HUMAN EVOLUTION CART
... Ardi is a hominin species dated at 4.4 million years ago. It lived in the Afar Rift region of northeastern Ethiopia. Research has shown Ardipithecus ramidus was a denizen of woodland with small patches of forest. Scientists also learned that Ardi was probably more omnivorous than chimpanzees and was ...
... Ardi is a hominin species dated at 4.4 million years ago. It lived in the Afar Rift region of northeastern Ethiopia. Research has shown Ardipithecus ramidus was a denizen of woodland with small patches of forest. Scientists also learned that Ardi was probably more omnivorous than chimpanzees and was ...
EVOLUTION
... A. The mechanism for evolution is B. A progressive change in the characteristics of organisms is C. A trait that makes a species survival more likely is called a(n) ...
... A. The mechanism for evolution is B. A progressive change in the characteristics of organisms is C. A trait that makes a species survival more likely is called a(n) ...
Homo
... THE HOMINID FAMILY TREE • Recent fossil specimens of early hominids have been found that date as far back as 6 to 7 million years. • These fossils are confusing because they show a mixture of primitive and modern traits. • There are too few of these very old fossils to make certain their connection ...
... THE HOMINID FAMILY TREE • Recent fossil specimens of early hominids have been found that date as far back as 6 to 7 million years. • These fossils are confusing because they show a mixture of primitive and modern traits. • There are too few of these very old fossils to make certain their connection ...
CHAPTER 23: HOW HUMANS EVOLVED
... researchers support the 3 species model with H. rudolfensis being most ancient and H. ergaster being most recent. H. erectus evolved 1.5 million years ago and includes Java man and Peking man. This species spread through Africa and migrated into Europe and Asia. They were human in appearance, used t ...
... researchers support the 3 species model with H. rudolfensis being most ancient and H. ergaster being most recent. H. erectus evolved 1.5 million years ago and includes Java man and Peking man. This species spread through Africa and migrated into Europe and Asia. They were human in appearance, used t ...
Last Name, First Name
... kit shows examples of large core tools such as handaxes, picks and cleavers. These “bifaced” tools were perfect for butchering and slicing meat from large animals, as described in class. These tools and Fialkowsky’s brain resistance theory provide evidence that the Homo erectus was more like a hunte ...
... kit shows examples of large core tools such as handaxes, picks and cleavers. These “bifaced” tools were perfect for butchering and slicing meat from large animals, as described in class. These tools and Fialkowsky’s brain resistance theory provide evidence that the Homo erectus was more like a hunte ...
chapter 19 - Geoclassroom Home
... Currently dubbed a new species, Homo floresiensis, the individuals reached the island a minimum of 38,000 years ago, and survived until 12,000 years ago. An adult female probably stood 3 feet, 3 inches tall and weighed approximately 35 pounds. Some researchers propose an early arrival for Flores man ...
... Currently dubbed a new species, Homo floresiensis, the individuals reached the island a minimum of 38,000 years ago, and survived until 12,000 years ago. An adult female probably stood 3 feet, 3 inches tall and weighed approximately 35 pounds. Some researchers propose an early arrival for Flores man ...
EHO Facts Booklet - Bangor Public Library
... ago, there were at least four human species on earth (H. erectus, H. floresiensis, H. neanderthalensis, H. sapiens). While our species, H. sapiens, has survived for about 200,000 years, some species of earlier humans thrived for several times longer before their extinction. Fossils of more than 6,00 ...
... ago, there were at least four human species on earth (H. erectus, H. floresiensis, H. neanderthalensis, H. sapiens). While our species, H. sapiens, has survived for about 200,000 years, some species of earlier humans thrived for several times longer before their extinction. Fossils of more than 6,00 ...
Homo sapiens - McGraw
... • recent fossil specimens of early hominids have been found that date as far back as 6 to 7 million years these fossils are confusing because they show a mixture of primitive and modern traits there are too few of these very old fossils to make certain their connections to australopithecines and ...
... • recent fossil specimens of early hominids have been found that date as far back as 6 to 7 million years these fossils are confusing because they show a mixture of primitive and modern traits there are too few of these very old fossils to make certain their connections to australopithecines and ...
Action Lecture powerpoint
... – Various species of Australopithecus date from about 4 to 1 million years ago – Our own species, Homo sapiens, is the only hominid that has not become extinct ...
... – Various species of Australopithecus date from about 4 to 1 million years ago – Our own species, Homo sapiens, is the only hominid that has not become extinct ...
The New Science of Human Evolution
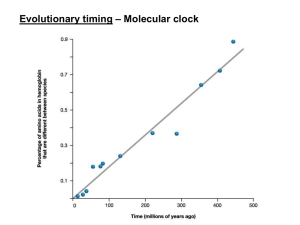
... and chimp DNA differ by no more than 1.2 percent, and DNA changes at a fairly regular rate. That lets scientists use this rate to calibrate a "molecular clock" whose tick-tocks measure how long ago a genetic change occurred. The fact that the DNA of living chimps and humans differ by about 35 millio ...
... and chimp DNA differ by no more than 1.2 percent, and DNA changes at a fairly regular rate. That lets scientists use this rate to calibrate a "molecular clock" whose tick-tocks measure how long ago a genetic change occurred. The fact that the DNA of living chimps and humans differ by about 35 millio ...
Multifactorial Traits - Study materials & Discussion
... • Humans share many traits with animals • We are most similar to apes – Same 206 bones – All but 3 of 650 muscles the same – DNA is 98% the same – Same blood types Albino Gorilla ...
... • Humans share many traits with animals • We are most similar to apes – Same 206 bones – All but 3 of 650 muscles the same – DNA is 98% the same – Same blood types Albino Gorilla ...
Evolution - Rosehill
... claimed to be the oldest hominin yet described. Thirteen pieces, consisting of teeth, fragments of the arm, thigh bone, and a finger, from at least five different individuals have been found. The size and morphology of the teeth are intermediate between those of a chimpanzee and those of a human. ...
... claimed to be the oldest hominin yet described. Thirteen pieces, consisting of teeth, fragments of the arm, thigh bone, and a finger, from at least five different individuals have been found. The size and morphology of the teeth are intermediate between those of a chimpanzee and those of a human. ...
The College of Health and Human Development
... populations, particularly those currently living on Flores, along with signs of abnormal development, including but not limited to microcephaly and marked skeletal asymmetry. Reasonable questions, including how members of a species with one third the brain size of Homo sapiens would be able to creat ...
... populations, particularly those currently living on Flores, along with signs of abnormal development, including but not limited to microcephaly and marked skeletal asymmetry. Reasonable questions, including how members of a species with one third the brain size of Homo sapiens would be able to creat ...
Notes on Human Development, Climate, and Technology
... evolved into chimpanzees, gorillas and other apes. Those that moved on evolved into humans through multiple intermediate species known as "hominids". Modern DNA studies can verify the family connections involved. For example, chimpanzee and human DNA show only a 1.5% difference. From this, it can be ...
... evolved into chimpanzees, gorillas and other apes. Those that moved on evolved into humans through multiple intermediate species known as "hominids". Modern DNA studies can verify the family connections involved. For example, chimpanzee and human DNA show only a 1.5% difference. From this, it can be ...
Human Evolution - MStew
... divine act of Creation as described in Genesis. Catastrophism is a modified version of Creationism, which accounts for the fossil record by positing divinely authored worldwide disasters that wiped out the creatures represented in the fossil record, who were then supplanted by newer, created species ...
... divine act of Creation as described in Genesis. Catastrophism is a modified version of Creationism, which accounts for the fossil record by positing divinely authored worldwide disasters that wiped out the creatures represented in the fossil record, who were then supplanted by newer, created species ...
Fulltext PDF
... forms. The Acheulian Tradition (1.5 my a - 60,000 ya) is characterised by true handaxes and cleavers and is the most widespread and longest lived cultural tradition. The Oldowan Tradition is usually associated with Homo habilis, though, due to the presence of australopithecine and Homo erectus fossi ...
... forms. The Acheulian Tradition (1.5 my a - 60,000 ya) is characterised by true handaxes and cleavers and is the most widespread and longest lived cultural tradition. The Oldowan Tradition is usually associated with Homo habilis, though, due to the presence of australopithecine and Homo erectus fossi ...
Origin and Dispersal of Modern Humans
... – Earliest dates from Lake Mungo, but mtDNA studies now place dates in question. – Kow Swamp: 14,000 and 9,000 y.a., with archaic traits such as brow ridges and receding forehead, but other modern t ...
... – Earliest dates from Lake Mungo, but mtDNA studies now place dates in question. – Kow Swamp: 14,000 and 9,000 y.a., with archaic traits such as brow ridges and receding forehead, but other modern t ...
Human Evolution
... Habilines were the first hominids to be associated with tools – they used large pebbles, chipped in at least two directions, as sharpened implements to crush, break and cut. Their additional brain capacity had resulted in advanced manual dexterity. It was applied to the making and using of simple to ...
... Habilines were the first hominids to be associated with tools – they used large pebbles, chipped in at least two directions, as sharpened implements to crush, break and cut. Their additional brain capacity had resulted in advanced manual dexterity. It was applied to the making and using of simple to ...
Human evolution
... diversity) emerged mainly during the past 100,000 years humans and the great apes of Africa (chimpanzees and gorillas) share a common ancestor that lived between 8 and 6 million years ago humans first evolved in Africa, and much of human evolution occurred on that continent the fossils of early huma ...
... diversity) emerged mainly during the past 100,000 years humans and the great apes of Africa (chimpanzees and gorillas) share a common ancestor that lived between 8 and 6 million years ago humans first evolved in Africa, and much of human evolution occurred on that continent the fossils of early huma ...
File
... hold the evidence of the extreme climate change in Africa, from very hot and wet to very cold and dry. Our ancestors had to adapt and slowly changed in order to survive. “Lucy” and “Selam” walked upright and looked like us from waist down, but from waist up they looked like apes. Those creatures liv ...
... hold the evidence of the extreme climate change in Africa, from very hot and wet to very cold and dry. Our ancestors had to adapt and slowly changed in order to survive. “Lucy” and “Selam” walked upright and looked like us from waist down, but from waist up they looked like apes. Those creatures liv ...
The Rise of Civilization Chapter 1 Prehistory * 2300 B.C.
... can figure out its age. • Works for objects no more than about 50,000 years old. ...
... can figure out its age. • Works for objects no more than about 50,000 years old. ...
Becoming Human Viewers Guide
... Bipedalism (n) word used to describe an animal who uses two legs to walk Aboriginal (adj) word used to describe people, animals or plants native to an area for a very long time before any colonists arrived Terms Donald Johanson A paleontologist who found the australophithecus afarensis hominid known ...
... Bipedalism (n) word used to describe an animal who uses two legs to walk Aboriginal (adj) word used to describe people, animals or plants native to an area for a very long time before any colonists arrived Terms Donald Johanson A paleontologist who found the australophithecus afarensis hominid known ...
Human evolution - Lancaster High School
... Latin australo, meaning “southern” Greek pithecus meaning “ape” Approximately 7 species Older genus-smaller brains ...
... Latin australo, meaning “southern” Greek pithecus meaning “ape” Approximately 7 species Older genus-smaller brains ...
Homo floresiensis

Homo floresiensis (""Flores Man""; nicknamed ""hobbit"" and ""Flo"") is an extinct species widely believed to be in the genus Homo. The remains of an individual that would have stood about 3.5 feet (1.1 m) in height were discovered in 2003 on the island of Flores in Indonesia. Partial skeletons of nine individuals have been recovered, including one complete skull, referred to as ""LB1"". These remains have been the subject of intense research to determine whether they represent a species distinct from modern humans. This hominin is remarkable for its small body and brain and for its survival until relatively recent times (possibly as recently as 12,000 years ago). Recovered alongside the skeletal remains were stone tools from archaeological horizons ranging from 94,000 to 13,000 years ago. Some scholars suggest that the historical H. floresiensis may be connected by folk memory to ebu gogo myths prevalent on the isle of Flores.The discoverers (archaeologist Mike Morwood and colleagues) proposed that a variety of features, both primitive and derived, identify these individuals as belonging to a new species, H. floresiensis, within the taxonomic tribe of Hominini, which includes all species that are more closely related to humans than to chimpanzees. The discoverers also proposed that H. floresiensis lived contemporaneously with modern humans on Flores.Doubts that the remains constitute a new species were soon voiced by the Indonesian anthropologist Teuku Jacob, who suggested that the skull of LB1 was a microcephalic modern human. Two studies by paleoneurologist Dean Falk and her colleagues (2005, 2007) rejected this possibility. Falk et al. (2005) has been rejected by Martin et al. (2006) and Jacob et al. (2006), but defended by Morwood (2005) and Argue, Donlon et al. (2006).Two orthopedic researches published in 2007 reported evidence to support species status for H. floresiensis. A study of three tokens of carpal (wrist) bones concluded there were similarities to the carpal bones of a chimpanzee or an early hominin such as Australopithecus and also differences from the bones of modern humans. A study of the bones and joints of the arm, shoulder, and lower limbs also concluded that H. floresiensis was more similar to early humans and apes than modern humans. In 2009, the publication of a cladistic analysis and a study of comparative body measurements provided further support for the hypothesis that H. floresiensis and Homo sapiens are separate species.Critics of the claim for species status continue to believe that these individuals are Homo sapiens possessing pathologies of anatomy and physiology. Several hypotheses in this category have been put forward, including that the individuals were born without a functioning thyroid, resulting in a type of endemic cretinism (myxoedematous, ME), and that the principal specimen LB1 suffered from Down syndrome.