key terms glossary
... themselves or requested automatic updates and information, etc. Any cost in the advertising production process that is not specifically below-the-line cost itemized in the production budget. A point of reference for measurement, often against other companies. benchmarking The process of grouping co ...
... themselves or requested automatic updates and information, etc. Any cost in the advertising production process that is not specifically below-the-line cost itemized in the production budget. A point of reference for measurement, often against other companies. benchmarking The process of grouping co ...
3.02 Part A Notes
... It is important to use positioning to your advantage. You want to position your product so that customers will continue to purchase from you rather than the competition. The pricing, promotion, product development, and distribution strategies are all planned with an eye toward the competition. ...
... It is important to use positioning to your advantage. You want to position your product so that customers will continue to purchase from you rather than the competition. The pricing, promotion, product development, and distribution strategies are all planned with an eye toward the competition. ...
Introduction to Business-to
... • USE IN PRODUCING THEIR PRODUCTS AND/OR TO FACILITATE THEIR OPERATIONS ...
... • USE IN PRODUCING THEIR PRODUCTS AND/OR TO FACILITATE THEIR OPERATIONS ...
Marketing communications
... Forces manufacturer to live up to conveyed image Protects and warns customers against false claims and inferior products Enables manufacturer to mass-produce product Continuous reminder Uninterrupted production a possibility Increases goodwill Raises standards of living (or perceptions thereof) Pric ...
... Forces manufacturer to live up to conveyed image Protects and warns customers against false claims and inferior products Enables manufacturer to mass-produce product Continuous reminder Uninterrupted production a possibility Increases goodwill Raises standards of living (or perceptions thereof) Pric ...
The Four Ps
... We must SUPPLY exactly what the customer wants. We can do this by offering the right MARKETING MIX: “The Four Ps” = the right PRODUCT at the right PRICE available through the right channels of distribution: PLACE presented in the tight way: PROMOTION. The Four Ps PRODUCT = the goods or the service t ...
... We must SUPPLY exactly what the customer wants. We can do this by offering the right MARKETING MIX: “The Four Ps” = the right PRODUCT at the right PRICE available through the right channels of distribution: PLACE presented in the tight way: PROMOTION. The Four Ps PRODUCT = the goods or the service t ...
position description - Australian Physiotherapy Association
... Actively pursuing improvements and innovation in the online and multimedia learning environment Selection Criteria Education and experience: Degree qualified in business, education or e-Learning Proven experience in developing and managing virtual learning products Demonstrated experience in ...
... Actively pursuing improvements and innovation in the online and multimedia learning environment Selection Criteria Education and experience: Degree qualified in business, education or e-Learning Proven experience in developing and managing virtual learning products Demonstrated experience in ...
World Film History !
... Experts approve this product, so you should use it “Four out of five dentists recommend sugarless gum for their patients who chew gum” ...
... Experts approve this product, so you should use it “Four out of five dentists recommend sugarless gum for their patients who chew gum” ...
- Chap 2 Jeopardy
... The process of developing and maintaining a strategic fit between the organization’s goals and capabilities and its changing marketing ...
... The process of developing and maintaining a strategic fit between the organization’s goals and capabilities and its changing marketing ...
THE FOUR P`S and TWO C`S OF INTERNATIONAL MARKETING:
... This strategy consists of all of the company’s manufacturing and marketing are performed in one location- usually the home country. Main Disadvantage: if the company becomes too large manufacturing and shipping all over the world can become complicated and impossible. 2. DECENTRALIZED STRATEGY: This ...
... This strategy consists of all of the company’s manufacturing and marketing are performed in one location- usually the home country. Main Disadvantage: if the company becomes too large manufacturing and shipping all over the world can become complicated and impossible. 2. DECENTRALIZED STRATEGY: This ...
Marketing Process
... product is sold in only a few retail outlets, usually because the product is expensive (for example, handmade chocolates) and has an elite image in the consumer's mind. ...
... product is sold in only a few retail outlets, usually because the product is expensive (for example, handmade chocolates) and has an elite image in the consumer's mind. ...
3.3.1 Product
... success or failure of a product • To understand the stages of the Product Life Cycle and possible extension strategies • To understand how marketing strategies and decisions can differ at each stage of the product life ...
... success or failure of a product • To understand the stages of the Product Life Cycle and possible extension strategies • To understand how marketing strategies and decisions can differ at each stage of the product life ...
Exam 2 Review - jacobwall.com
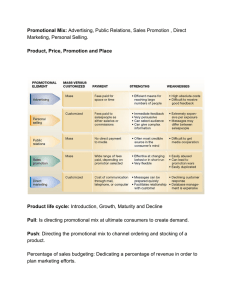
... o Problem of competitive knowledge of your test. Maybe they don’t know or care what else is out there. o Problem of translation national media pans into local equivalents Chapter 11: Managing Products and Brands 4 stages of the product life cycle (introduction, growth, maturity, decline) o Introdu ...
... o Problem of competitive knowledge of your test. Maybe they don’t know or care what else is out there. o Problem of translation national media pans into local equivalents Chapter 11: Managing Products and Brands 4 stages of the product life cycle (introduction, growth, maturity, decline) o Introdu ...
Chapter 6: notes
... Sporting events are considered services, so buying tickets from a team’s box office is an example of direct distribution ...
... Sporting events are considered services, so buying tickets from a team’s box office is an example of direct distribution ...
Business Marketing Channels
... • which is already serving other product needs of a wide user customer base. ...
... • which is already serving other product needs of a wide user customer base. ...
adv -www.itworkss.com
... • Firstly, does the business/product have any Unique Selling Proposition (“USP”) – A unique selling proposition is a customer benefit that no other product can claim ...
... • Firstly, does the business/product have any Unique Selling Proposition (“USP”) – A unique selling proposition is a customer benefit that no other product can claim ...
Economic Benefits presentation
... quantities, therefore, reducing the cost of each item When a product becomes popular, the number of merchants offering the product will increase, thus increasing competition and reducing price Competition causes manufacturers to improve products to better satisfy customer wants and needs ...
... quantities, therefore, reducing the cost of each item When a product becomes popular, the number of merchants offering the product will increase, thus increasing competition and reducing price Competition causes manufacturers to improve products to better satisfy customer wants and needs ...
MNM2602 Study Unit 8 – The Marketing Mix The 4 P`s OF
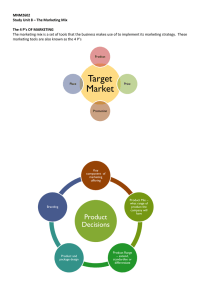
... Study Unit 8 – The Marketing Mix The 4 P’s OF MARKETING The marketing mix is a set of tools that the business makes use of to implement its marketing strategy. These marketing tools are also known as the 4 P’s ...
... Study Unit 8 – The Marketing Mix The 4 P’s OF MARKETING The marketing mix is a set of tools that the business makes use of to implement its marketing strategy. These marketing tools are also known as the 4 P’s ...
10.02-A Content Outline
... c. Advantages and disadvantages of publicity (1) Advantages include helping to create positive image, therefore increasing profits and saving advertising money. Introduces new products and fosters good human relations. (2) Disadvantages are that timing and method of presentation may fail to reach th ...
... c. Advantages and disadvantages of publicity (1) Advantages include helping to create positive image, therefore increasing profits and saving advertising money. Introduces new products and fosters good human relations. (2) Disadvantages are that timing and method of presentation may fail to reach th ...
b. define business strategy
... Greater present value of member spending much buying things in taobao ...
... Greater present value of member spending much buying things in taobao ...
File - Mr. Catalano
... What to watch out for…. Fraud: Lying to a consumer for financial gain Trading-up: Getting pressured to buy a more expensive product Bait and Switch: Luring customers with items that don’t exist with the hope of selling them a more expensive product. ...
... What to watch out for…. Fraud: Lying to a consumer for financial gain Trading-up: Getting pressured to buy a more expensive product Bait and Switch: Luring customers with items that don’t exist with the hope of selling them a more expensive product. ...