
File
... (a) temporary weakness and cramping of skeletal muscle after exercise (b) no rise in blood lactate after strenuous exercise (c) High levels of glycogen ...
... (a) temporary weakness and cramping of skeletal muscle after exercise (b) no rise in blood lactate after strenuous exercise (c) High levels of glycogen ...
Q1. The photograph shows one type of artificial heart. The diagram
... A student pedalled an exercise cycle at constant speed for 5 minutes. The student’s heart rate was recorded at one-minute intervals during the exercise. The results are shown in the graph. ...
... A student pedalled an exercise cycle at constant speed for 5 minutes. The student’s heart rate was recorded at one-minute intervals during the exercise. The results are shown in the graph. ...
Karbohidrat Metabolizması
... • Secreted by pancreas in response to low blood [glucose] • Stimulates glycogen breakdown • Acts primarily in liver Ephinephrine • Secrete by adrenal gland (“fight or flight” response) • Stimulates glycogen breakdown. • Increases rates of glycolysis in muscles and release of glucose from the liver ...
... • Secreted by pancreas in response to low blood [glucose] • Stimulates glycogen breakdown • Acts primarily in liver Ephinephrine • Secrete by adrenal gland (“fight or flight” response) • Stimulates glycogen breakdown. • Increases rates of glycolysis in muscles and release of glucose from the liver ...
Karbohidrat Metabolizması
... • Secreted by pancreas in response to low blood [glucose] • Stimulates glycogen breakdown • Acts primarily in liver Ephinephrine • Secrete by adrenal gland (“fight or flight” response) • Stimulates glycogen breakdown. • Increases rates of glycolysis in muscles and release of glucose from the liver ...
... • Secreted by pancreas in response to low blood [glucose] • Stimulates glycogen breakdown • Acts primarily in liver Ephinephrine • Secrete by adrenal gland (“fight or flight” response) • Stimulates glycogen breakdown. • Increases rates of glycolysis in muscles and release of glucose from the liver ...
What Your Biometric Numbers Mean
... • Keep a food journal • Drink enough water daily • Eat 5 servings of fruits & vegetables ...
... • Keep a food journal • Drink enough water daily • Eat 5 servings of fruits & vegetables ...
Blood groups
... -This system includes 2 types of antigens A and B agglutinogens. -According to the presence of A and B antigens there are 4 groups of human blood : 1- Group A (about 41% ) : when only type A antigen is present. 2- Group B (about 9 % ) : when only type B antigen is present. 3- Group AB (about 3 % ): ...
... -This system includes 2 types of antigens A and B agglutinogens. -According to the presence of A and B antigens there are 4 groups of human blood : 1- Group A (about 41% ) : when only type A antigen is present. 2- Group B (about 9 % ) : when only type B antigen is present. 3- Group AB (about 3 % ): ...
ANIMAL BLOOD PRODUcTs
... and DS/EN ISO 13485:2012. Blood products which form part of culture media or analyses for human diagnostics are CE-marked. Blood from horses, cattle, and sheep is collected and treated aseptically. From all lots of donor blood, a sample is tested by cultivating it for 48 hours in a medium suitable f ...
... and DS/EN ISO 13485:2012. Blood products which form part of culture media or analyses for human diagnostics are CE-marked. Blood from horses, cattle, and sheep is collected and treated aseptically. From all lots of donor blood, a sample is tested by cultivating it for 48 hours in a medium suitable f ...
Cellular Respiration Activity 9 1. The summary formula for cellular
... If NAD is unavailable, the cell is unable to conduct any processes that involve the conversion of NAD to NADH. Because both glycolysis and the Krebs cycle produce NADH, both of these processes shut down when there is no available.NAD. 5. If the Krebs cycle does not require oxygen, why does cellula ...
... If NAD is unavailable, the cell is unable to conduct any processes that involve the conversion of NAD to NADH. Because both glycolysis and the Krebs cycle produce NADH, both of these processes shut down when there is no available.NAD. 5. If the Krebs cycle does not require oxygen, why does cellula ...
Hypoxia Oxidative phosphorylation contribution to ATP production
... Field studies of the Weddell seal showing increase in hematocrit during diving. Also, in the field, the lactate washout peak was often small or absent during short dives, and large during long dives. This led to the concept of the aerobic dive limit (ADL). ...
... Field studies of the Weddell seal showing increase in hematocrit during diving. Also, in the field, the lactate washout peak was often small or absent during short dives, and large during long dives. This led to the concept of the aerobic dive limit (ADL). ...
Circulatory System and Blood
... Which of the following are the correct order of phagocytosis? A. Engulfment by endocytosis, formation of phagosome, phagosome-lysosome merger phagolysosome, killing and digestion of the invading organism, exocytosis of the debris B. Engulfment by endocytosis, phagosome-lysosome merger phagolysosome ...
... Which of the following are the correct order of phagocytosis? A. Engulfment by endocytosis, formation of phagosome, phagosome-lysosome merger phagolysosome, killing and digestion of the invading organism, exocytosis of the debris B. Engulfment by endocytosis, phagosome-lysosome merger phagolysosome ...
Second Sample Exam
... A) hypoglycemia between meals B) hyperglycemia after meals C) enlarged liver D) muscle weakness E) decreased glycogen stores 10. Which of the following is not true about gluconeogenesis? A) B) C) D) E) ...
... A) hypoglycemia between meals B) hyperglycemia after meals C) enlarged liver D) muscle weakness E) decreased glycogen stores 10. Which of the following is not true about gluconeogenesis? A) B) C) D) E) ...
Figure 17-3 Degradation of glucose via the glycolytic pathway.
... •lactate, end-product under anaerobic conditions, diffuses thru cell membrane as waste into blood - salvaged by liver and rebuilt to form glucose (gluconeogenesis). This occurs in skeletal muscle during periods of strenuous exertion: Cells use O2 faster than can be supplied by circulatory system; ce ...
... •lactate, end-product under anaerobic conditions, diffuses thru cell membrane as waste into blood - salvaged by liver and rebuilt to form glucose (gluconeogenesis). This occurs in skeletal muscle during periods of strenuous exertion: Cells use O2 faster than can be supplied by circulatory system; ce ...
ppt-file
... producing lysine [4]. 2 modes only use glucose as a substrate (yield: ¾), five modes only use acetate, and 29 use both. The optimal lysine over glucose yield of ¾ coincides with earlier results obtained by metabolite balancing in [3]. It is understandable that the yield is lower than when ATP and AD ...
... producing lysine [4]. 2 modes only use glucose as a substrate (yield: ¾), five modes only use acetate, and 29 use both. The optimal lysine over glucose yield of ¾ coincides with earlier results obtained by metabolite balancing in [3]. It is understandable that the yield is lower than when ATP and AD ...
Nutrition, Metabolism and Thermoregulation
... – Only about 10-30% of the energy released by catabolic reactions can be used ...
... – Only about 10-30% of the energy released by catabolic reactions can be used ...
Diabetes Care: The ABC's to better health Take-Home Instructions for the Patient
... someone is. It is measured in kg/m2 ...
... someone is. It is measured in kg/m2 ...
Unit three: - Life Science Academy
... The model must be 3-D with moveable parts. The model should be labeled clearly. The model must accurately show the role of insulin as it relates to glucose in the body. The model must accurately depict the role of the following terms in blood sugar regulation: ...
... The model must be 3-D with moveable parts. The model should be labeled clearly. The model must accurately show the role of insulin as it relates to glucose in the body. The model must accurately depict the role of the following terms in blood sugar regulation: ...
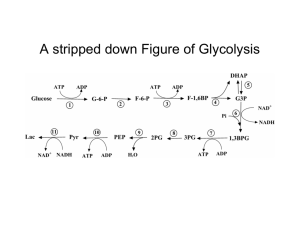
JVB112 gluconeogenesis[1]
... -The biosynthesis of new glucose -Substrates for gluconeogenesis include lactate, pyruvate, glycerol and glucogenic amino acids -Under normal circumstances, the liver is responsible for 85%95% of the glucose that is made **during starvation or metabolic acidosis, the kidney is capable of making gluc ...
... -The biosynthesis of new glucose -Substrates for gluconeogenesis include lactate, pyruvate, glycerol and glucogenic amino acids -Under normal circumstances, the liver is responsible for 85%95% of the glucose that is made **during starvation or metabolic acidosis, the kidney is capable of making gluc ...
JVB112 gluconeogenesis[1]
... 1. interconversion of lactate and pyruvate is catalyzed by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), an oxidized NAD+dependent enzyme Lactate + NAD+ <-> pyruvate +NADH + H+ a. In gluconeogenic tissues (liver), LDH usually runs this reaction in the direction of pyruvate formation b. In muscle cells and erythrocyt ...
... 1. interconversion of lactate and pyruvate is catalyzed by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), an oxidized NAD+dependent enzyme Lactate + NAD+ <-> pyruvate +NADH + H+ a. In gluconeogenic tissues (liver), LDH usually runs this reaction in the direction of pyruvate formation b. In muscle cells and erythrocyt ...
Document
... Enters glycolysis by two different pathways depending on the tissue. Skeletal muscles The glycolytic enzyme, hexokinase accepts fructose as a substrate but with only 5% of the affinity of glucose. ...
... Enters glycolysis by two different pathways depending on the tissue. Skeletal muscles The glycolytic enzyme, hexokinase accepts fructose as a substrate but with only 5% of the affinity of glucose. ...
Chapter 13 (part 1) - University of Nevada, Reno
... • Secreted by pancreas in response to low blood [glucose] • Stimulates glycogen breakdown • Acts primarily in liver Ephinephrine • Secrete by adrenal gland (“fight or flight” response) • Stimulates glycogen breakdown. • Increases rates of glycolysis in muscles and release of glucose from the liver ...
... • Secreted by pancreas in response to low blood [glucose] • Stimulates glycogen breakdown • Acts primarily in liver Ephinephrine • Secrete by adrenal gland (“fight or flight” response) • Stimulates glycogen breakdown. • Increases rates of glycolysis in muscles and release of glucose from the liver ...
Biochemical Tests - Courses Taught by Kathleen Devlin, MBA
... Similar to phenol red broth, but has a 3 sugars in one slant ...
... Similar to phenol red broth, but has a 3 sugars in one slant ...
Metabolism of Carbohydrates
... Use glycogen to export glucose to the bloodstream when blood sugar is low Glycogen stores are depleted after approximately 24 hrs of fasting (in humans) De novo synthesis of glucose for glycogen ...
... Use glycogen to export glucose to the bloodstream when blood sugar is low Glycogen stores are depleted after approximately 24 hrs of fasting (in humans) De novo synthesis of glucose for glycogen ...
Lecture_4_Glycolysis
... NAD+ can be regenerated by further oxidation of pyruvate to CO2, or by the formation of ethanol or lactate from pyruvate. ...
... NAD+ can be regenerated by further oxidation of pyruvate to CO2, or by the formation of ethanol or lactate from pyruvate. ...
Feedback Mechanisms for Maintaining Homeostasis
... body and many materials are passed into and out of the cells by way of the fluid. Thus, this fluid is key in helping the body’s systems maintain optimal temperature and pressure levels, as well as proper levels of acids and bases, carbon dioxide and oxygen and the concentrations of water, nutrients ...
... body and many materials are passed into and out of the cells by way of the fluid. Thus, this fluid is key in helping the body’s systems maintain optimal temperature and pressure levels, as well as proper levels of acids and bases, carbon dioxide and oxygen and the concentrations of water, nutrients ...














![JVB112 gluconeogenesis[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000939420_1-ae0fa12f0b4eac306770097ba9ecae40-300x300.png)
![JVB112 gluconeogenesis[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005255251_1-e457e3f80be2f5d8ecf577d50c416034-300x300.png)






