AMPK and mTOR: Antagonist ATP Sensors
... ATP decreases, which works antagonistically to mTOR). The main energy-consuming process in a cell is protein synthesis. When mTOR is activated (high ATP levels sensed) protein synthesis is increased and when mTOR is suppressed (low ATP levels are sensed) protein synthesis is blunted. mTOR activation ...
... ATP decreases, which works antagonistically to mTOR). The main energy-consuming process in a cell is protein synthesis. When mTOR is activated (high ATP levels sensed) protein synthesis is increased and when mTOR is suppressed (low ATP levels are sensed) protein synthesis is blunted. mTOR activation ...
File
... After about 3 days of starvation, the liver forms large amounts of acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate (ketone bodies). Their synthesis from acetyl CoA increases markedly because the citric acid cycle is unable to oxidize all the acetyl units generated by the degradation of fatty acids. Gluconeogenes ...
... After about 3 days of starvation, the liver forms large amounts of acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate (ketone bodies). Their synthesis from acetyl CoA increases markedly because the citric acid cycle is unable to oxidize all the acetyl units generated by the degradation of fatty acids. Gluconeogenes ...
Problem-Set Solutions
... phosphoenolpyruvate, can also act as an intermediate in the first step of the citric acid cycle; oxaloacetate combines with acetyl CoA, which can go directly into the citric acid cycle. 24.70 GTP and ATP 24.71 Lactate formed by muscle activity diffuses into the blood and is carried to the liver wher ...
... phosphoenolpyruvate, can also act as an intermediate in the first step of the citric acid cycle; oxaloacetate combines with acetyl CoA, which can go directly into the citric acid cycle. 24.70 GTP and ATP 24.71 Lactate formed by muscle activity diffuses into the blood and is carried to the liver wher ...
AP Biology Ch. 9 Cellular Respiration
... without oxygen. It only releases a small amount of ATP. Glycolysis: the first step of breaking down glucose—it splits glucose (6C) into 2 pyruvic acid molecules (3C each) ...
... without oxygen. It only releases a small amount of ATP. Glycolysis: the first step of breaking down glucose—it splits glucose (6C) into 2 pyruvic acid molecules (3C each) ...
PPT slides - USD Biology
... – Main stores of glycogen in the body are in the liver, but stores are also present in the heart and in skeletal muscle. – Skeletal muscle stores important for burst activity. ...
... – Main stores of glycogen in the body are in the liver, but stores are also present in the heart and in skeletal muscle. – Skeletal muscle stores important for burst activity. ...
BIOL 103 Ch5-2 for Students
... High Blood Glucose: Diabetes Mellitus • What is diabetes? Disorder of carbohydrate metabolism – Normally: • Eat food with glucose ________________________________ • If too much blood glucose pancreas releases ___________ _______________________________ ...
... High Blood Glucose: Diabetes Mellitus • What is diabetes? Disorder of carbohydrate metabolism – Normally: • Eat food with glucose ________________________________ • If too much blood glucose pancreas releases ___________ _______________________________ ...
Regulation of plasmodesmal transport by phosphorylation of
... 1997; Rhee et al., 2000; Tz®ra et al., 2000). Potentially, MP activity within infected cells may be negatively regulated to prevent its continuous interference with the host plant intercellular communication. The molecular mechanism by which such regulation may occur is unknown. Here, we address thi ...
... 1997; Rhee et al., 2000; Tz®ra et al., 2000). Potentially, MP activity within infected cells may be negatively regulated to prevent its continuous interference with the host plant intercellular communication. The molecular mechanism by which such regulation may occur is unknown. Here, we address thi ...
Ketamalt® 50
... – sugars, starches, amino acids and propylene glycol. In addition, Ketamalt® contains DIASTASE, a natural starch converting enzyme that converts starches present in the rumen to simple sugars. Propylene glycol is only one source of oral glucose precursor used to reverse ketosis in ruminants. Althoug ...
... – sugars, starches, amino acids and propylene glycol. In addition, Ketamalt® contains DIASTASE, a natural starch converting enzyme that converts starches present in the rumen to simple sugars. Propylene glycol is only one source of oral glucose precursor used to reverse ketosis in ruminants. Althoug ...
Phosphorylation of Single Stranded RNA Virus Proteins and
... transfer that mediates host transcriptional regulation. Signal transduction through Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) cascades constitutes another prominent example where multiple kinases are successively phosphorylated that ultimately leads to transcriptional activation involving a phosphoryl ...
... transfer that mediates host transcriptional regulation. Signal transduction through Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) cascades constitutes another prominent example where multiple kinases are successively phosphorylated that ultimately leads to transcriptional activation involving a phosphoryl ...
Cellular Respiration
... Cellular Respiration, process in which cells produce the energy they need to survive. In cellular respiration, cells use oxygen to break down the sugar glucose and store its energy in molecules of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Cellular respiration is critical for the survival of most organisms becau ...
... Cellular Respiration, process in which cells produce the energy they need to survive. In cellular respiration, cells use oxygen to break down the sugar glucose and store its energy in molecules of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Cellular respiration is critical for the survival of most organisms becau ...
Sources of blood glucose
... • insulin stimulates the synthesis of an enzyme (glucokinase) • Required to ‘trap’ glucose in the cell • initiates glycogen production ...
... • insulin stimulates the synthesis of an enzyme (glucokinase) • Required to ‘trap’ glucose in the cell • initiates glycogen production ...
Protein
... an athlete would need an extra 7-8 g protein/day intake. – 1 oz meat, 1 cup milk, 3 slices bread. ...
... an athlete would need an extra 7-8 g protein/day intake. – 1 oz meat, 1 cup milk, 3 slices bread. ...
Cell Respiration
... You should now be able to: 1. Explain in general terms how redox reactions are involved in energy exchanges 2. Name the three stages of cellular respiration; for each, state the region of the eukaryotic cell where it occurs and the products that result 3. In general terms, explain the role of the e ...
... You should now be able to: 1. Explain in general terms how redox reactions are involved in energy exchanges 2. Name the three stages of cellular respiration; for each, state the region of the eukaryotic cell where it occurs and the products that result 3. In general terms, explain the role of the e ...
Mock Exam 1 Chapters 1 – 7 Anthony Todd http
... hydrophilic surfaces facing the cytoplasm b. Only certain membranes of the cell are selectively permeable c. Certain proteins are unique to each membrane d. Only certain membranes have phospholipids e. Only certain membranes consist of amphipathic molecules 25. The maximum size of a cell is limited ...
... hydrophilic surfaces facing the cytoplasm b. Only certain membranes of the cell are selectively permeable c. Certain proteins are unique to each membrane d. Only certain membranes have phospholipids e. Only certain membranes consist of amphipathic molecules 25. The maximum size of a cell is limited ...
Cellular Respiration
... Phosphofructokinase (catalyzes step 3 of Glycolysis) controls C.R. It is activated by ADP and inhibited by ATP NADH inhibits pyruvate decarboxylase and prevents Acetyl-CoA from forming An organism’s Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy consumed by an organism in a given time. ...
... Phosphofructokinase (catalyzes step 3 of Glycolysis) controls C.R. It is activated by ADP and inhibited by ATP NADH inhibits pyruvate decarboxylase and prevents Acetyl-CoA from forming An organism’s Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy consumed by an organism in a given time. ...
Cell Respiration
... You should now be able to: 1. Explain in general terms how redox reactions are involved in energy exchanges 2. Name the three stages of cellular respiration; for each, state the region of the eukaryotic cell where it occurs and the products that result 3. In general terms, explain the role of the e ...
... You should now be able to: 1. Explain in general terms how redox reactions are involved in energy exchanges 2. Name the three stages of cellular respiration; for each, state the region of the eukaryotic cell where it occurs and the products that result 3. In general terms, explain the role of the e ...
Cellular respiration occurs in three stages
... in the presence of oxygen, the two pyruvate molecules produced by glycolysis travel to mitochondria Krebs Cycle has 8 steps, each step is catalyzed by a different enzyme Each cycling requires the input of 2-carbon acetyl-CoA and two carbons are released as C02 glycolysis results in the product ...
... in the presence of oxygen, the two pyruvate molecules produced by glycolysis travel to mitochondria Krebs Cycle has 8 steps, each step is catalyzed by a different enzyme Each cycling requires the input of 2-carbon acetyl-CoA and two carbons are released as C02 glycolysis results in the product ...
Signal Transduction Pathways • Signal Transduction
... triggers smooth muscle contraction, glycogen breakdown, and vesicle release Calcium is also a signal molecule: it can bind proteins called calmodulin and enzymes such as protein kinase C ...
... triggers smooth muscle contraction, glycogen breakdown, and vesicle release Calcium is also a signal molecule: it can bind proteins called calmodulin and enzymes such as protein kinase C ...
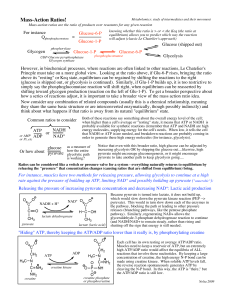
Mass-Action Ratios!
... Ratios can be considered like a switch or pressure valve for a system - everything naturally returns to equilibrium by releasing the "pressure" that concentration changes (causing ratios that are shifted from equilibrium) bring. ...
... Ratios can be considered like a switch or pressure valve for a system - everything naturally returns to equilibrium by releasing the "pressure" that concentration changes (causing ratios that are shifted from equilibrium) bring. ...
Chapter 9 review sheet
... phosphofructokinase, G3P, FAD, FADH2, glycolysis, glucose, cytosol, inner mitochondrial membrane, outer mitochondrial membrane, preparatory phase, energy payoff phase, intermembrane space, ATP synthase, oxygen, hydrolysed, ATP, ADP, Pi, H+(protons), electrochemical gradient, cristae, Coenzyme A, pyr ...
... phosphofructokinase, G3P, FAD, FADH2, glycolysis, glucose, cytosol, inner mitochondrial membrane, outer mitochondrial membrane, preparatory phase, energy payoff phase, intermembrane space, ATP synthase, oxygen, hydrolysed, ATP, ADP, Pi, H+(protons), electrochemical gradient, cristae, Coenzyme A, pyr ...
Muscles
... calmodulin: CM-4Ca2+ • Ca2+-CM stimulates all Ca2+-pumps (some by phosphorylation) which decrease the Ca2+ concentration in sarcoplasm • the increase of intracellular [Ca2+] triggers contraction but, at the same time, stimulates relaxation processes ...
... calmodulin: CM-4Ca2+ • Ca2+-CM stimulates all Ca2+-pumps (some by phosphorylation) which decrease the Ca2+ concentration in sarcoplasm • the increase of intracellular [Ca2+] triggers contraction but, at the same time, stimulates relaxation processes ...
aerobic respiration
... ↑ surface area of inner membrane, which ↑ capacity to generate ATP Matrix Contains 100s of enzymes which oxidize pyruvate and fatty acids, and control the Krebs cycle ...
... ↑ surface area of inner membrane, which ↑ capacity to generate ATP Matrix Contains 100s of enzymes which oxidize pyruvate and fatty acids, and control the Krebs cycle ...
BCHM 463 Supplemental Problems for Friday, April 2, 2004 1. Write
... Rxn 3: phosphofructo kinase: ATP is an allosteric inhibitor; AMP, ADP, F2,6P, and other compounds overcome this inhibition and therefore serve as activators Rxn 10: pyruvate kinase: product inhibition by ATP (allosteric); FBP acts as an allosteric activator 11. Xylose has the same structure as gluco ...
... Rxn 3: phosphofructo kinase: ATP is an allosteric inhibitor; AMP, ADP, F2,6P, and other compounds overcome this inhibition and therefore serve as activators Rxn 10: pyruvate kinase: product inhibition by ATP (allosteric); FBP acts as an allosteric activator 11. Xylose has the same structure as gluco ...
2. tissue - specific metabolism - cmb
... When glucose levels are adequate, the production of dihydroxyacetone phosphate generates enough glycerol-3-phosphate for the resynthesis of triacylglycerols from the released fatty acids. When intracellular glucose levels fall, the concentration of glycerol-3-phosphate falls also, and fatty acids ar ...
... When glucose levels are adequate, the production of dihydroxyacetone phosphate generates enough glycerol-3-phosphate for the resynthesis of triacylglycerols from the released fatty acids. When intracellular glucose levels fall, the concentration of glycerol-3-phosphate falls also, and fatty acids ar ...
Structural biology reveals links between Inflammation and Metabolic
... 1. To characterize the binding properties of superantigens with gp130 through structural and functional in vitro analyses. Results: The Superantigen, SEA, was shown to bind to gp130 in the micromolar range using SPR-analyses (Banke et al., 2014). Moreover, SEA was also shown to activate gp130 signal ...
... 1. To characterize the binding properties of superantigens with gp130 through structural and functional in vitro analyses. Results: The Superantigen, SEA, was shown to bind to gp130 in the micromolar range using SPR-analyses (Banke et al., 2014). Moreover, SEA was also shown to activate gp130 signal ...
Phosphorylation

Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation and its counterpart, dephosphorylation, turn many protein enzymes on and off, thereby altering their function and activity. Protein phosphorylation is one type of post-translational modification.Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes. Its prominent role in biochemistry is the subject of a very large body of research (as of March 2015, the Medline database returns over 240,000 articles on the subject, largely on protein phosphorylation).