m5zn_2ab2252f39932cd
... B) Particles called pangenes, which originate in each part of an organism's body, collect in the sperm or eggs and are passed on to the next generation. 100) Which of the following statements regarding hypotheses about inheritance is false? D) The blending hypothesis suggests that all of the traits ...
... B) Particles called pangenes, which originate in each part of an organism's body, collect in the sperm or eggs and are passed on to the next generation. 100) Which of the following statements regarding hypotheses about inheritance is false? D) The blending hypothesis suggests that all of the traits ...
1. Living Things - The Physics Teacher.ie
... If another animal attacked a koala bear or a bunny rabbit who would you like to see win the fight? Why? Every single one of us will die someday - have you ever discussed your death with anyone? Has anyone else ever discussed their death with you? Nearly 30,000 people die every year in Ireland. Shoul ...
... If another animal attacked a koala bear or a bunny rabbit who would you like to see win the fight? Why? Every single one of us will die someday - have you ever discussed your death with anyone? Has anyone else ever discussed their death with you? Nearly 30,000 people die every year in Ireland. Shoul ...
1-2 Notes
... • All organisms are made up of cells, some of one cell, others of many • All living things are mainly water, but with other chemicals too, such as DNA • All living things need energy, some make their own, others must eat things • All organisms grow and develop, some more complex than others • All li ...
... • All organisms are made up of cells, some of one cell, others of many • All living things are mainly water, but with other chemicals too, such as DNA • All living things need energy, some make their own, others must eat things • All organisms grow and develop, some more complex than others • All li ...
WEB . WHRSD . ORG - Whitman-Hanson Regional School District
... the nervous system, the neuron, and explain generally how it works. 4.5 Explain how the muscular/skeletal system (skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles, bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons) works with other systems to support the body and allow for movement. Recognize that bones produce blood cells. ...
... the nervous system, the neuron, and explain generally how it works. 4.5 Explain how the muscular/skeletal system (skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles, bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons) works with other systems to support the body and allow for movement. Recognize that bones produce blood cells. ...
Cnidaria and Ctenophores
... ii. Gastrovascular cavity = functions in both digestion and gas exchange J. Reproduction by asexual budding (in polyps) or sexual reproduction by gametes (in all medusae and some polyps). Sexual forms monoecious or dioecious; planula larva. i. Monoecious = have both male a female sexual organs withi ...
... ii. Gastrovascular cavity = functions in both digestion and gas exchange J. Reproduction by asexual budding (in polyps) or sexual reproduction by gametes (in all medusae and some polyps). Sexual forms monoecious or dioecious; planula larva. i. Monoecious = have both male a female sexual organs withi ...
1. What is true of all fungi? They are a. eukaryotic, heterotrophic
... a. means that sexual reproduction can occur in specialized structures. b. results in more genetic variation during sexual reproduction. c. allows fungi to reproduce asexually most of the time. d. creates dikaryotic cells. e. is strong support for the claim that fungi are not truly eukaryotic. The qu ...
... a. means that sexual reproduction can occur in specialized structures. b. results in more genetic variation during sexual reproduction. c. allows fungi to reproduce asexually most of the time. d. creates dikaryotic cells. e. is strong support for the claim that fungi are not truly eukaryotic. The qu ...
Revision Sheet Quarter 1 2014-2015 Department:
... Phospholipid molecules form the double layer of the cell membrane. The heads of one layer face the outside of the cell. The heads of the other layer face the inside of the cell. The heads attract water. The tails face each other and they repel water. Water is regulated into and outside the cell by o ...
... Phospholipid molecules form the double layer of the cell membrane. The heads of one layer face the outside of the cell. The heads of the other layer face the inside of the cell. The heads attract water. The tails face each other and they repel water. Water is regulated into and outside the cell by o ...
Meiosis (Gametogenesis)
... (2N) somatic (body) cells. Mitosis allows an organism’s body to grow and to replace cells. In organisms that reproduce asexually, new organisms are produced by mitosis. • Meiosis (or gametogenesis) produces four genetically different haploid (N) cells. Meiosis produces gametes for use in sexual repr ...
... (2N) somatic (body) cells. Mitosis allows an organism’s body to grow and to replace cells. In organisms that reproduce asexually, new organisms are produced by mitosis. • Meiosis (or gametogenesis) produces four genetically different haploid (N) cells. Meiosis produces gametes for use in sexual repr ...
Content Domain 2: Organisms
... organisms and waste from the environment. Multicellular eukaryotes that photosynthesize. Have cellulose in their cell walls. ...
... organisms and waste from the environment. Multicellular eukaryotes that photosynthesize. Have cellulose in their cell walls. ...
meiosis_1
... In each diploid cell there are two chromosomes that have copies of genes on them that code for the same things. One of the pair came from the mother; the other chromosome in the pair came from the father. These pairs of chromosomes that code for the same thing are called homologous pairs. ...
... In each diploid cell there are two chromosomes that have copies of genes on them that code for the same things. One of the pair came from the mother; the other chromosome in the pair came from the father. These pairs of chromosomes that code for the same thing are called homologous pairs. ...
Review_Animals
... 3. What are the likely causes of the Cambrian Explosion? What new animal phyla arose during the period? 4. Describe the following characteristics by which animals can be categorized. Give examples of animals in each category. What is the importance of each characteristic? Body symmetry: radial, bi ...
... 3. What are the likely causes of the Cambrian Explosion? What new animal phyla arose during the period? 4. Describe the following characteristics by which animals can be categorized. Give examples of animals in each category. What is the importance of each characteristic? Body symmetry: radial, bi ...
UPcellprepro.10131154
... 7. Describe the purpose of mitosis and identify cells that undergo mitosis. 8. Summarize the phases of mitosis. 9. Compare cytokinesis in animal cells with cytokinesis in plant cells. 10. Describe the purpose of meiosis and identify cells that undergo meiosis. 11. List and describe the phases of mei ...
... 7. Describe the purpose of mitosis and identify cells that undergo mitosis. 8. Summarize the phases of mitosis. 9. Compare cytokinesis in animal cells with cytokinesis in plant cells. 10. Describe the purpose of meiosis and identify cells that undergo meiosis. 11. List and describe the phases of mei ...
Biology STAAR Review
... ORGANISMAL REPRODUCTION & MEIOSIS Sexual reproduction – the union of gametes from two parents; results in greater genetic variation. Meiosis – reduces chromosome number by half and results in new genetic combinations in gametes (which is enhanced further by crossing over). To insure proper chromosom ...
... ORGANISMAL REPRODUCTION & MEIOSIS Sexual reproduction – the union of gametes from two parents; results in greater genetic variation. Meiosis – reduces chromosome number by half and results in new genetic combinations in gametes (which is enhanced further by crossing over). To insure proper chromosom ...
2421_Ch12.ppt
... body of multicellular alga is called a thallus some have holdfasts, stem-like stipes, and leaf-like blades live in water habitats divisions determined by a number of characteristics, including: pigments, cell wall types, and food storage polymers ...
... body of multicellular alga is called a thallus some have holdfasts, stem-like stipes, and leaf-like blades live in water habitats divisions determined by a number of characteristics, including: pigments, cell wall types, and food storage polymers ...
Exam 1 Review - Iowa State University
... A) each cell will develop into a full-sized, normal embryo B) each cell may develop into a smaller than average, but normal embryo C) each cell may continue to develop, but only into an embryo that lacks many parts D) all 4 cells will die 34. If you separate 4 cells that are indeterminate, what will ...
... A) each cell will develop into a full-sized, normal embryo B) each cell may develop into a smaller than average, but normal embryo C) each cell may continue to develop, but only into an embryo that lacks many parts D) all 4 cells will die 34. If you separate 4 cells that are indeterminate, what will ...
File
... migratory routes. » D The largest organisms in a species receive the only breeding opportunities ...
... migratory routes. » D The largest organisms in a species receive the only breeding opportunities ...
Name: Date: Subject: Sexual vs. Asexual Reproduction Objectives
... Asexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent organism. We call them clones. This doesn’t mean that they are exactly the same, it just means that they have the same DNA or genes. Asexual reproduction requires only 1 parent so asexually reproducing organisms do ...
... Asexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent organism. We call them clones. This doesn’t mean that they are exactly the same, it just means that they have the same DNA or genes. Asexual reproduction requires only 1 parent so asexually reproducing organisms do ...
Important Concepts - Alaska K-12 Science Curricular Initiative (AKSCI)
... many of them microscopic, cannot be neatly classified as either plants or animals. · Similarities among organisms are found in internal anatomical features, which can be used to infer the degree of relatedness among organisms. · Traditionally, a species has been defined as all organisms that can mat ...
... many of them microscopic, cannot be neatly classified as either plants or animals. · Similarities among organisms are found in internal anatomical features, which can be used to infer the degree of relatedness among organisms. · Traditionally, a species has been defined as all organisms that can mat ...
File
... Asexual and Sexual Reproduction: Asexual Reproduction – a single parent produces one or more identical offspring by dividing into two cells - mitosis (protists, arthropods, bacteria by binary fission, fungi, plants); produces large numbers of offspring - offspring are clones of parents (genetically ...
... Asexual and Sexual Reproduction: Asexual Reproduction – a single parent produces one or more identical offspring by dividing into two cells - mitosis (protists, arthropods, bacteria by binary fission, fungi, plants); produces large numbers of offspring - offspring are clones of parents (genetically ...
File
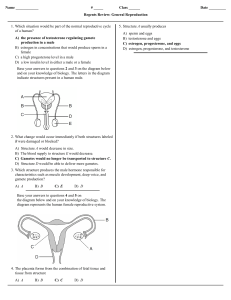
... Base your answers to questions 73 through 76 on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. All organisms need to reproduce for the continuation of their species. Discuss the process of reproduction in humans. 73. Identify one action by the mother that can influence the development of th ...
... Base your answers to questions 73 through 76 on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. All organisms need to reproduce for the continuation of their species. Discuss the process of reproduction in humans. 73. Identify one action by the mother that can influence the development of th ...
Handout
... body of multicellular alga is called a thallus some have holdfasts, stem-like stipes, and leaf-like blades live in water habitats divisions determined by a number of characteristics, including: pigments, cell wall types, and food storage polymers ...
... body of multicellular alga is called a thallus some have holdfasts, stem-like stipes, and leaf-like blades live in water habitats divisions determined by a number of characteristics, including: pigments, cell wall types, and food storage polymers ...
2421_Ch12.ppt
... body of multicellular alga is called a thallus some have holdfasts, stem-like stipes, and leaf-like blades live in water habitats divisions determined by a number of characteristics, including: pigments, cell wall types, and food storage polymers ...
... body of multicellular alga is called a thallus some have holdfasts, stem-like stipes, and leaf-like blades live in water habitats divisions determined by a number of characteristics, including: pigments, cell wall types, and food storage polymers ...
Sex

Organisms of many species are specialized into male and female varieties, each known as a sex. Sexual reproduction involves the combining and mixing of genetic traits: specialized cells known as gametes combine to form offspring that inherit traits from each parent. Gametes can be identical in form and function (known as isogamy), but in many cases an asymmetry has evolved such that two sex-specific types of gametes (heterogametes) exist (known as anisogamy). By definition, male gametes are small, motile, and optimized to transport their genetic information over a distance, while female gametes are large, non-motile and contain the nutrients necessary for the early development of the young organism. Among humans and other mammals, males typically carry XY chromosomes, whereas females typically carry XX chromosomes, which are a part of the XY sex-determination system. Other animals have a sex-determination system as well, such as the ZW sex-determination system in birds, and the X0 sex-determination system in insects. The gametes produced by an organism are determined by its sex: males produce male gametes (spermatozoa, or sperm, in animals; pollen in plants) while females produce female gametes (ova, or egg cells); individual organisms which produce both male and female gametes are termed hermaphroditic. Frequently, physical differences are associated with the different sexes of an organism; these sexual dimorphisms can reflect the different reproductive pressures the sexes experience.