing from a log, it is a mass of tightly packed hyphae. 5) Fungi have no ability to move, but can grow very quickly. Hyphae grow in length but not in width (unlike plant shoots and roots). This allows fungi to quickly spread over a wide area. The bulk of a fungal body is often underground or with ...
... growing from a log, it is a mass of tightly packed hyphae. 5) Fungi have no ability to move, but can grow very quickly. Hyphae grow in length but not in width (unlike plant shoots and roots). This allows fungi to quickly spread over a wide area. The bulk of a fungal body is often underground or with ...
Human Development
... prostate, seminal vesicles begin adult functions Secondary sexual characteristics develop: Enlargement of clitoris/penis, labia/scrotum Growth of pubic, anal, and axillary (armpit) hair; ...
... prostate, seminal vesicles begin adult functions Secondary sexual characteristics develop: Enlargement of clitoris/penis, labia/scrotum Growth of pubic, anal, and axillary (armpit) hair; ...
KINDS OF WORMS
... TAPEWORMS • NO MOUTH or ANUS or digestive system nutrients absorbed through tegument • Breathe through skin • Flame cells for excreting nitrogen waste • 2 Cerebral ganglia with 2 nerve cords ...
... TAPEWORMS • NO MOUTH or ANUS or digestive system nutrients absorbed through tegument • Breathe through skin • Flame cells for excreting nitrogen waste • 2 Cerebral ganglia with 2 nerve cords ...
Protists and Fungi
... fungi? Eukaryotic Heterotrophs Rigid cell walls Diverse shapes, methods of obtaining food Various modes of reproduction ...
... fungi? Eukaryotic Heterotrophs Rigid cell walls Diverse shapes, methods of obtaining food Various modes of reproduction ...
Rat Dissection - SLHS Academic biology
... If the rat is on its back, it is lying on its dorsal side. If the rat is on its stomach, it is lying on its ventral side. A rat’s food enters the body in the anterior side. A rat’s wastes exits the body from the posterior side. ...
... If the rat is on its back, it is lying on its dorsal side. If the rat is on its stomach, it is lying on its ventral side. A rat’s food enters the body in the anterior side. A rat’s wastes exits the body from the posterior side. ...
Bio Keystone Review
... break down, if conditions are not right. Enzyme activity can be impacted by temperature, pH, substrate concentration and salinity. ...
... break down, if conditions are not right. Enzyme activity can be impacted by temperature, pH, substrate concentration and salinity. ...
Oviparity or viviparity? That is the question…
... nutrition to offspring should be favored by natural selection due to the consequent increase in the offspring’s fitness [4,5], but retaining the zygotes and early embryos within the female’s body is a strategy whereby numerous animals protect their offspring during the most vulnerable stage of their ...
... nutrition to offspring should be favored by natural selection due to the consequent increase in the offspring’s fitness [4,5], but retaining the zygotes and early embryos within the female’s body is a strategy whereby numerous animals protect their offspring during the most vulnerable stage of their ...
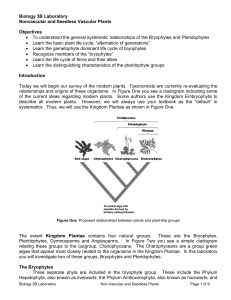
Biology 3B Laboratory Nonvascular and Seedless Vascular Plants
... and roots. The sporophyte is dominant in all plants in this group. There are two groups identified within the pteridophytes based upon leaf size. The megaphylls (large leaves) includes the fern, which have large leaves with many veins. The microphylls (small leaves) represent the balance of the seed ...
... and roots. The sporophyte is dominant in all plants in this group. There are two groups identified within the pteridophytes based upon leaf size. The megaphylls (large leaves) includes the fern, which have large leaves with many veins. The microphylls (small leaves) represent the balance of the seed ...
Class: - 09 Chapter: - Diversity in Living Organisms
... 4. Notochord: it is a long rod like structure, which runs along the body between nervous tissues and gut and provides place for muscle to attach for ease of movement. Organisms could be: ...
... 4. Notochord: it is a long rod like structure, which runs along the body between nervous tissues and gut and provides place for muscle to attach for ease of movement. Organisms could be: ...
ap biology exam essay (free response) questions
... In most aquatic environments, primary production is affected by the light available to the community of organisms. Using measurements of dissolved oxygen concentration to determine primary productivity, design a controlled experiment to test the hypothesis that primary productivity is affected by ei ...
... In most aquatic environments, primary production is affected by the light available to the community of organisms. Using measurements of dissolved oxygen concentration to determine primary productivity, design a controlled experiment to test the hypothesis that primary productivity is affected by ei ...
Sex

Organisms of many species are specialized into male and female varieties, each known as a sex. Sexual reproduction involves the combining and mixing of genetic traits: specialized cells known as gametes combine to form offspring that inherit traits from each parent. Gametes can be identical in form and function (known as isogamy), but in many cases an asymmetry has evolved such that two sex-specific types of gametes (heterogametes) exist (known as anisogamy). By definition, male gametes are small, motile, and optimized to transport their genetic information over a distance, while female gametes are large, non-motile and contain the nutrients necessary for the early development of the young organism. Among humans and other mammals, males typically carry XY chromosomes, whereas females typically carry XX chromosomes, which are a part of the XY sex-determination system. Other animals have a sex-determination system as well, such as the ZW sex-determination system in birds, and the X0 sex-determination system in insects. The gametes produced by an organism are determined by its sex: males produce male gametes (spermatozoa, or sperm, in animals; pollen in plants) while females produce female gametes (ova, or egg cells); individual organisms which produce both male and female gametes are termed hermaphroditic. Frequently, physical differences are associated with the different sexes of an organism; these sexual dimorphisms can reflect the different reproductive pressures the sexes experience.