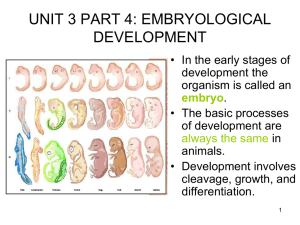
Unit 3 part 4 PPT
... • A third layer of cells begins to grow between the inner and outer layers forming three primary germ layers. • The cells in these germ layers will differentiate to become different endoderm types of cells. ...
... • A third layer of cells begins to grow between the inner and outer layers forming three primary germ layers. • The cells in these germ layers will differentiate to become different endoderm types of cells. ...
... the second meiotic division: follows immediately the first division without DNA replication and without a normal interphase, each chromosome divides in two chromatids that are then drawn to opposite poles, the haploid number of chromosomes is retained, and daughter cells formed during the second div ...
Fertilization
... the second meiotic division: follows immediately the first division without DNA replication and without a normal interphase, each chromosome divides in two chromatids that are then drawn to opposite poles, the haploid number of chromosomes is retained, and daughter cells formed during the second div ...
... the second meiotic division: follows immediately the first division without DNA replication and without a normal interphase, each chromosome divides in two chromatids that are then drawn to opposite poles, the haploid number of chromosomes is retained, and daughter cells formed during the second div ...
What you absolutely must know to pass the regent`s test
... due to replication and mitosis. Why are some cells different than others like heart cells and lung cells? Each cells has the same genes, but different genes are turned on in different cells. Skins cells have all the genes to make nerve cells, but those genes are turned off. ...
... due to replication and mitosis. Why are some cells different than others like heart cells and lung cells? Each cells has the same genes, but different genes are turned on in different cells. Skins cells have all the genes to make nerve cells, but those genes are turned off. ...
A Brief Survey of Animals
... Systems: When moving form simpler to more complex animals forms the number and complexity of systems increases. In the case of digestion, all animals except Poriferans digest food extracellularly, meaning outside of their cells. Poriferans digest food intracellularly, within their cells. Animal dige ...
... Systems: When moving form simpler to more complex animals forms the number and complexity of systems increases. In the case of digestion, all animals except Poriferans digest food extracellularly, meaning outside of their cells. Poriferans digest food intracellularly, within their cells. Animal dige ...
Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata
... – “Monotreme” means single opening • Only three species of monotremes exist today: they are found in Australia and New Guinea – Duckbill Platypus and two species of Spiny Anteaters ...
... – “Monotreme” means single opening • Only three species of monotremes exist today: they are found in Australia and New Guinea – Duckbill Platypus and two species of Spiny Anteaters ...
Additional Resources
... A legal term which means the movement and location of evidence from the time it is obtained to the time it is presented in court. Chain of custody requires testimony of continuous possession by each individual having possession, together with testimony by each that the object remained in substantial ...
... A legal term which means the movement and location of evidence from the time it is obtained to the time it is presented in court. Chain of custody requires testimony of continuous possession by each individual having possession, together with testimony by each that the object remained in substantial ...
APCHap9Motivation_revised2014
... refractory period. A refractory period is a time following orgasm during which males are largely unresponsive to further stimulation. Masters and Johnson found that sexual behavior, like eating and hunger, involves a combination of biological and social processes ...
... refractory period. A refractory period is a time following orgasm during which males are largely unresponsive to further stimulation. Masters and Johnson found that sexual behavior, like eating and hunger, involves a combination of biological and social processes ...
Reproductive System Pt 2 Development
... released a burst of oxytocin to allow for strong bonding between mom and baby. • The pituitary also releases a hormone called prolactin that stimulates the production of milk in the breast tissues of the mother. • Nutrients in the milk contain everything the baby needs for growth and development dur ...
... released a burst of oxytocin to allow for strong bonding between mom and baby. • The pituitary also releases a hormone called prolactin that stimulates the production of milk in the breast tissues of the mother. • Nutrients in the milk contain everything the baby needs for growth and development dur ...
The human body
... They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food, convert those nutrients into energy, and carry out specialized functions. Cells also contain the body’s hereditary material and can make copies of themselves. Cells have many parts, each with a different function. Some of these parts, ...
... They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food, convert those nutrients into energy, and carry out specialized functions. Cells also contain the body’s hereditary material and can make copies of themselves. Cells have many parts, each with a different function. Some of these parts, ...
Sexuality and Society
... a. people no longer care about incest. b. attitudes about sexuality become more permissive. c. the birth rate actually goes up. d. social control of sexuality becomes more strict. ...
... a. people no longer care about incest. b. attitudes about sexuality become more permissive. c. the birth rate actually goes up. d. social control of sexuality becomes more strict. ...
Biology Learning Targets Explained
... 5. A scientific theory is an unproven set of hypothesis that is generally accepted as true due to many tests by multiple individuals that gave the same result. On the other hand, a scientific law has been verified many times and is considered to be true and accurate. It is a combination of multiple ...
... 5. A scientific theory is an unproven set of hypothesis that is generally accepted as true due to many tests by multiple individuals that gave the same result. On the other hand, a scientific law has been verified many times and is considered to be true and accurate. It is a combination of multiple ...
Chapter 24
... • Within the uterus, a specialized structure called the placenta forms • It is through the placenta that the exchange of nutrients, wastes, and respiratory gases between the embryo and the mother take place • The umbilical cord, which contains blood vessels, attaches the embryo to the placenta ...
... • Within the uterus, a specialized structure called the placenta forms • It is through the placenta that the exchange of nutrients, wastes, and respiratory gases between the embryo and the mother take place • The umbilical cord, which contains blood vessels, attaches the embryo to the placenta ...
Lesson 2 | Asexual Reproduction
... allowing us to ultimately decipher the genetic makeup of the mammoth.” The baby mammoth, named Lyuba, once again raised hopes of cloning a mammoth. Dr. Ian Barnes of the University of London stated that he now believes a mammoth will be cloned in his lifetime. ...
... allowing us to ultimately decipher the genetic makeup of the mammoth.” The baby mammoth, named Lyuba, once again raised hopes of cloning a mammoth. Dr. Ian Barnes of the University of London stated that he now believes a mammoth will be cloned in his lifetime. ...
Bio II Chapter 32 - Marissa Junior/Senior High School
... Fish: mainly used to process sensory information. Limited amount is used to decision making ...
... Fish: mainly used to process sensory information. Limited amount is used to decision making ...
Vertebrates: Part II
... open and down feathers. Leave nest within two days. They follow parents and find their own food. ...
... open and down feathers. Leave nest within two days. They follow parents and find their own food. ...
Video Notes: Shape of Life III – Flatworms All animals need to obtain
... exotic methods attracting and fertilizing mates. They are all hermaphrodites. In an environment where finding a mate is difficult, hermaphrodites have an advantage because they can mate with any member of the same species they encounter. Some species engage in “penis fencing”, a rather brutal practi ...
... exotic methods attracting and fertilizing mates. They are all hermaphrodites. In an environment where finding a mate is difficult, hermaphrodites have an advantage because they can mate with any member of the same species they encounter. Some species engage in “penis fencing”, a rather brutal practi ...
Chapter 20
... • Is sex for fun, or does it have a special meaning beyond pleasure and physical gratification? • Is sex a way of saying “I like and enjoy being with you” or a commitment to future involvement? • Does sex mean “I love you and want to be with you right now” or “I want to be with you forever”? • Is se ...
... • Is sex for fun, or does it have a special meaning beyond pleasure and physical gratification? • Is sex a way of saying “I like and enjoy being with you” or a commitment to future involvement? • Does sex mean “I love you and want to be with you right now” or “I want to be with you forever”? • Is se ...
Cells - WordPress.com
... Your unique DNA sequence can be analysed from a body fluid sample. Forensic scientists can match the DNA taken from a crime scene with suspects DNA profiles to determine who committed the crime. ...
... Your unique DNA sequence can be analysed from a body fluid sample. Forensic scientists can match the DNA taken from a crime scene with suspects DNA profiles to determine who committed the crime. ...
Biology - Shelbyville Central Schools
... Many organisms start as one cell. That cell divides and become two, two becomes four, four becomes eight, and so on. Multi-cellular organisms grow because cell division increases the number of cells. Even after growth stops, cell division is important. Every day, billions of red blood cells wear out ...
... Many organisms start as one cell. That cell divides and become two, two becomes four, four becomes eight, and so on. Multi-cellular organisms grow because cell division increases the number of cells. Even after growth stops, cell division is important. Every day, billions of red blood cells wear out ...
Lori R. Daniels, Ph.D., LCSW Military Sexual Trauma
... ◦ “If I report it, will it ruin my career?” ◦ “Everyone else likes (the perpetrator), so what ...
... ◦ “If I report it, will it ruin my career?” ◦ “Everyone else likes (the perpetrator), so what ...
Three Groups of Bacteria
... Obligate aerobes must have oxygen to survive Obligate anaerobes only grow in the absence of oxygen Facultative anaerobes can survive and grow with or without oxygen ...
... Obligate aerobes must have oxygen to survive Obligate anaerobes only grow in the absence of oxygen Facultative anaerobes can survive and grow with or without oxygen ...
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a form of reproduction where two morphologically distinct types of specialized reproductive cells called gametes fuse together, involving a female's large ovum (or egg) and a male's smaller sperm. Each gamete contains half the number of chromosomes of normal cells. They are created by a specialized type of cell division, which only occurs in eukaryotic cells, known as meiosis. The two gametes fuse during fertilization to produce DNA replication and the creation of a single-celled zygote which includes genetic material from both gametes. In a process called genetic recombination, genetic material (DNA) joins up so that homologous chromosome sequences are aligned with each other, and this is followed by exchange of genetic information. Two rounds of cell division then produce four daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes from each original parent cell, and the same number of chromosomes as both parents, though self-fertilization can occur. For instance, in human reproduction each human cell contains 46 chromosomes, 23 pairs, except gamete cells, which only contain 23 chromosomes, so the child will have 23 chromosomes from each parent genetically recombined into 23 pairs. Cell division initiates the development of a new individual organism in multicellular organisms, including animals and plants, for the vast majority of whom this is the primary method of reproduction. A species is defined as a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms where two hybrids are capable of reproducing fertile offspring, typically using sexual reproduction, although the species problem encompasses a series of difficult related questions that often come up when biologists define the word species. The evolution of sexual reproduction is a major puzzle because asexual reproduction should be able to outcompete it as every young organism created can bear its own young. This implies that an asexual population has an intrinsic capacity to grow more rapidly with each generation. This 50% cost is a fitness disadvantage of sexual reproduction. The two-fold cost of sex includes this cost and the fact that any organism can only pass on 50% of its own genes to its offspring. One definite advantage of sexual reproduction is that it prevents the accumulation of genetic mutations.Sexual selection is a mode of natural selection in which some individuals out-reproduce others of a population because they are better at securing mates for sexual reproduction. It has been described as ""a powerful evolutionary force that does not exist in asexual populations""Prokaryotes reproduce through asexual reproduction but may display processes similar to sexual reproduction (mechanisms for lateral gene transfer such as bacterial conjugation, transformation and transduction), but they do not lead to reproduction. In prokaryotes, the initial cell has additional or transformed genetic material.