Regulation of carbohydrate metabolism
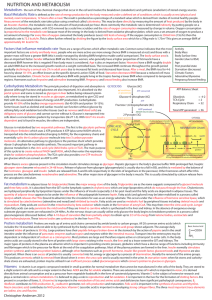
... Major sites of glucagone action on fuel metabolism: Mobilization of energy stores 1. release of glucose from liver glycogen 2. stimulating gluconeogenesis from lactate, glycerol, and amino acids (liver) 3. mobilizing fatty acids (adipose tissue) ...
... Major sites of glucagone action on fuel metabolism: Mobilization of energy stores 1. release of glucose from liver glycogen 2. stimulating gluconeogenesis from lactate, glycerol, and amino acids (liver) 3. mobilizing fatty acids (adipose tissue) ...
Nutrition and Metabolism
... glucose (although fructose and galactose are also important). It is absorbed via the hexokinase ATP consumed or glucokinase portal system and some is stored as glycogen in liver before being released sytemically where is may be stored in muscles as glycogen, or metabolised to give CO2 and Glycolysis ...
... glucose (although fructose and galactose are also important). It is absorbed via the hexokinase ATP consumed or glucokinase portal system and some is stored as glycogen in liver before being released sytemically where is may be stored in muscles as glycogen, or metabolised to give CO2 and Glycolysis ...
WEEK FOUR
... is needed in metabolic processes. The glucose is released from glycogen by enzymatic breakdown of glycogenolysis. The glycogen stored are derived from absorbed glucose or from glucose formed by gluconeogenesis. The fate of glucose removed from the blood - the glucose removed from the blood into cell ...
... is needed in metabolic processes. The glucose is released from glycogen by enzymatic breakdown of glycogenolysis. The glycogen stored are derived from absorbed glucose or from glucose formed by gluconeogenesis. The fate of glucose removed from the blood - the glucose removed from the blood into cell ...
Balance Between Protein Synthesis and Degradation
... negative balanced is observed when amino acids used for tissue building and energy are not replaced. In eukaryotes nitrogen balance can be affected by several catabolic conditions, such as disease, starvation, trauma, metabolic acidosis, composition of diet, and stage of growth. Regulation of Protei ...
... negative balanced is observed when amino acids used for tissue building and energy are not replaced. In eukaryotes nitrogen balance can be affected by several catabolic conditions, such as disease, starvation, trauma, metabolic acidosis, composition of diet, and stage of growth. Regulation of Protei ...
Overview of Absorptive/Post-Absorptive States
... stores (glycogenolysis) into glucose in response to the rising levels of glucagon (released by alpha cells of the pancreatic islets) and epinephrine, thus beginning the post-‐absorptive state (step “1” in Fi ...
... stores (glycogenolysis) into glucose in response to the rising levels of glucagon (released by alpha cells of the pancreatic islets) and epinephrine, thus beginning the post-‐absorptive state (step “1” in Fi ...
Cellular Respiration
... “Reduced” means that the overall positive charge of the molecule has decreased (due to accepting the electons!) ...
... “Reduced” means that the overall positive charge of the molecule has decreased (due to accepting the electons!) ...
NME2.31 - Energy Production
... One mole of NADH goes through steps 1 to 5 producing 2.5 ATP One mole of FADH2 goes through steps 2 to 5 producing 1.5 ATP Low ATP usage results in an accumulated proton gradient stopping electron transport ...
... One mole of NADH goes through steps 1 to 5 producing 2.5 ATP One mole of FADH2 goes through steps 2 to 5 producing 1.5 ATP Low ATP usage results in an accumulated proton gradient stopping electron transport ...
Bauman Chapter 1 Answers to Critical Thinking Questions
... which release the energy stored in complex molecules, but the energy capture is not highly efficient, much energy is lost, and it requires more energy to re-form the metabolites than is captured from their catabolism. Photophosphorylation is ultimately driven by light energy, which provides enough e ...
... which release the energy stored in complex molecules, but the energy capture is not highly efficient, much energy is lost, and it requires more energy to re-form the metabolites than is captured from their catabolism. Photophosphorylation is ultimately driven by light energy, which provides enough e ...
Cellular Respiration Review
... What are the number and type of input molecules for the ETC? What molecule gets reduced during the ETC? What molecule gets oxidized during the ETC? What are the number and type of output molecules for the ETC? How is each output molecule from the ETC used? What is the net gain of ATP from the ETC? W ...
... What are the number and type of input molecules for the ETC? What molecule gets reduced during the ETC? What molecule gets oxidized during the ETC? What are the number and type of output molecules for the ETC? How is each output molecule from the ETC used? What is the net gain of ATP from the ETC? W ...
GenLysate, Mouse Liver Mitochondria Cell Fraction
... 1. Briefly spin the tube containing GenLysate™ and reconstitute in 30μl de-ionized water to give 5μg/μl concentration. 2. Add an appropriate volume of sample buffer containing a reducing agent (e.g. 5% β−mercaptoethanol or 5-20mM DTT final concentration) in the reconstituted GenLysate tube. 3. The G ...
... 1. Briefly spin the tube containing GenLysate™ and reconstitute in 30μl de-ionized water to give 5μg/μl concentration. 2. Add an appropriate volume of sample buffer containing a reducing agent (e.g. 5% β−mercaptoethanol or 5-20mM DTT final concentration) in the reconstituted GenLysate tube. 3. The G ...
HERE
... Which of the following is the correct sequence for the oxidation of glucose to produce ATP? A. Electron transport chain. B. Kreb’s cycle. C. Glycolysis. D. Formation of acetyl CoA. Correct order: ___→ __ → __ → _ ANSWER ...
... Which of the following is the correct sequence for the oxidation of glucose to produce ATP? A. Electron transport chain. B. Kreb’s cycle. C. Glycolysis. D. Formation of acetyl CoA. Correct order: ___→ __ → __ → _ ANSWER ...
Chapter 16 solutions
... two- to fivefold increase in the level of lactate in the blood, a far greater increase than that observed after the infusion of the same amount of glucose. (a) Why is glycolysis more rapid after the infusion of fructose? (b) Fructose has been used in place of glucose for intravenous feeding. Why is ...
... two- to fivefold increase in the level of lactate in the blood, a far greater increase than that observed after the infusion of the same amount of glucose. (a) Why is glycolysis more rapid after the infusion of fructose? (b) Fructose has been used in place of glucose for intravenous feeding. Why is ...
Bio Rad Proposal
... 1. Students will generate protein profile from the muscles of distantly and closely related species of fish. 2. Compare and contrast these profiles to the hypothesis that protein profiles are indicators of genetic and evolutionary relatedness: DNA>RNA>Protein>Trait Background: Changes in proteins re ...
... 1. Students will generate protein profile from the muscles of distantly and closely related species of fish. 2. Compare and contrast these profiles to the hypothesis that protein profiles are indicators of genetic and evolutionary relatedness: DNA>RNA>Protein>Trait Background: Changes in proteins re ...
Cell Respiration RG
... 16. Complete the summary diagram of cellular respiration. You are responsible for these #’s and locations! ...
... 16. Complete the summary diagram of cellular respiration. You are responsible for these #’s and locations! ...
Cori Cycle - COFFEE BREAK CORNER
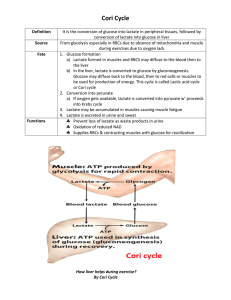
... It is the conversion of glucose into lactate in peripheral tissues, followed by conversion of lactate into glucose in liver From glycolysis especially in RBCs due to absence of mitochondria and muscle ...
... It is the conversion of glucose into lactate in peripheral tissues, followed by conversion of lactate into glucose in liver From glycolysis especially in RBCs due to absence of mitochondria and muscle ...
Supplemental Materials and Methods
... Linked heterodimer fusion protein constructs for Bcl-xL–Bak, Mcl1–Bak, and Bax–Bcl-2 were made using synthetic DNA (Life Technologies) with Gateway attB1 and attB2 sites flanking the insert region. His6MBP (maltose binding protein) tags were used to enhance solubility and permit affinity purificatio ...
... Linked heterodimer fusion protein constructs for Bcl-xL–Bak, Mcl1–Bak, and Bax–Bcl-2 were made using synthetic DNA (Life Technologies) with Gateway attB1 and attB2 sites flanking the insert region. His6MBP (maltose binding protein) tags were used to enhance solubility and permit affinity purificatio ...
Spotlight on Metabolism
... – The prolonged fast: In the beginning • Blood glucose drops, liver breaks down glycogen to glucose • Gluconeogenesis • Fat and protein are primary fuel ...
... – The prolonged fast: In the beginning • Blood glucose drops, liver breaks down glycogen to glucose • Gluconeogenesis • Fat and protein are primary fuel ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... The third step is attachment of a second phosphate group to fructose-6-phosphate to form fructose-1,6-diphosphate. This step is driven also by phosphate transfer from ATP and its Go’ is ________________. ...
... The third step is attachment of a second phosphate group to fructose-6-phosphate to form fructose-1,6-diphosphate. This step is driven also by phosphate transfer from ATP and its Go’ is ________________. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Ch. 6 Cellular Respiration
... • When ATP is made by movement of Hydrogen ions from high to low concentration via the protein ATP synthase. • How does a high concentration of hydrogen ions form in the first place? • H+ ions are actively transported using electron energy ...
... • When ATP is made by movement of Hydrogen ions from high to low concentration via the protein ATP synthase. • How does a high concentration of hydrogen ions form in the first place? • H+ ions are actively transported using electron energy ...
taqman protein assays
... protein input can be done (suitable endogenous controls do no yet exist). Fold change comparison between samples is also possible. ...
... protein input can be done (suitable endogenous controls do no yet exist). Fold change comparison between samples is also possible. ...
dependent phosphotransferase system – two highly similar glucose
... reaction by potential substrate analogues. A negative control was performed by adding the inhibitors as substrates. The reaction was performed using a glucose concentration five times higher than the calculated Km value, and a 10-, 100- or 1000-fold excess of the potential inhibitor was added. In th ...
... reaction by potential substrate analogues. A negative control was performed by adding the inhibitors as substrates. The reaction was performed using a glucose concentration five times higher than the calculated Km value, and a 10-, 100- or 1000-fold excess of the potential inhibitor was added. In th ...
Lecture 26
... A multienzyme complexes are groups of non covalently associated enzymes that catalyze two or more sequential steps in a metabolic pathway. Molecular weight of 4,600,000 Da E. coli ...
... A multienzyme complexes are groups of non covalently associated enzymes that catalyze two or more sequential steps in a metabolic pathway. Molecular weight of 4,600,000 Da E. coli ...
Phosphorylation

Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation and its counterpart, dephosphorylation, turn many protein enzymes on and off, thereby altering their function and activity. Protein phosphorylation is one type of post-translational modification.Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes. Its prominent role in biochemistry is the subject of a very large body of research (as of March 2015, the Medline database returns over 240,000 articles on the subject, largely on protein phosphorylation).