The origin of music as seen from evolutionary science and from
... Darwin (1981[1871]) reflected on its evolutionary emergence: “As neither the enjoyment nor the capacity of producing musical notes are faculties of the least direct use to man in reference to his ordinary habits of life, they must be ranked amongst the most mysterious with which he is endowed” (p. 3 ...
... Darwin (1981[1871]) reflected on its evolutionary emergence: “As neither the enjoyment nor the capacity of producing musical notes are faculties of the least direct use to man in reference to his ordinary habits of life, they must be ranked amongst the most mysterious with which he is endowed” (p. 3 ...
History - Bloom Public School
... sapiens originated in different regions (continents) and gradually evolved at different rates into modern humans. • According to the replacement model human beings first originated in a single region, which is Africa and migrated to all the other regions (continents). Pg.16 Early Humans: Ways of Obt ...
... sapiens originated in different regions (continents) and gradually evolved at different rates into modern humans. • According to the replacement model human beings first originated in a single region, which is Africa and migrated to all the other regions (continents). Pg.16 Early Humans: Ways of Obt ...
PDF 565k - Signata
... we all too readily assume that this utility itself drove the evolution of language by natural selection in our line (for which see Pinker & Bloom 1995). If so, one would expect that some of the other large-brained animals on earth would have evolved some version of it as well. Yet among the 15000 sp ...
... we all too readily assume that this utility itself drove the evolution of language by natural selection in our line (for which see Pinker & Bloom 1995). If so, one would expect that some of the other large-brained animals on earth would have evolved some version of it as well. Yet among the 15000 sp ...
Fulltext PDF
... dependence on material culture and the evolution of language. Language underlies and makes possible much of our social behaviour and interactions: "its most essential feature is that it allows human behaviour to be governed by the complex and subtle rules that together make up human culture". The an ...
... dependence on material culture and the evolution of language. Language underlies and makes possible much of our social behaviour and interactions: "its most essential feature is that it allows human behaviour to be governed by the complex and subtle rules that together make up human culture". The an ...
Language, gesture, skill: the co-evolutionary
... they are organized into subfunctions, rather than being a concatenated sequence of behavioural atoms. Thus he has argued that the Social Intelligence Hypothesis needs to be supplemented by a Technical Intelligence Hypothesis [46]. Byrne is right to emphasize the skilled basis of great ape life, but ...
... they are organized into subfunctions, rather than being a concatenated sequence of behavioural atoms. Thus he has argued that the Social Intelligence Hypothesis needs to be supplemented by a Technical Intelligence Hypothesis [46]. Byrne is right to emphasize the skilled basis of great ape life, but ...
Language, gesture, skill - Philosophical Transactions of the Royal
... they are organized into subfunctions, rather than being a concatenated sequence of behavioural atoms. Thus he has argued that the Social Intelligence Hypothesis needs to be supplemented by a Technical Intelligence Hypothesis [46]. Byrne is right to emphasize the skilled basis of great ape life, but ...
... they are organized into subfunctions, rather than being a concatenated sequence of behavioural atoms. Thus he has argued that the Social Intelligence Hypothesis needs to be supplemented by a Technical Intelligence Hypothesis [46]. Byrne is right to emphasize the skilled basis of great ape life, but ...
Ch 22 ppt
... • Neandertals cared for the aged and the sick, an indication of advanced social cooperation • They apparently had rituals, possibly of religious significance, and sometimes buried their dead ...
... • Neandertals cared for the aged and the sick, an indication of advanced social cooperation • They apparently had rituals, possibly of religious significance, and sometimes buried their dead ...
Chapter 10 - Non-verbal Information and Artistic Expression in the
... are their audience have a mind similar to their own and hence will comprehend their communication whether that is verbal or artistic. Those who study the origin of language consider the human capability of a theory of mind was a cognitive capability unique to humans that made verbal language possibl ...
... are their audience have a mind similar to their own and hence will comprehend their communication whether that is verbal or artistic. Those who study the origin of language consider the human capability of a theory of mind was a cognitive capability unique to humans that made verbal language possibl ...
EHO Facts Booklet - Bangor Public Library
... While our species, H. sapiens, has survived for about 200,000 years, some species of earlier humans thrived for several times longer before their extinction. Fossils of more than 6,000 individuals have been discovered so far, representing more than a dozen species of early humans. Only our species, ...
... While our species, H. sapiens, has survived for about 200,000 years, some species of earlier humans thrived for several times longer before their extinction. Fossils of more than 6,000 individuals have been discovered so far, representing more than a dozen species of early humans. Only our species, ...
Why Possibly Language Evolved - Department of Environmental
... intercellular communication systems for formal analogies to language, but as we learn more about how these systems work, they might be grist for comparative analysis. Interestingly, biologists have described many mechanisms by which rich internal communication systems are ‘policed’ to ensure a commu ...
... intercellular communication systems for formal analogies to language, but as we learn more about how these systems work, they might be grist for comparative analysis. Interestingly, biologists have described many mechanisms by which rich internal communication systems are ‘policed’ to ensure a commu ...
Chapter 4 - Glenelg High School
... Lower Paleolithic, the first part of the Old Stone Age, from about 200,000 to 2.6 million years ago. – Flakes were obtained from a “core” stone by striking it with stone or against a large rock. – The flakes that broke off had sharp edges, effective for cutting meat and scraping hides. – Leftover co ...
... Lower Paleolithic, the first part of the Old Stone Age, from about 200,000 to 2.6 million years ago. – Flakes were obtained from a “core” stone by striking it with stone or against a large rock. – The flakes that broke off had sharp edges, effective for cutting meat and scraping hides. – Leftover co ...
Human evolution
... - their brain are bigger than those of Prosimians - most of them are diurnal - bigger body size - they usually have single offspring than litters • humans bear particularly close affinity to other members of a group known as hominoids, or apes, which includes orangutans, gibbons, gorillas, chimpanze ...
... - their brain are bigger than those of Prosimians - most of them are diurnal - bigger body size - they usually have single offspring than litters • humans bear particularly close affinity to other members of a group known as hominoids, or apes, which includes orangutans, gibbons, gorillas, chimpanze ...
1 What makes humans special? - Assets
... Finally, chimpanzees (but not monkeys) are able to determine the mental states of others and to engage in mirror self-recognition (Lock and Colombo, 1996), attributes normally considered part of a general mental capability known as the “theory of mind” (see later chapters). What mostly defines humans ...
... Finally, chimpanzees (but not monkeys) are able to determine the mental states of others and to engage in mirror self-recognition (Lock and Colombo, 1996), attributes normally considered part of a general mental capability known as the “theory of mind” (see later chapters). What mostly defines humans ...
Section 7 - HCC Learning Web
... 8. During the Miocene there were many more forms of hominoids than there are today and it was known as ________________________ 9. hominoids ...
... 8. During the Miocene there were many more forms of hominoids than there are today and it was known as ________________________ 9. hominoids ...
The Consequences of Language
... and published were highly speculative and the evidence upon which they were based extremely limited. As a result, they concluded that they concluded that it was all a waste of time, because such theories, while interesting, did not advance our understandings of language origins beyond the earlier bi ...
... and published were highly speculative and the evidence upon which they were based extremely limited. As a result, they concluded that they concluded that it was all a waste of time, because such theories, while interesting, did not advance our understandings of language origins beyond the earlier bi ...
The New Science of Human Evolution
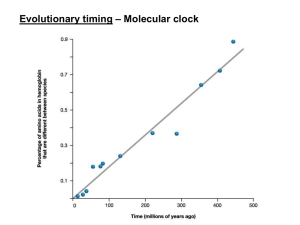
... scientists use this rate to calibrate a "molecular clock" whose tick-tocks measure how long ago a genetic change occurred. The fact that the DNA of living chimps and humans differ by about 35 million chemical "letters," for instance, implies that the two lineages split 5 million to 6 million years a ...
... scientists use this rate to calibrate a "molecular clock" whose tick-tocks measure how long ago a genetic change occurred. The fact that the DNA of living chimps and humans differ by about 35 million chemical "letters," for instance, implies that the two lineages split 5 million to 6 million years a ...
Evolutionary Narratives: A Cautionary Tale
... competition for these resources. If, and this is certainly not always the case, the randomly variable and inherited traits give those members of a species which possess them a competitive advantage over those who lack these traits (and by advantage here Darwin meant only an increased likelihood of s ...
... competition for these resources. If, and this is certainly not always the case, the randomly variable and inherited traits give those members of a species which possess them a competitive advantage over those who lack these traits (and by advantage here Darwin meant only an increased likelihood of s ...
Human Evolution
... additional brain capacity had resulted in advanced manual dexterity. It was applied to the making and using of simple tools (selected strong stones) to chip pebbles, for a purpose. Using tools to make tools (i.e. the development of a tool industry) is what distinguishes hominid toolmakers from all o ...
... additional brain capacity had resulted in advanced manual dexterity. It was applied to the making and using of simple tools (selected strong stones) to chip pebbles, for a purpose. Using tools to make tools (i.e. the development of a tool industry) is what distinguishes hominid toolmakers from all o ...
PowerPoint Chapter 4 - Bakersfield College
... Lower Paleolithic, the first part of the Old Stone Age, from about 200,000 to 2.6 million years ago. Flakes were obtained from a “core” stone by striking it with stone or against a large rock. The flakes that broke off had sharp edges, effective for cutting meat and scraping hides. Leftover co ...
... Lower Paleolithic, the first part of the Old Stone Age, from about 200,000 to 2.6 million years ago. Flakes were obtained from a “core” stone by striking it with stone or against a large rock. The flakes that broke off had sharp edges, effective for cutting meat and scraping hides. Leftover co ...
chapter 19 - Geoclassroom Home
... Classification of the Primates Enrichment Topic 1. Changing Tectonics, Climate, and Human Evolution East Africa is one of the most changed landscapes in recent geological history. Tectonic movements and climate changes influenced the area during the time that humans were evolving. As the Himalayans ...
... Classification of the Primates Enrichment Topic 1. Changing Tectonics, Climate, and Human Evolution East Africa is one of the most changed landscapes in recent geological history. Tectonic movements and climate changes influenced the area during the time that humans were evolving. As the Himalayans ...
Action Lecture powerpoint
... Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
human evolution
... 4. They were apelike above the waist and humanlike below the waist; human characteristics probably did not evolve all together at the same time. This is an example of mosaic evolution. D. East African Australopiths 1. Australopithecus afarensis is based on many skeletal fragments (Lucy) dated at 3.1 ...
... 4. They were apelike above the waist and humanlike below the waist; human characteristics probably did not evolve all together at the same time. This is an example of mosaic evolution. D. East African Australopiths 1. Australopithecus afarensis is based on many skeletal fragments (Lucy) dated at 3.1 ...