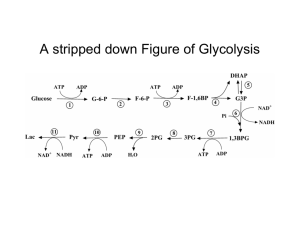
Figure 17-3 Degradation of glucose via the glycolytic pathway.
... Other sugars feed into glycolysis Lactase expression can be repressed, depending on environment. This is basis for lactose intolerance. ...
... Other sugars feed into glycolysis Lactase expression can be repressed, depending on environment. This is basis for lactose intolerance. ...
Unit 3. Basic of Biopolymers (3) Control of Protein Function
... Protein is only present in its active form in the specific compartment where it is needed, or when bound in a complex with other macromolecules that participate in its function. Localization Specification ...
... Protein is only present in its active form in the specific compartment where it is needed, or when bound in a complex with other macromolecules that participate in its function. Localization Specification ...
handout
... tumour cell and its progeny into uncontrolled expansion and invasion. One of these is deregulated cell proliferation, which, together with the suppression of apoptosis needed to support it, provides a minimal 'platform' necessary to support further neoplastic progression. Pathways that restrict this ...
... tumour cell and its progeny into uncontrolled expansion and invasion. One of these is deregulated cell proliferation, which, together with the suppression of apoptosis needed to support it, provides a minimal 'platform' necessary to support further neoplastic progression. Pathways that restrict this ...
Gluconeogenesis
... The enzymes of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis in the liver are reciprocally regulated so that either glucose is converted to pyruvate or pyruvate is converted to glucose. Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate, which we have already seen serves to activate phosphofructokinase, is an inhibitor of fructose-1,6-bis ...
... The enzymes of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis in the liver are reciprocally regulated so that either glucose is converted to pyruvate or pyruvate is converted to glucose. Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate, which we have already seen serves to activate phosphofructokinase, is an inhibitor of fructose-1,6-bis ...
An Introduction to Metabolism by Dr. Ty C.M. Hoffman
... When cellular respiration is unable to occur (either because oxygen is absent or because the cell is not capable of cellular respiration), glycolysis must still be allowed to occur to produce ATP using ...
... When cellular respiration is unable to occur (either because oxygen is absent or because the cell is not capable of cellular respiration), glycolysis must still be allowed to occur to produce ATP using ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION Fates of Pyruvate from glycolysis (2
... CELLULAR RESPIRATION Metabolism—the sum of all biochemical reactions in an organism or cell. a) anabolic—synthesis of compounds; an example is photosynthesis b) catabolic—breakdown of compounds; an example is cellular respiration Metabolic pathways—are the steps (enzymes, substrates and products) us ...
... CELLULAR RESPIRATION Metabolism—the sum of all biochemical reactions in an organism or cell. a) anabolic—synthesis of compounds; an example is photosynthesis b) catabolic—breakdown of compounds; an example is cellular respiration Metabolic pathways—are the steps (enzymes, substrates and products) us ...
aea Organic compounds.wpd
... Lipids are not one chemical class of molecules like carbohydrates. However, all lipids are nonpolar: they do not mix in water and they will dissolve certain nonpolar substances that will not dissolve in water. Triglycerides, phospholipids, waxes, and sterols are all examples of lipids. In this activ ...
... Lipids are not one chemical class of molecules like carbohydrates. However, all lipids are nonpolar: they do not mix in water and they will dissolve certain nonpolar substances that will not dissolve in water. Triglycerides, phospholipids, waxes, and sterols are all examples of lipids. In this activ ...
Lect 8 hormones 4
... • Secreted by β cells • Leads to glucose uptake and storage in liver, muscle and fat tissue. • Effect is to ↓ blood glucose ...
... • Secreted by β cells • Leads to glucose uptake and storage in liver, muscle and fat tissue. • Effect is to ↓ blood glucose ...
AnSc 5311 Ruminant Nutrition Microbial Fermentation of
... Proton pumping is energy-dependent – usually coupled to ATP hydrolysis or electron transport systems ...
... Proton pumping is energy-dependent – usually coupled to ATP hydrolysis or electron transport systems ...
G-protein - cloudfront.net
... Intracellular part functions as a “kinase”, which transfers P from ATP to tyrosine on a substrate protein. ...
... Intracellular part functions as a “kinase”, which transfers P from ATP to tyrosine on a substrate protein. ...
• In the cell, nutrients and oxygen, have different electron affinities.
... kinases or ATPases. Phosphate group from ATP is transferred to some other molecule, energizing that molecule by altering its electron configuration. Phosphorylation Via ATP synthase enzymes ...
... kinases or ATPases. Phosphate group from ATP is transferred to some other molecule, energizing that molecule by altering its electron configuration. Phosphorylation Via ATP synthase enzymes ...
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration
... carbon molecule called Acetyl-CoA before entering the Krebs Cycle. • The Krebs cycle breaks down carbon compounds into carbon dioxide (waste), ATP, NADH, and FADH2 ...
... carbon molecule called Acetyl-CoA before entering the Krebs Cycle. • The Krebs cycle breaks down carbon compounds into carbon dioxide (waste), ATP, NADH, and FADH2 ...
Chapter 1
... to the 5-carbon sugar ribose • Second and third groups are joined by phosphoanhydride bonds = high-energy bonds ...
... to the 5-carbon sugar ribose • Second and third groups are joined by phosphoanhydride bonds = high-energy bonds ...
Fermentation Milos Babic Abstract Fermentation is the process many
... Fermentation is the process many living organisms use in absence of oxygen, in order to replenish NAD+ expended during glycolysis. In one type of fermentation, this is accomplished through conversion of pyruvic acid into CO2 and ethanol. We have examined the process by allowing yeast to ferment gluc ...
... Fermentation is the process many living organisms use in absence of oxygen, in order to replenish NAD+ expended during glycolysis. In one type of fermentation, this is accomplished through conversion of pyruvic acid into CO2 and ethanol. We have examined the process by allowing yeast to ferment gluc ...
+ 2
... Ethanolic fermentation occurs in many kinds of cells during times that they are deprived of oxygen. It occurs in some kinds of yeast even in the presence of oxygen. Note: In fermentation all products of glucose metabolism may be discarded except ATP. ...
... Ethanolic fermentation occurs in many kinds of cells during times that they are deprived of oxygen. It occurs in some kinds of yeast even in the presence of oxygen. Note: In fermentation all products of glucose metabolism may be discarded except ATP. ...
Responses to challenges
... though the large negative free energy reaction tells us that it is spontaneous and will go to completion eventually. however this only tells us about the thermodynamics of the reactions. therefore, yes an enzyme be used to to speed up the process (showing us the kinetics). now since we are talking a ...
... though the large negative free energy reaction tells us that it is spontaneous and will go to completion eventually. however this only tells us about the thermodynamics of the reactions. therefore, yes an enzyme be used to to speed up the process (showing us the kinetics). now since we are talking a ...
Citric Acid Cycle Regulation
... For next round of glycolysis to occur need NADH converted to NAD+ for use in step 5. How cells (muscle especially) accomplish this? Pyruvate (Py), the end product of glycolysis, is converted to lactate. At the same time NADH is converted to NAD+. This regenerates NAD+ for use in glycolysis. lactate ...
... For next round of glycolysis to occur need NADH converted to NAD+ for use in step 5. How cells (muscle especially) accomplish this? Pyruvate (Py), the end product of glycolysis, is converted to lactate. At the same time NADH is converted to NAD+. This regenerates NAD+ for use in glycolysis. lactate ...
Magic Lysis Buffer Improves the Efficiency of
... bait-prey binding partners. In addition, caution must be taken about the stringency of lysis buffer since it can strip the bait protein of true binding partners. These problems are especially true for IPs using antibodies against endogenous proteins. However, IPs using endogenous antibodies are nece ...
... bait-prey binding partners. In addition, caution must be taken about the stringency of lysis buffer since it can strip the bait protein of true binding partners. These problems are especially true for IPs using antibodies against endogenous proteins. However, IPs using endogenous antibodies are nece ...
6. Respiration - WordPress.com
... 5. State that Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of cells 6. Outline the process of Glycolysis, beginning with the phosphorylation of glucose to hexose bisphosphate, splitting of hexose bisphosphate into two triose phosphate molecules and further oxidation to pyruvate, producing a small yield of ATP ...
... 5. State that Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of cells 6. Outline the process of Glycolysis, beginning with the phosphorylation of glucose to hexose bisphosphate, splitting of hexose bisphosphate into two triose phosphate molecules and further oxidation to pyruvate, producing a small yield of ATP ...
ENZYMES Characteristics of enzymes: Enzymes are proteins
... Remember that enzymes are protein catalysts and are easily denatured by changes in TEMPERATURE. Every enzyme has an OPTIMAL TEMPERATURE at which it works best. Too cold - enzyme and substrate take longer to combine Too hot – enzyme denatures and can no longer function properly Most enzymes function ...
... Remember that enzymes are protein catalysts and are easily denatured by changes in TEMPERATURE. Every enzyme has an OPTIMAL TEMPERATURE at which it works best. Too cold - enzyme and substrate take longer to combine Too hot – enzyme denatures and can no longer function properly Most enzymes function ...
Scientific articles
... this study, we investigated the involvement of CSP1 in insulin-dependent GLUT4 recruitment in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Over-expression of wild-type CSP1 led to attenuated insulin-stimulated glucose uptake without any change in GLUT4 content in the plasma membrane, rather it inhibits docking by blocking th ...
... this study, we investigated the involvement of CSP1 in insulin-dependent GLUT4 recruitment in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Over-expression of wild-type CSP1 led to attenuated insulin-stimulated glucose uptake without any change in GLUT4 content in the plasma membrane, rather it inhibits docking by blocking th ...
Glycolysis & Fermentation
... 5 Steps in Krebs cycle Step 1 – produces citric acid Step 2 – releases CO2 Step 3 – releases CO2 Step 4 – conversion of 4-carbon compound Step 5 – 4-carbon compound converted back to oxaloacetic acid ...
... 5 Steps in Krebs cycle Step 1 – produces citric acid Step 2 – releases CO2 Step 3 – releases CO2 Step 4 – conversion of 4-carbon compound Step 5 – 4-carbon compound converted back to oxaloacetic acid ...
LowSlides
... INTRACELLULAR RECEPTORS:“LIGAND-ACTIVATED TRANSCRIPTION FACTORS” HORMONES WITH INTRACELLULAR RECEPTORS ARE HYDROPHOBIC ALLOWING ...
... INTRACELLULAR RECEPTORS:“LIGAND-ACTIVATED TRANSCRIPTION FACTORS” HORMONES WITH INTRACELLULAR RECEPTORS ARE HYDROPHOBIC ALLOWING ...
Phosphorylation

Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation and its counterpart, dephosphorylation, turn many protein enzymes on and off, thereby altering their function and activity. Protein phosphorylation is one type of post-translational modification.Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes. Its prominent role in biochemistry is the subject of a very large body of research (as of March 2015, the Medline database returns over 240,000 articles on the subject, largely on protein phosphorylation).























