Respiration II
... citric acid cycle 1) completes the oxidation of glucose it i id l 1) l t th id ti f l (releases CO2); and 2) produces NADH and FADH2 that feed the ETC feed the ETC. ...
... citric acid cycle 1) completes the oxidation of glucose it i id l 1) l t th id ti f l (releases CO2); and 2) produces NADH and FADH2 that feed the ETC feed the ETC. ...
Smor gas bord, January 16 2012 Blood Donation Month
... Approximately 32,000 pints of blood are used each day in the United States. Every three seconds someone needs blood. One out of every 10 people entering a hospital needs blood Just one pint of donated blood can help save as many as three people's lives. There are four main blood types: A, B, AB, and ...
... Approximately 32,000 pints of blood are used each day in the United States. Every three seconds someone needs blood. One out of every 10 people entering a hospital needs blood Just one pint of donated blood can help save as many as three people's lives. There are four main blood types: A, B, AB, and ...
Photosynthesis and Cell Respiration Test Review
... 15. Which stage finishes breaking down sugar all the way to CO2? Kreb’s (we have taken all of the hydrogens off of glucose to make NADH and FADH2) 16. Which process occurs in ALL organisms (prokaryotic/eukaryotic, aerobic/anaerobic)? Glycolysis. It occurs in the cytoplasm which all cells have. If al ...
... 15. Which stage finishes breaking down sugar all the way to CO2? Kreb’s (we have taken all of the hydrogens off of glucose to make NADH and FADH2) 16. Which process occurs in ALL organisms (prokaryotic/eukaryotic, aerobic/anaerobic)? Glycolysis. It occurs in the cytoplasm which all cells have. If al ...
FARMACOLOGFIA e TOSSICOLOGIA applicate ai nanofarmaci.
... Enhanced “in vivo” imaging: QDs A)Functionalized QDs imaging of a rat with muscle sarcoma. B)The same as A: in this case the QDs did not have been functionalized. (Cai & Chen, Small, 2007, 3: 1840.) ...
... Enhanced “in vivo” imaging: QDs A)Functionalized QDs imaging of a rat with muscle sarcoma. B)The same as A: in this case the QDs did not have been functionalized. (Cai & Chen, Small, 2007, 3: 1840.) ...
How to donate blood - Greater Madison Chamber of Commerce
... A blood donation is a gift that doesn’t cost a thing but can provide hope to hospital patients in need. Every day, the Red Cross must collect about 15,000 pints of blood to meet the needs of patients at 2,700 hospitals and transfusion centers nationwide, including 34 in the BadgerHawkeye Region. The ...
... A blood donation is a gift that doesn’t cost a thing but can provide hope to hospital patients in need. Every day, the Red Cross must collect about 15,000 pints of blood to meet the needs of patients at 2,700 hospitals and transfusion centers nationwide, including 34 in the BadgerHawkeye Region. The ...
Abstract - Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology
... and Test Group subjects (-0.58) at the 3 month visit, a clinically significant change. The Control Group’s A1C levels, however, increased at each succeeding visit, so that at 9 and 12 months it was statistically indistinguishable from baseline, whereas the Test Group’s A1C remained significantly low ...
... and Test Group subjects (-0.58) at the 3 month visit, a clinically significant change. The Control Group’s A1C levels, however, increased at each succeeding visit, so that at 9 and 12 months it was statistically indistinguishable from baseline, whereas the Test Group’s A1C remained significantly low ...
Name - Mr. Lesiuk
... ___ 2. Carbon (#6) must share electrons to become stable, therefore, it forms what type of chemical bonds with the other atoms it bonds with? ___ 3. How many extra electrons must carbon share to reach the octet rule? ___ 4. A large molecule made up of several smaller unit molecules (monomers) is cal ...
... ___ 2. Carbon (#6) must share electrons to become stable, therefore, it forms what type of chemical bonds with the other atoms it bonds with? ___ 3. How many extra electrons must carbon share to reach the octet rule? ___ 4. A large molecule made up of several smaller unit molecules (monomers) is cal ...
lecture notes-metabolism pathways-web
... degrading a compound into smaller and simpler products and generating energy. Glucose to CO2, and H2O, protein to amino acids. - Anabolism: the synthesis of more complex compounds and requires energy. Synthesis of glycan (polysaccharide), DNA, RNA, and lipid. ...
... degrading a compound into smaller and simpler products and generating energy. Glucose to CO2, and H2O, protein to amino acids. - Anabolism: the synthesis of more complex compounds and requires energy. Synthesis of glycan (polysaccharide), DNA, RNA, and lipid. ...
Functions of Blood
... (1) The NPN value is the result of many interfering and interacting factors. The route of elimination of various NPN compounds differs considerably. Some are excreted by glomerular filtrations only e.g. creatinine, uric acid is excreted by tubular excretion. Urea is excreted by glomerular filtration ...
... (1) The NPN value is the result of many interfering and interacting factors. The route of elimination of various NPN compounds differs considerably. Some are excreted by glomerular filtrations only e.g. creatinine, uric acid is excreted by tubular excretion. Urea is excreted by glomerular filtration ...
CARBOHYDRATES: METABOLISM (cont.)
... • Insulin: secreted by beta cells to decrease blood glucose level • Glucagon increases the blood glucose level by increasing the activity of the enzyme phosphorylase promoting glycogenolysis • Incretins: GI hormones that, in the presence of glucose in the gut, stimulate insulin release from the panc ...
... • Insulin: secreted by beta cells to decrease blood glucose level • Glucagon increases the blood glucose level by increasing the activity of the enzyme phosphorylase promoting glycogenolysis • Incretins: GI hormones that, in the presence of glucose in the gut, stimulate insulin release from the panc ...
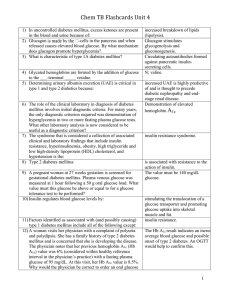
Chem TB Flashcards Unit 4
... laboratory values, what state of acid-base balance is this patient in? 73) An overweight 55-year-old single woman from a rural farming area was brought to the emergency department by her neighbor. The woman had a large abscess on the bottom of her foot; she was irritable and complained of blurred vi ...
... laboratory values, what state of acid-base balance is this patient in? 73) An overweight 55-year-old single woman from a rural farming area was brought to the emergency department by her neighbor. The woman had a large abscess on the bottom of her foot; she was irritable and complained of blurred vi ...
KINES 2015 NICE T2DM guidance Jan 16
... o They should be used in combination therapy with metformin and an SU. o They can also be considered for people with less severe obesity where weight loss is particularly beneficial or where insulin might cause occupational problems (driving or operating machinery). It advises to stop the GLP-1 mime ...
... o They should be used in combination therapy with metformin and an SU. o They can also be considered for people with less severe obesity where weight loss is particularly beneficial or where insulin might cause occupational problems (driving or operating machinery). It advises to stop the GLP-1 mime ...
Bio 210 Cell Chemistry Lecture 4 “Sugars and Fats”
... combination of large molecules that they assemble and use, but are highly similar to each other in the building blocks used in making the macromolecules. 2. Carbohydrates are sugars and long polymers of sugars, such as starches and cellulose. We will discuss three levels of organization of carbohydr ...
... combination of large molecules that they assemble and use, but are highly similar to each other in the building blocks used in making the macromolecules. 2. Carbohydrates are sugars and long polymers of sugars, such as starches and cellulose. We will discuss three levels of organization of carbohydr ...
MACROMOLECULES - Savitha Sastry
... Saturated fats - solids at room temp. - have all Carbons SATURATED - that means every carbon has max. number of hydrogen attached Ex. butter Unsaturated fats - liquid at room temp. - have some Carbons UNSATURATED that means DOUBLE BONDS from some carbons having less than max. number of hydrogen att ...
... Saturated fats - solids at room temp. - have all Carbons SATURATED - that means every carbon has max. number of hydrogen attached Ex. butter Unsaturated fats - liquid at room temp. - have some Carbons UNSATURATED that means DOUBLE BONDS from some carbons having less than max. number of hydrogen att ...
Chapter 3
... How the body stores fuel • ________ accounts for up to 64% of total body weight. • ___ is the largest energy store in the body. – Carbohydrate stores are relatively small. • If only carbohydrate was used as a fuel during a marathon, the storage would last about 2 hours (fat: 59 hours). ...
... How the body stores fuel • ________ accounts for up to 64% of total body weight. • ___ is the largest energy store in the body. – Carbohydrate stores are relatively small. • If only carbohydrate was used as a fuel during a marathon, the storage would last about 2 hours (fat: 59 hours). ...
Ch 12 Blood Cells
... EPO, or erythropoietin (pronounced, ahrith-ro-poy-tin), is a hormone produced by the liver and kidneys. In the first part of a twonight interview broadcast in January, ...
... EPO, or erythropoietin (pronounced, ahrith-ro-poy-tin), is a hormone produced by the liver and kidneys. In the first part of a twonight interview broadcast in January, ...
INSTRUCTIONS FOR BLOOD TESTING Fasting
... Kristin Tarbet, MD, Mike Symond, MD & Gay Sleight, PA-C ...
... Kristin Tarbet, MD, Mike Symond, MD & Gay Sleight, PA-C ...
Metabolism
... • Stores glucose by converting glucose to glycogen. • Takes place in liver and skeletal muscle. • Operates when high levels of glucose-6-phosphate are formed in the first reaction of glycolysis. • Does not operate when energy stores (glycogen) are full, which means that additional glucose is convert ...
... • Stores glucose by converting glucose to glycogen. • Takes place in liver and skeletal muscle. • Operates when high levels of glucose-6-phosphate are formed in the first reaction of glycolysis. • Does not operate when energy stores (glycogen) are full, which means that additional glucose is convert ...
Properties of the Major Biological Molecules
... Glucose is made of 6 carbon atoms, 12 hydrogens, and 6 oxygens. In what foods would I find glucose? Many foods have glucose or some form of similar sugar. These include fruits, milk, juices, candies, and anything with table sugar. Where does the glucose in all food originally come from? All gluc ...
... Glucose is made of 6 carbon atoms, 12 hydrogens, and 6 oxygens. In what foods would I find glucose? Many foods have glucose or some form of similar sugar. These include fruits, milk, juices, candies, and anything with table sugar. Where does the glucose in all food originally come from? All gluc ...
Metabolism
... • seek to regain the electron by removing it from other molecules, thus oxidizing them. • set up a chain reaction that may damage cell structures such as DNA, cell membranes, or needed enzymes. ...
... • seek to regain the electron by removing it from other molecules, thus oxidizing them. • set up a chain reaction that may damage cell structures such as DNA, cell membranes, or needed enzymes. ...
Glyconeogenesis
... is an important source of glucose (through glucogenolysis) to meet the tissue needs for 10-‐18 hours. • During prolonged fasting, liver glycogen stores are depleted, and glucose is formed by gluconeogenesis. ...
... is an important source of glucose (through glucogenolysis) to meet the tissue needs for 10-‐18 hours. • During prolonged fasting, liver glycogen stores are depleted, and glucose is formed by gluconeogenesis. ...
Glucose, insulin, coagulation: endotoxin as
... In this issue of Blood, Liu and colleagues demonstrate a novel mechanism for regulation of thymocyte-fate decisions by which a sugar-binding protein, galectin-1, enforces death while opposing survival of developing thymocytes. T cells such as the CD8␣␣ intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs).1 ...
... In this issue of Blood, Liu and colleagues demonstrate a novel mechanism for regulation of thymocyte-fate decisions by which a sugar-binding protein, galectin-1, enforces death while opposing survival of developing thymocytes. T cells such as the CD8␣␣ intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs).1 ...
Acc_Bio_Blood_Notes
... Hypertension, or high blood pressure, increases the chances that a vessel will burst. Atherosclerosis – Blood flow is blocked by the buildup of fatty deposits inside the arteries. Arteriosclerosis - Blood flow is blocked by the buildup of calcium deposits inside the arteries. Literally means harde ...
... Hypertension, or high blood pressure, increases the chances that a vessel will burst. Atherosclerosis – Blood flow is blocked by the buildup of fatty deposits inside the arteries. Arteriosclerosis - Blood flow is blocked by the buildup of calcium deposits inside the arteries. Literally means harde ...
Cellular Respiration
... H+ ions across the inner membrane. This involves active pumping of H+s. • The H+s then diffuse down their concentration gradient through an ATP Synthase enzyme that produces ATP • Process produces about 32 ATP ...
... H+ ions across the inner membrane. This involves active pumping of H+s. • The H+s then diffuse down their concentration gradient through an ATP Synthase enzyme that produces ATP • Process produces about 32 ATP ...