Ch. 9: Cellular Respiration
... compounds other than O2 Fermentation: partial degradation of sugars that occurs without O2 Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins all consumed as fuel, however it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy (ATP + heat) ...
... compounds other than O2 Fermentation: partial degradation of sugars that occurs without O2 Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins all consumed as fuel, however it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy (ATP + heat) ...
2-Phospho
... • Oxidative phosphorylation accounts for almost 90% of the ATP generated by cellular respiration • A smaller amount of ATP is formed in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle by substrate-level phosphorylation 受質階層 磷酸化反應 • For each molecule of glucose degraded to CO2 and water by respiration, the cel ...
... • Oxidative phosphorylation accounts for almost 90% of the ATP generated by cellular respiration • A smaller amount of ATP is formed in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle by substrate-level phosphorylation 受質階層 磷酸化反應 • For each molecule of glucose degraded to CO2 and water by respiration, the cel ...
"Central Pathways of Carbohydrate Metabolism". In: Microbial
... ALTERNATE PATHWAYS OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM ...
... ALTERNATE PATHWAYS OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM ...
NAD - wwphs
... Enzymes (Cytochromes) and ATP synthase on membrane to shuttle electrons and protons NADH, FADH2 gives up the H H+ + e Electrons are passed through the membrane proteins and the energy released is used to transport the H to the outer membrane The gradient established is the force needed to allow the ...
... Enzymes (Cytochromes) and ATP synthase on membrane to shuttle electrons and protons NADH, FADH2 gives up the H H+ + e Electrons are passed through the membrane proteins and the energy released is used to transport the H to the outer membrane The gradient established is the force needed to allow the ...
glycolysis and respiration
... Anabolism - the chemical reactions that form larger molecules from smaller molecules. It is usually an endergonic process. Autotroph - an organism that obtains its energy from sunlight or inorganic chemicals. Plants, photosynthetic protists, and photosynthetic prokaryotes are autotrophs. Heterotroph ...
... Anabolism - the chemical reactions that form larger molecules from smaller molecules. It is usually an endergonic process. Autotroph - an organism that obtains its energy from sunlight or inorganic chemicals. Plants, photosynthetic protists, and photosynthetic prokaryotes are autotrophs. Heterotroph ...
Characterization of a AT-Bromoacetyl-L-Thyroxine Affinity
... the Kd1/3 was 4.14 ± 0.1 nm (Fig. 5, inset). A second smaller peak (27%) present in fractions 35-37 (p55-II) migrated with an estimated mol wt of ~54,000 and a Stokes radius of 3.07 ± 0.09 nm, and most likely represents a protein monomer. The hydrodynamic properties of glial-p55 were determined from ...
... the Kd1/3 was 4.14 ± 0.1 nm (Fig. 5, inset). A second smaller peak (27%) present in fractions 35-37 (p55-II) migrated with an estimated mol wt of ~54,000 and a Stokes radius of 3.07 ± 0.09 nm, and most likely represents a protein monomer. The hydrodynamic properties of glial-p55 were determined from ...
Figure E Functional classification of crop proteins into COG
... microbiome analyses, 6 pens/diet were first chosen. All other animals were used for other investigations. For metaproteomic analyses, 4 animals each from 2 pens/diets were randomly selected. Collected content of crop and ceca was homogenized on a pen basis yielding two crop and cecal samples per die ...
... microbiome analyses, 6 pens/diet were first chosen. All other animals were used for other investigations. For metaproteomic analyses, 4 animals each from 2 pens/diets were randomly selected. Collected content of crop and ceca was homogenized on a pen basis yielding two crop and cecal samples per die ...
Stress signaling from the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum
... (Masuda et al. 1983). In addition to changes in the transcriptional machinery, the immediate response to the accumulation of unfolded proteins in the ER occurs at the translational level to inhibit translation initiation, thereby protecting from further accumulation of unfolded proteins, as well as ...
... (Masuda et al. 1983). In addition to changes in the transcriptional machinery, the immediate response to the accumulation of unfolded proteins in the ER occurs at the translational level to inhibit translation initiation, thereby protecting from further accumulation of unfolded proteins, as well as ...
Citric acid cycle
... • Before the citric acid cycle can begin – Pyruvate must first be converted to acetyl CoA, which links the cycle to glycolysis – Fully oxidized carboxyl group is removed as a CO2 – The remaining two-carbon fragment is oxidized to acetate. The extracted electrons are transferred to NAD+, forming NAD ...
... • Before the citric acid cycle can begin – Pyruvate must first be converted to acetyl CoA, which links the cycle to glycolysis – Fully oxidized carboxyl group is removed as a CO2 – The remaining two-carbon fragment is oxidized to acetate. The extracted electrons are transferred to NAD+, forming NAD ...
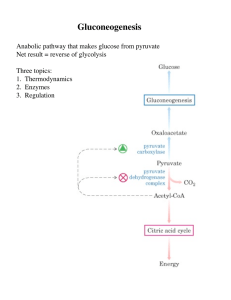
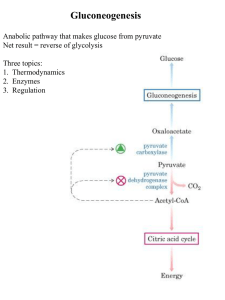
Gluconeogenesis - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... (2) Inhibits FBPase-1 and slows -genesis (3) not an intermediate of -lysis or -genesis (4) a regulator whose cellular level reflects level of glucagon in blood, ...
... (2) Inhibits FBPase-1 and slows -genesis (3) not an intermediate of -lysis or -genesis (4) a regulator whose cellular level reflects level of glucagon in blood, ...
No Slide Title
... (2) Inhibits FBPase-1 and slows -genesis (3) not an intermediate of -lysis or -genesis (4) a regulator whose cellular level reflects level of glucagon in blood, ...
... (2) Inhibits FBPase-1 and slows -genesis (3) not an intermediate of -lysis or -genesis (4) a regulator whose cellular level reflects level of glucagon in blood, ...
1+1+1 - Computer Science, Columbia University
... TAHIIYNSVDKRLSAVVSYPNADSATVSYDVDLDNVLPEWVRVGLSAS TGLYKETNTILSWSFTSKLKSNSTHETNALHFMFNQFSKDQKDLILQG DATTGTDGNLELTRVSSNGPQGSSVGRALFYAPVHIWESSAVVASFEA TFTFLIKSPDSHPADGIAFFISNIDSSIPSGSTGRLLGLFPDAN ...
... TAHIIYNSVDKRLSAVVSYPNADSATVSYDVDLDNVLPEWVRVGLSAS TGLYKETNTILSWSFTSKLKSNSTHETNALHFMFNQFSKDQKDLILQG DATTGTDGNLELTRVSSNGPQGSSVGRALFYAPVHIWESSAVVASFEA TFTFLIKSPDSHPADGIAFFISNIDSSIPSGSTGRLLGLFPDAN ...
ATP - HEDCen Science
... • The process in cell respiration that generates most of the ATP is oxidative phosphorylation (powered by redox reactions). • Oxidative phosphorylation accounts for almost 90% of the ATP generated by cellular respiration. • A smaller amount of ATP is formed in glycolysis and the citric acid / Krebs ...
... • The process in cell respiration that generates most of the ATP is oxidative phosphorylation (powered by redox reactions). • Oxidative phosphorylation accounts for almost 90% of the ATP generated by cellular respiration. • A smaller amount of ATP is formed in glycolysis and the citric acid / Krebs ...
Phosphoketolase pathway dominates in
... the dry weights of the samples, and, hence, the signal-to-noise levels vary between the spectra. Duplicate samples from different batch cultures were analyzed in this study, and the spectra showed the same results. Enzyme assays. Cell extracts were prepared from cultures harvested in the late expone ...
... the dry weights of the samples, and, hence, the signal-to-noise levels vary between the spectra. Duplicate samples from different batch cultures were analyzed in this study, and the spectra showed the same results. Enzyme assays. Cell extracts were prepared from cultures harvested in the late expone ...
Analysis of Kinase Effects on Viral Replication of the Papillomavirus
... papillomavims DNA replication can only occur during the host cellS-phase of the cell cycle [7, 10, 17, 24]. Following viral attachment, entry, and nucleocapsid disassembly, initial infection and viral latency are characterized by low viral genome copy number (50-200 per cell) and minimal gene expres ...
... papillomavims DNA replication can only occur during the host cellS-phase of the cell cycle [7, 10, 17, 24]. Following viral attachment, entry, and nucleocapsid disassembly, initial infection and viral latency are characterized by low viral genome copy number (50-200 per cell) and minimal gene expres ...
Lecture 9
... • The body uses small molecules to build other substances • These small molecules may come directly from food, from glycolysis, or from the citric acid cycle ...
... • The body uses small molecules to build other substances • These small molecules may come directly from food, from glycolysis, or from the citric acid cycle ...
You Light Up My Life
... Electrons from first-stage reactions are delivered to NAD+ in mitochondria ...
... Electrons from first-stage reactions are delivered to NAD+ in mitochondria ...
Chapter 6
... have a positive charge. So there is now a greater positive charge on one side of the membrane than the other. There is an electrochemical gradient. The hydrogen ions are now allowed to diffuse down this gradient. They have to pass through a group of protein molecules in the membrane that form a spec ...
... have a positive charge. So there is now a greater positive charge on one side of the membrane than the other. There is an electrochemical gradient. The hydrogen ions are now allowed to diffuse down this gradient. They have to pass through a group of protein molecules in the membrane that form a spec ...
Molecular Mechanisms of Transforming Growth Factor
... a variety of biological processes, and loss of TGF-b responsiveness as an important correlate of certain diseases, a tremendous effort has been undertaken in the last decade to elucidate the mechanisms by which TGF-b propagates its signal. An important step in understanding TGF-b signaling came with ...
... a variety of biological processes, and loss of TGF-b responsiveness as an important correlate of certain diseases, a tremendous effort has been undertaken in the last decade to elucidate the mechanisms by which TGF-b propagates its signal. An important step in understanding TGF-b signaling came with ...
©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies
... biochemistry, sugars play another role besides being the main energy source for metabolism via the process of glycolysis – they can also combine with proteins to create glycoprotein hormones that are essential for all mammal reproduction or combine with lipids to create glycolipids which make up par ...
... biochemistry, sugars play another role besides being the main energy source for metabolism via the process of glycolysis – they can also combine with proteins to create glycoprotein hormones that are essential for all mammal reproduction or combine with lipids to create glycolipids which make up par ...
PDF
... first considered the use of 32PO4 metabolic labeling. However, because the expression level of NPR2 in native tissues is low, this approach has only been feasible for overexpressing cells (Potter, 1998). The NPR2 fraction of the total cell protein in ovarian follicles is ∼5% of that in the 3T3 cells ...
... first considered the use of 32PO4 metabolic labeling. However, because the expression level of NPR2 in native tissues is low, this approach has only been feasible for overexpressing cells (Potter, 1998). The NPR2 fraction of the total cell protein in ovarian follicles is ∼5% of that in the 3T3 cells ...
Phosphorylation

Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation and its counterpart, dephosphorylation, turn many protein enzymes on and off, thereby altering their function and activity. Protein phosphorylation is one type of post-translational modification.Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes. Its prominent role in biochemistry is the subject of a very large body of research (as of March 2015, the Medline database returns over 240,000 articles on the subject, largely on protein phosphorylation).