BIOL 1407 Review Sheet Ch
... 3) Different hyphae may come together and fuse their cytoplasm together in a process called plasmogamy. 4) Hyphae branch and form the mycelium, the body of the fungus. E.g. when you see a mushroom growing from a log, it is a mass of tightly packed hyphae. 5) Fungi have no ability to move, but can gr ...
... 3) Different hyphae may come together and fuse their cytoplasm together in a process called plasmogamy. 4) Hyphae branch and form the mycelium, the body of the fungus. E.g. when you see a mushroom growing from a log, it is a mass of tightly packed hyphae. 5) Fungi have no ability to move, but can gr ...
Biology Form 3
... fond with sori on under-surface vascular tissues present sporophyte generation is dominant ...
... fond with sori on under-surface vascular tissues present sporophyte generation is dominant ...
KCSE ONLINE REVISION BIOLOGY NOTES FORM 3 This
... fond with sori on under-surface vascular tissues present sporophyte generation is dominant ...
... fond with sori on under-surface vascular tissues present sporophyte generation is dominant ...
Lecture 13: The Fungus Among Us I. What are they? A. Fungi are
... discussion largely on the classifications presented in the Prescott text. A. __________________________ 1. Very simple, __________________________ fungi that live in freshwater, mud, soil and sometimes the rumen. 2. Reproduce both sexually and asexually and spores are ____________________ via a post ...
... discussion largely on the classifications presented in the Prescott text. A. __________________________ 1. Very simple, __________________________ fungi that live in freshwater, mud, soil and sometimes the rumen. 2. Reproduce both sexually and asexually and spores are ____________________ via a post ...
Human versus Amoeba - Valhalla High School
... from each parent. Both males and females have specialized reproductive systems which produce gametes. The reproductive system works in conjunction with the endocrine and nervous systems. ...
... from each parent. Both males and females have specialized reproductive systems which produce gametes. The reproductive system works in conjunction with the endocrine and nervous systems. ...
biology 11 – end of term review
... Section 16-1: Genes and Variation Biologists have discovered that there are two main sources of genetic variation: mutations and the genetic shuffling that results from sexual reproduction. The number of phenotypes produced for a given trait depends on how many genes control the trait. Section 16-2: ...
... Section 16-1: Genes and Variation Biologists have discovered that there are two main sources of genetic variation: mutations and the genetic shuffling that results from sexual reproduction. The number of phenotypes produced for a given trait depends on how many genes control the trait. Section 16-2: ...
Part III
... which generation produces spores? Which generation produces sperm and egg? Is the spore-producing generation haploid or diploid? Is the gamete-producing generation haploid or diploid?In what type of habitat is fertilization likely to occur? Which generation is photosynthetic? Which generation is mos ...
... which generation produces spores? Which generation produces sperm and egg? Is the spore-producing generation haploid or diploid? Is the gamete-producing generation haploid or diploid?In what type of habitat is fertilization likely to occur? Which generation is photosynthetic? Which generation is mos ...
FUNGI
... by the formation of multinucleated spores called conidia and by the formation of croziers and an ascus in sexual reproduction. Ascus - The structure that forms ascospores in the ascomycetes ...
... by the formation of multinucleated spores called conidia and by the formation of croziers and an ascus in sexual reproduction. Ascus - The structure that forms ascospores in the ascomycetes ...
Unit 4 NERVOUS AND REPRODUCTION SYSTEM
... The nervous system is the system through which we send and receive information. It also coordinates other systems like the digestive system. The nervous system is the control center of the body. It’s divided into two main systems, the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. ...
... The nervous system is the system through which we send and receive information. It also coordinates other systems like the digestive system. The nervous system is the control center of the body. It’s divided into two main systems, the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. ...
1 A. Biology: Glossary
... analogous structure structure that is similar in unrelated organisms because it evolved to do the same job, not because it was inherited from a common ancestor anaphase third phase of mitosis during which sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell angiosperm type of seed plant ...
... analogous structure structure that is similar in unrelated organisms because it evolved to do the same job, not because it was inherited from a common ancestor anaphase third phase of mitosis during which sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell angiosperm type of seed plant ...
5b Eukaryotic Microbial S and F Fungi
... In pathogenic fungi, dimorphism is temperature-dependent. They are yeast-like at 37°C and mold-like at 25°C. However, some dimorphism will occur with changes in carbon dioxide concentration. ...
... In pathogenic fungi, dimorphism is temperature-dependent. They are yeast-like at 37°C and mold-like at 25°C. However, some dimorphism will occur with changes in carbon dioxide concentration. ...
B1 Revision Mind Maps
... large area •Roots deep – collect water because surface likely to dry out quickly •No leaves – reduce surface area from which water can be lost •Stem able to swell – store water ...
... large area •Roots deep – collect water because surface likely to dry out quickly •No leaves – reduce surface area from which water can be lost •Stem able to swell – store water ...
Porifera and Cnidaria Study Guide
... Refer to the illustration above. Which organism is most closely related to a jellyfish? a. 1 c. 3 b. 2 d. 4 2. Which of the following distinguishes sponges from other invertebrates? a. They are not motile in any stage of their life cycle. b. They obtain nutrients by diffusion rather than by ingestio ...
... Refer to the illustration above. Which organism is most closely related to a jellyfish? a. 1 c. 3 b. 2 d. 4 2. Which of the following distinguishes sponges from other invertebrates? a. They are not motile in any stage of their life cycle. b. They obtain nutrients by diffusion rather than by ingestio ...
Invertebrates
... 2. No nerves or muscles (no tissue differentiation) 3. Mostly marine 4. Filter feeders: Collect food particles from water 5. Most sponges are hermaphrodites. Hermaphrodites function as both male and female in sexual reproduction by producing eggs and sperm. **All other animals are in the clade Eumet ...
... 2. No nerves or muscles (no tissue differentiation) 3. Mostly marine 4. Filter feeders: Collect food particles from water 5. Most sponges are hermaphrodites. Hermaphrodites function as both male and female in sexual reproduction by producing eggs and sperm. **All other animals are in the clade Eumet ...
Lab 6
... coelom lined with mesoderm and they are soft bodied and segmented which makes them different from other animals. They have an organ system level of organization and are triploblastic. They are worms whose bodies are divided into segments with bristles called setae and false feet called parapodia. Bo ...
... coelom lined with mesoderm and they are soft bodied and segmented which makes them different from other animals. They have an organ system level of organization and are triploblastic. They are worms whose bodies are divided into segments with bristles called setae and false feet called parapodia. Bo ...
Lab 6
... coelom lined with mesoderm and they are soft bodied and segmented which makes them different from other animals. They have an organ system level of organization and are triploblastic. They are worms whose bodies are divided into segments with bristles called setae and false feet called parapodia. Bo ...
... coelom lined with mesoderm and they are soft bodied and segmented which makes them different from other animals. They have an organ system level of organization and are triploblastic. They are worms whose bodies are divided into segments with bristles called setae and false feet called parapodia. Bo ...
Pregnanc and Fetal Development
... surrounding the fetus, fetal cells in the fluid are cultured for 2 to 4 weeks and then analyzed for chromosomal defects and other genetic disorders ...
... surrounding the fetus, fetal cells in the fluid are cultured for 2 to 4 weeks and then analyzed for chromosomal defects and other genetic disorders ...
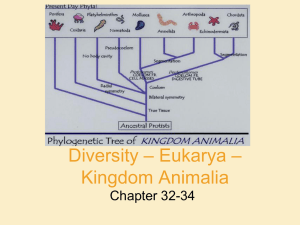
Diversity – Eukarya – Kingdom Animalia
... structural protein - ECM • Store carbs as glycogen • Nervous tissue and muscle tissue – except sponges (porifera) • Usually reproduce sexually w/ dominant diploid stage – Flagellated sperm ...
... structural protein - ECM • Store carbs as glycogen • Nervous tissue and muscle tissue – except sponges (porifera) • Usually reproduce sexually w/ dominant diploid stage – Flagellated sperm ...
Chapter 27
... Other animals, especially terrestrial animals, _______________________________ to nontoxic chemicals, like __________. As the excretory system ___________________ ______________________, water and other useful substances are returned to the body. Asexual Reproduction Reproduction that ______________ ...
... Other animals, especially terrestrial animals, _______________________________ to nontoxic chemicals, like __________. As the excretory system ___________________ ______________________, water and other useful substances are returned to the body. Asexual Reproduction Reproduction that ______________ ...
Fish have gills for breathing underwater
... In the chrysalis there is a miracle change The grub spins a silk pad attaching itself to a twig. Hanging upside down it then wriggles out of its skin. Inside is a soft chrysalis case which becomes hard. The caterpillar inside then breaks down to a goo it re-assembles and out comes something new! Wha ...
... In the chrysalis there is a miracle change The grub spins a silk pad attaching itself to a twig. Hanging upside down it then wriggles out of its skin. Inside is a soft chrysalis case which becomes hard. The caterpillar inside then breaks down to a goo it re-assembles and out comes something new! Wha ...
The Scientific Method - Academic Computer Center
... Some examples include: Trees, mosses, ferns Fungi The members of the kingdom fungi are distinguished by the following characteristics: • They have a cell walls like plant cells do; fungi were once classified as plants • They are heterotrophic (cannot make own food); this is what distinguishes fungi ...
... Some examples include: Trees, mosses, ferns Fungi The members of the kingdom fungi are distinguished by the following characteristics: • They have a cell walls like plant cells do; fungi were once classified as plants • They are heterotrophic (cannot make own food); this is what distinguishes fungi ...
CHAPTER
... classification of living organisms into different groups are :- Whether they are made of prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells. - Whether the cells occur singly or they are grouped together and live as an indivisible group. - Whether they produce their own food by photosynthesis or get their food from out ...
... classification of living organisms into different groups are :- Whether they are made of prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells. - Whether the cells occur singly or they are grouped together and live as an indivisible group. - Whether they produce their own food by photosynthesis or get their food from out ...
Characteristics and classification of living organisms
... Where did life come from? No-one knows how or even exactly when living things first appeared on Earth. Each religion and culture has its own viewpoint about the origin of life. Most scientists think that this probably happened between 3.8 billion and 4 billion years ago. The most generally believed ...
... Where did life come from? No-one knows how or even exactly when living things first appeared on Earth. Each religion and culture has its own viewpoint about the origin of life. Most scientists think that this probably happened between 3.8 billion and 4 billion years ago. The most generally believed ...
Sex

Organisms of many species are specialized into male and female varieties, each known as a sex. Sexual reproduction involves the combining and mixing of genetic traits: specialized cells known as gametes combine to form offspring that inherit traits from each parent. Gametes can be identical in form and function (known as isogamy), but in many cases an asymmetry has evolved such that two sex-specific types of gametes (heterogametes) exist (known as anisogamy). By definition, male gametes are small, motile, and optimized to transport their genetic information over a distance, while female gametes are large, non-motile and contain the nutrients necessary for the early development of the young organism. Among humans and other mammals, males typically carry XY chromosomes, whereas females typically carry XX chromosomes, which are a part of the XY sex-determination system. Other animals have a sex-determination system as well, such as the ZW sex-determination system in birds, and the X0 sex-determination system in insects. The gametes produced by an organism are determined by its sex: males produce male gametes (spermatozoa, or sperm, in animals; pollen in plants) while females produce female gametes (ova, or egg cells); individual organisms which produce both male and female gametes are termed hermaphroditic. Frequently, physical differences are associated with the different sexes of an organism; these sexual dimorphisms can reflect the different reproductive pressures the sexes experience.